22 what is the best network topology for large businesses explain your choice
22 what is the best network topology for large businesses explain your choice
What Is Network Topology? Best Guide to Types and Diagrams
The configuration, or topology, of a network is key to determining its performance. Network topology is the way a network is arranged, including the physical or logical description of how links and nodes are set up to relate to each other.
There are numerous ways a network can be arranged, all with different pros and cons, and some are more useful in certain circumstances than others. Admins have a range of options when it comes to choosing a network topology, and this decision must account for the size and scale of their business, its goals, and budget. Several tasks go into effective network topology management, including configuration management, visual mapping, and general performance monitoring. The key is to understand your objectives and requirements to create and manage the network topology in the right way for your business.
Following an in-depth network topology definition, this article will look at the main types of network topologies, their benefits and drawbacks, and considerations for determining which one is best for your business. I’ll also discuss the use and benefits of network topology mapping software like SolarWinds ® Network Topology Mapper in configuring your network, visualizing the way devices connect, and troubleshooting network issues.
What Is Network Topology?
Network topology refers to how various nodes, devices, and connections on your network are physically or logically arranged in relation to each other. Think of your network as a city, and the topology as the road map. Just as there are many ways to arrange and maintain a city—such as making sure the avenues and boulevards can facilitate passage between the parts of town getting the most traffic—there are several ways to arrange a network. Each has advantages and disadvantages and depending on the needs of your company, certain arrangements can give you a greater degree of connectivity and security.
There are two approaches to network topology: physical and logical. Physical network topology, as the name suggests, refers to the physical connections and interconnections between nodes and the network—the wires, cables, and so forth. Logical network topology is a little more abstract and strategic, referring to the conceptual understanding of how and why the network is arranged the way it is, and how data moves through it.
Why Is Network Topology Important?
The layout of your network is important for several reasons. Above all, it plays an essential role in how and how well your network functions. Choosing the right topology for your company’s operational model can increase performance while making it easier to locate faults, troubleshoot errors, and more effectively allocate resources across the network to ensure optimal network health. A streamlined and properly managed network topology can increase energy and data efficiency, which can in turn help to reduce operational and maintenance costs.
The design and structure of a network are usually shown and manipulated in a software-created network topology diagram. These diagrams are essential for a few reasons, but especially for how they can provide visual representations of both physical and logical layouts, allowing administrators to see the connections between devices when troubleshooting.
The way a network is arranged can make or break network functionality, connectivity, and protection from downtime. The question of, “What is network topology?” can be answered with an explanation of the two categories in the network topology.
Effective network management and monitoring require a strong grasp of both the physical and logical topology of a network to ensure your network is efficient and healthy.
What’s the Most Common Type of Network Topology?
Building a local area network (LAN) topology can be make-or-break for your business, as you want to set up a resilient, secure, and easy-to-maintain topology. There are several different types of network topology and all are suitable for different purposes, depending on the overall network size and your objectives.
As with most things, there’s no “right” or one-size-fits-all option. With this in mind, I’ll walk you through the most common network topology definitions to give you a feel for the advantages and disadvantages of each.
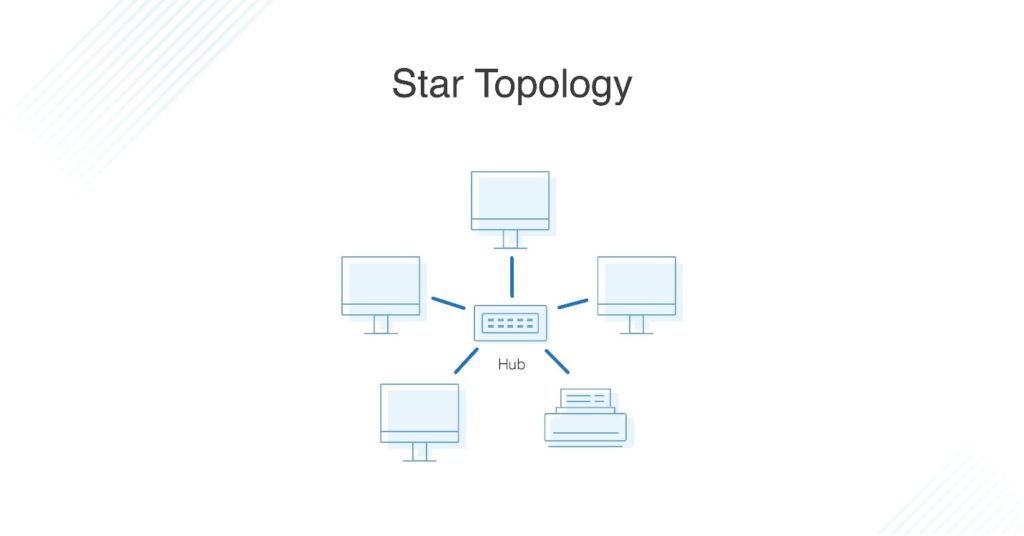
What Is Star Topology?
A star topology, the most common network topology, is laid out so every node in the network is directly connected to one central hub via coaxial, twisted-pair, or fiber-optic cable. Acting as a server, this central node manages data transmission—as information sent from any node on the network has to pass through the central one to reach its destination—and functions as a repeater, which helps prevent data loss.
Advantages of Star Topology
Star topologies are common since they allow you to conveniently manage your entire network from a single location. Because each of the nodes is independently connected to the central hub, should one go down, the rest of the network will continue functioning unaffected, making the star topology a stable and secure network layout.
Additionally, devices can be added, removed, and modified without taking the entire network offline.
On the physical side of things, the structure of the star topology uses relatively little cabling to fully connect the network, which allows for both straightforward setup and management over time as the network expands or contracts. The simplicity of the network design makes life easier for administrators, too, because it’s easy to identify where errors or performance issues are occurring.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
On the flipside, if the central hub goes down, the rest of the network can’t function. But if the central hub is properly managed and kept in good health, administrators shouldn’t have too many issues.
The overall bandwidth and performance of the network are also limited by the central node’s configurations and technical specifications, making star topologies expensive to set up and operate.
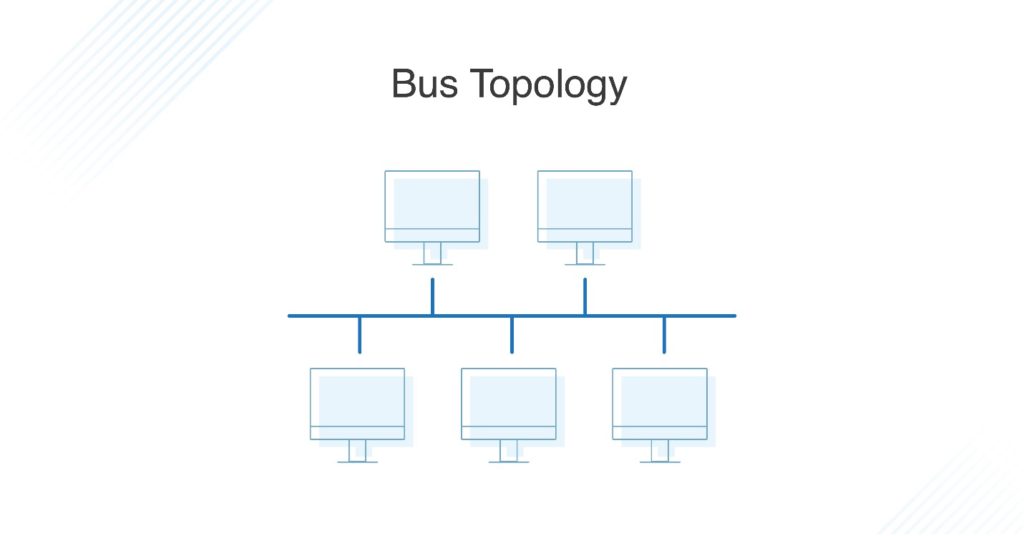
What Is Bus Topology?
A bus topology orients all the devices on a network along a single cable running in a single direction from one end of the network to the other—which is why it’s sometimes called a “line topology” or “backbone topology.” Data flow on the network also follows the route of the cable, moving in one direction.
Advantages of Bus Topology
Bus topologies are a good, cost-effective choice for smaller networks because the layout is simple, allowing all devices to be connected via a single coaxial or RJ45 cable. If needed, more nodes can be easily added to the network by joining additional cables.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology
However, because bus topologies use a single cable to transmit data, they’re somewhat vulnerable. If the cable experiences a failure, the whole network goes down, which can be time-consuming and expensive to restore, which can be less of an issue with smaller networks.
Bus topologies are best suited for small networks because there’s only so much bandwidth, and every additional node will slow transmission speeds.
Furthermore, data is “half-duplex,” which means it can’t be sent in two opposite directions at the same time, so this layout is not the ideal choice for networks with huge amounts of traffic.
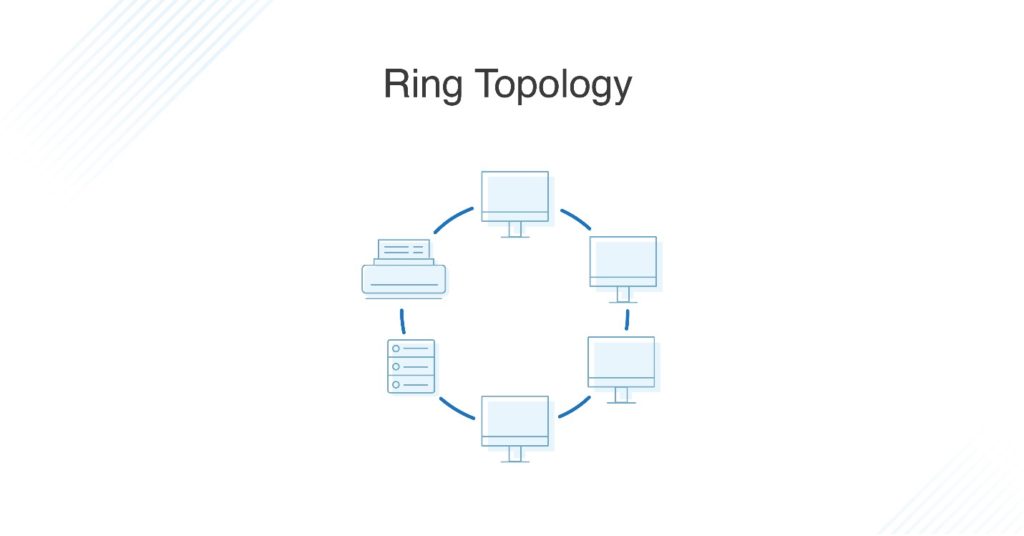
What Is Ring Topology? Single vs. Dual
Ring topology is where nodes are arranged in a circle (or ring). The data can travel through the ring network in either one direction or both directions, with each device having exactly two neighbors.
Pros of Ring Topology
Since each device is only connected to the ones on either side, when data is transmitted, the packets also travel along the circle, moving through each of the intermediate nodes until they arrive at their destination. If a large network is arranged in a ring topology, repeaters can be used to ensure packets arrive correctly and without data loss.
Only one station on the network is permitted to send data at a time, which greatly reduces the risk of packet collisions, making ring topologies efficient at transmitting data without errors.
By and large, ring topologies are cost-effective and inexpensive to install, and the intricate point-to-point connectivity of the nodes makes it relatively easy to identify issues or misconfigurations on the network.
Cons of Ring Topology
Even though it’s popular, a ring topology is still vulnerable to failure without proper network management. Since the flow of data transmission moves unidirectionally between nodes along each ring, if one node goes down, it can take the entire network with it. That’s why it’s imperative for each of the nodes to be monitored and kept in good health. Nevertheless, even if you’re vigilant and attentive to node performance, your network can still be taken down by a transmission line failure.
The question of scalability should also be taken into consideration. In a ring topology, all the devices on the network share bandwidth, so the addition of more devices can contribute to overall communication delays. Network administrators need to be mindful of the devices added to the topology to avoid overburdening the network’s resources and capacity.
Additionally, the entire network must be taken offline to reconfigure, add, or remove nodes. And while that’s not the end of the world, scheduling downtime for the network can be inconvenient and costly.
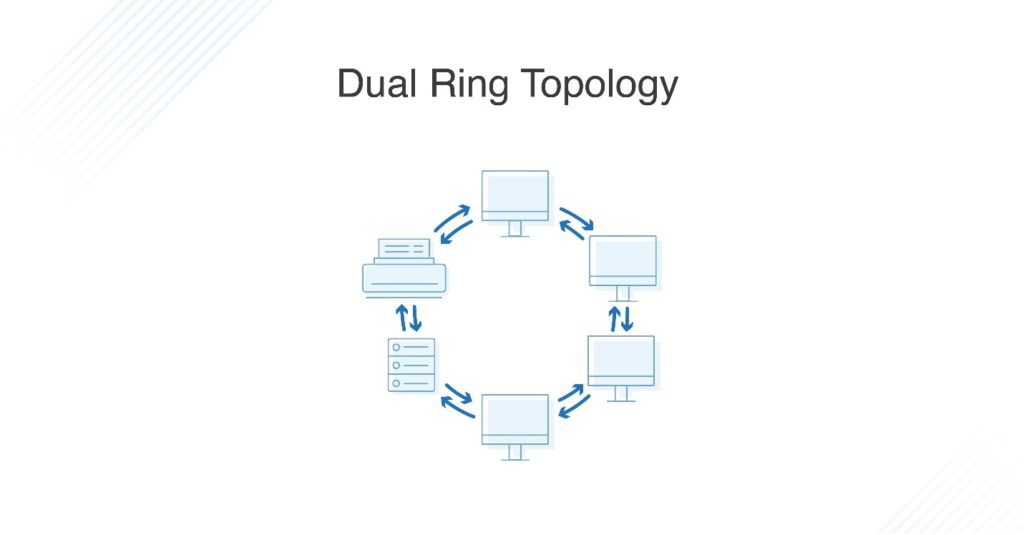
What Is Dual-Ring Topology?
A network with ring topology is half-duplex, meaning data can only move in one direction at a time. Ring topologies can be made full-duplex by adding a second connection between network nodes, creating a dual ring topology.
Advantages of Dual-Ring Topology
The primary advantage of dual ring topology is its efficiency: because each node has two connections on either side, information can be sent both clockwise and counterclockwise along the network. The secondary ring included in a dual-ring topology setup can act as a redundant layer and backup, which helps solve for many of the disadvantages of traditional ring topology. Dual ring topologies offer a little extra security, too: if one ring fails within a node, the other ring is still able to send data.
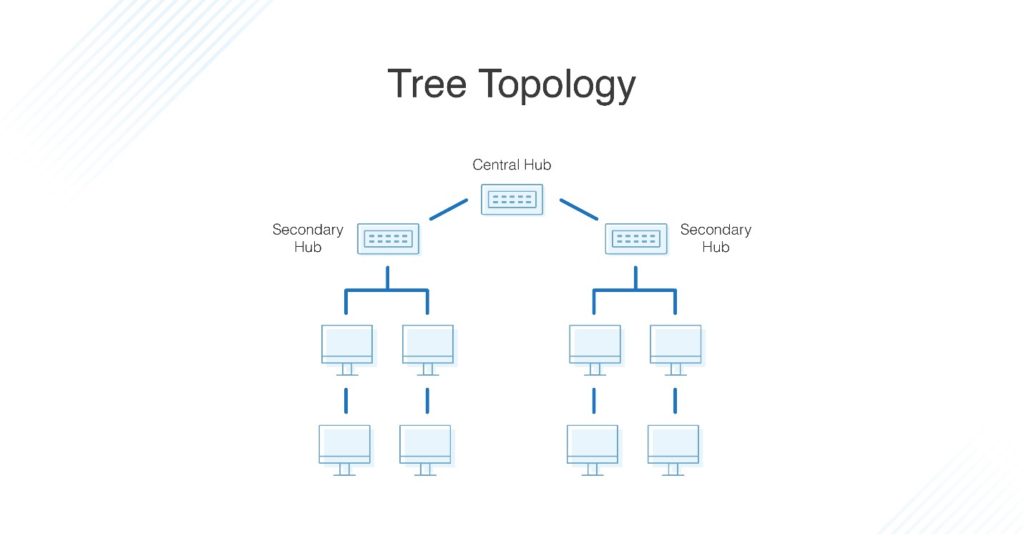
What Is Tree Topology?
The tree topology structure gets its name from how the central node functions as a sort of trunk for the network, with nodes extending outward in a branch-like fashion. However, where each node in a star topology is directly connected to the central hub, a tree topology has a parent-child hierarchy to how the nodes are connected. Those connected to the central hub are connected linearly to other nodes, so two connected nodes only share one mutual connection. Because the tree topology structure is both extremely flexible and scalable, it’s often used for wide area networks to support many spread-out devices.
Pros of Tree Topology
Combining elements of the star and bus topologies allows for the easy addition of nodes and network expansion. Troubleshooting errors on the network is also a straightforward process, as each of the branches can be individually assessed for performance issues.
Cons of Tree Topology
As with the star topology, the entire network depends on the health of the root node in a tree topology structure. Should the central hub fail, the various node branches will become disconnected, though connectivity within—but not between—branch systems will remain.
Because of the hierarchical complexity and linear structure of the network layout, adding more nodes to a tree topology can quickly make proper management an unwieldy, not to mention costly, experience. Tree topologies are expensive because of the sheer amount of cabling required to connect each device to the next within the hierarchical layout.
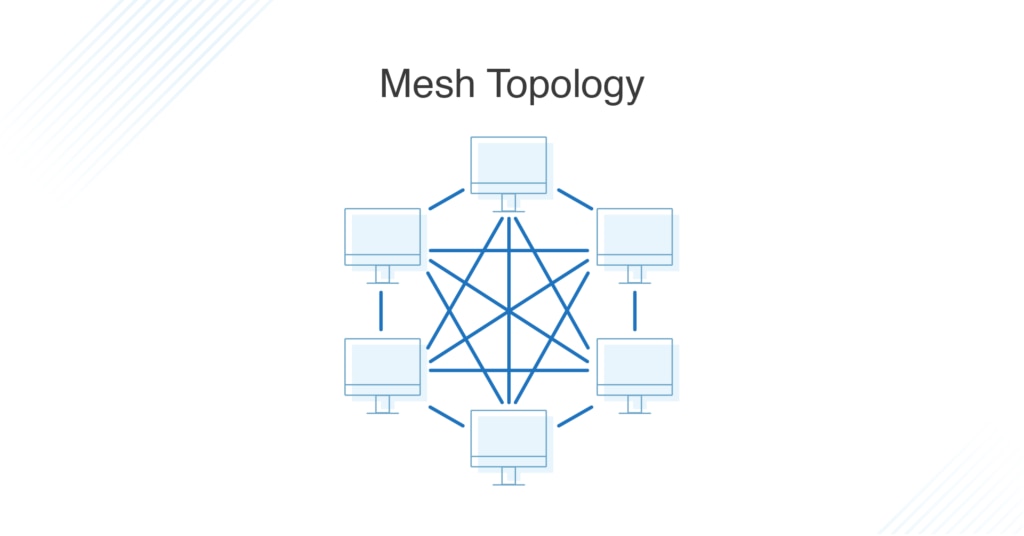
What Is Mesh Topology?
A mesh topology is an intricate and elaborate structure of point-to-point connections where the nodes are interconnected. Mesh networks can be full or partial mesh. Partial mesh topologies are mostly interconnected, with a few nodes with only two or three connections, while full-mesh topologies are—surprise!—fully interconnected.
The web-like structure of mesh topologies offers two different methods of data transmission: routing and flooding. When data is routed, the nodes use logic to determine the shortest distance from the source to destination, and when data is flooded, the information is sent to all nodes within the network without the need for routing logic.
Advantages of Mesh Topology
Mesh topologies are reliable and stable, and the complex degree of interconnectivity between nodes makes the network resistant to failure. For instance, no single device going down can bring the network offline.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
Mesh topologies are incredibly labor-intensive. Each interconnection between nodes requires a cable and configuration once deployed, so it can also be time-consuming to set up. As with other topology structures, the cost of cabling adds up fast, and to say mesh networks require a lot of cabling is an understatement.
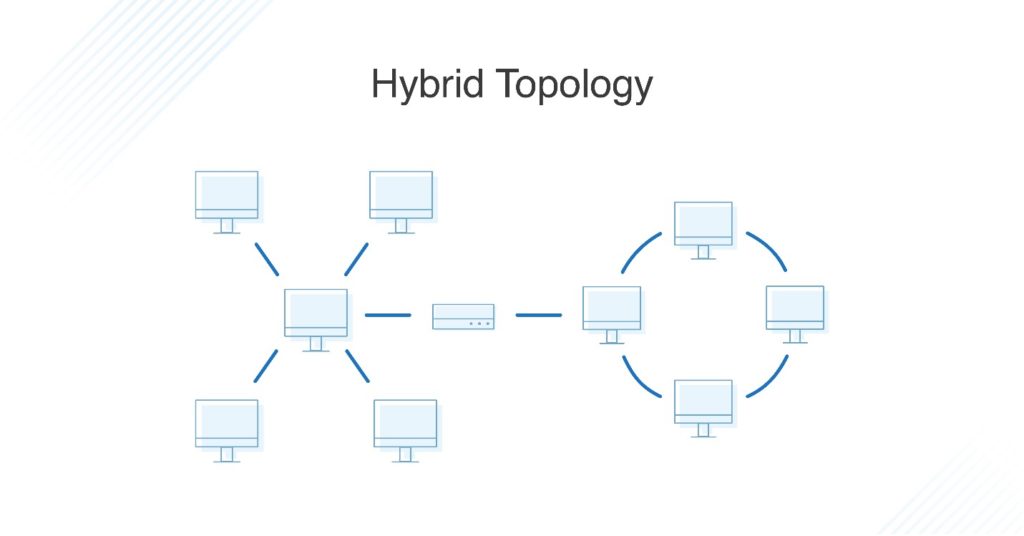
What Is Hybrid Topology?
Hybrid topologies combine two or more different topology structures—the tree topology is a good example, integrating the bus and star layouts. Hybrid structures are most commonly found in larger companies where individual departments have personalized network topologies adapted to suit their needs and network usage.
Advantages of Hybrid Topology
The main advantage of hybrid structures is the degree of flexibility they provide, as there are few limitations on the network structure itself that a hybrid setup can’t accommodate.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology
However, each type of network topology comes with its own disadvantages, and as a network grows in complexity, so too does the experience and know-how required on the part of the admins to keep everything functioning optimally. There’s also the monetary cost to consider when creating a hybrid network topology.
Which Topology Is Best for Your Network?
No network topology is perfect, or even inherently better than the others, so determining the right structure for your business will depend on the needs and size of your network. Here are the key elements to consider:
Cable Length
Generally, the more cable involved in network topology, the more work it’ll require to set up. The bus and star topologies are on the simpler side of things, both being fairly lightweight, while mesh networks are much more cable- and labor-intensive.
Cable Type
The second point to consider is the type of cable you’ll install. Coaxial and twisted-pair cables both use insulated copper or copper-based wiring, while fiber-optic cables are made from thin and pliable plastic or glass tubes. Twisted-pair cables are cost-effective but have less bandwidth than coaxial cables. Fiber-optic cables are high performing and can transmit data far faster than twisted-pair or coaxial cables, but they also tend to be far more expensive to install, because they require additional components like optical receivers. So, as with your choice of network topology, the wiring you select depends on the needs of your network, including which applications you’ll be running, the transmission distance, and desired performance.
As I’ve mentioned, the installation cost is important to account for, as the more complex network topologies will require more time and funding to set up. This can be compounded if you’re combining different elements, such as connecting a more complex network structure via more expensive cables (though using fiber-optic cables in a mesh network is overdoing it, if you ask me, because of how interconnected the topology is). Determining the right topology for your needs, then, is a matter of striking the right balance between installation and operating costs and the level of performance you require from the network.
Scalability
The last element to consider is scalability. If you anticipate your company and network expanding—or if you’d like it to be able to—it’ll save you time and hassle down the line to use an easily modifiable network topology. Star topologies are so common because they allow you to add, remove, and alter nodes with minimal disruption to the rest of the network. Ring networks, on the other hand, have to be taken entirely offline for any changes to be made to any of the nodes.
How to Map Network Topology
When you’re starting to design a network, topology diagrams come in handy. They allow you to see how the information will move across the network, which, in turn, allows you to predict potential choke points. Visual representation makes it easier to create a streamlined and efficient network design, while also acting as a good reference point if you find yourself needing to troubleshoot errors.
A topology diagram is also essential for having a comprehensive understanding of your network’s functionality. In addition to assisting with the troubleshooting process, the bird’s-eye view provided by a topology diagram can help you visually identify the pieces of the infrastructure your network is lacking, or which nodes need monitoring, upgrading, or replacing.
The good news is you don’t have to do it manually: you can easily create a map of your network topology with tools.
What Tools Help Manage and Monitor Networks?
There are a few network topology mapping products on the market. One of the more common ones is Microsoft Visio, which lets you “draw” your network by adding different nodes and devices to a canvas-like interface. While this can work for smaller networks, drawing each additional node quickly becomes unwieldy if you’re working with a multitude of devices and topologies spread across an entire company. Other options, like Lucidchart and LibreOffice Draw, are either free or offer free trials, and while they’re viable options, especially if the cost is a concern, they don’t come with a full set of premium network mapping tools to make managing a network easier and less time-consuming.
Due to variations in network topology and the different ways networks can behave—including their unique security issues, pressure points, and management challenges—it’s often useful to automate configuration and management tasks using network software.
Network Configuration
First, consider using a network configuration management tool. This kind of tool can help you configure your network correctly and automate repetitive tasks to take the pressure off the network administrator. As your organization or network grows, the network topology may become more layered or more complex, and it can become harder to deploy configurations across the entire network with certainty. However, with configuration management tools, the complicated network topology is no issue: tools can usually auto-detect each node on the network, allowing you to deploy standard configurations that may be required for compliance reasons, or flag any configurations outside what is expected.
Network configuration management tools can also highlight vulnerabilities, so you can correct these issues and keep your network more secure. Finally, these kinds of tools should also display the lifecycle of the devices on your network, alerting you to devices coming to their end-of-service or end-of-life points, so you can replace them before problems begin to arise.
Network Performance Troubleshooting
You should use network management software to track overall performance. A performance manager can keep track of network issues, outages, and performance issues. A performance management tool will also have the functionality to set network performance baselines and establish a clear picture of how your network typically behaves when healthy. Then, by setting alerts when your network performs unexpectedly or outside of these baselines, you can quickly track, pinpoint, and troubleshoot issues.
With complex network topologies, it may be hard to figure out exactly which part of the network is having issues. Some performance managers will create a visual display of your network topology, so you can see the entire network in a one-map overview. This can show you how your network is laid out, bring your attention to changes in the topology, and flag where problems are arising. To get started understanding your network topology, you can try a tool like Network Topology Mapper free for 14 days. This tool automatically discovers and generates detailed topology maps of your network and can create multiple map types without having to rescan your network every time.
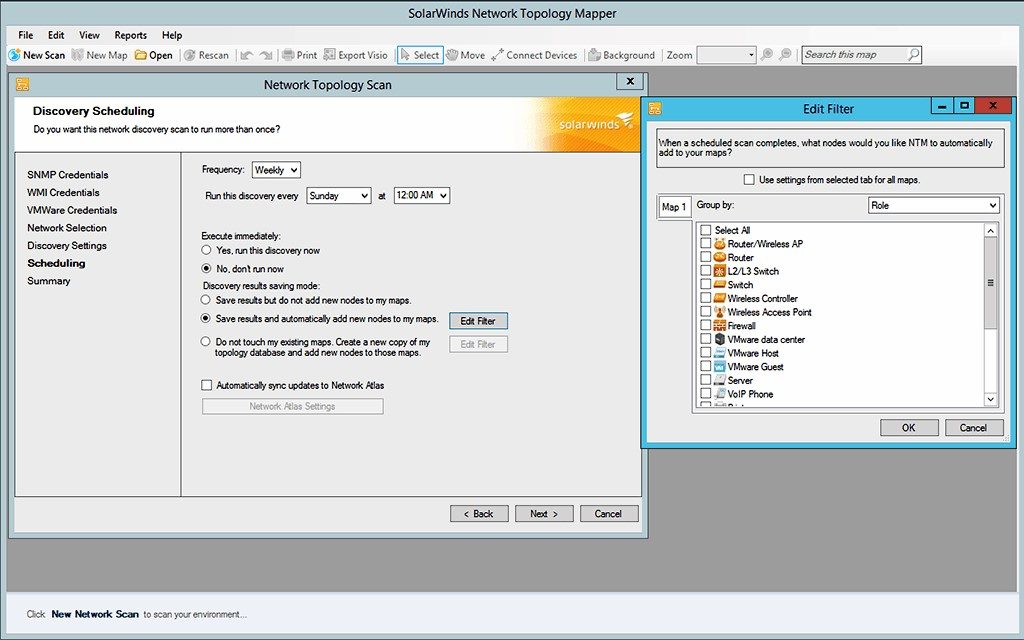
That’s one reason I really like SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper (NTM). No matter the size of your network, it can not only automatically discover all the devices and create a diagram of your network topology for you, but also populate the map with industry-specific icons for easy visual differentiation. In addition to the auto-discovery feature, the software offers an intuitive network wizard so you can drag and drop nodes and node groups (which you can also customize). Visualizing the various connections between nodes in a single map or diagram can be cumbersome, especially if you’re working with an expansive wide area network, but the interface in NTM lets you sort through different layers of connections, depending on the level you’re trying to inspect.
You can configure NTM to periodically rescan your network to keep your diagrams up to date. It integrates easily with other programs, and it offers a robust reporting system so you can track metrics, from device inventory to network performance, all while helping keep you PCI compliant.
Topology Mapping for Managed Services Providers
Topology mapping isn’t just important for managing a single network. It’s also a key aspect of managed services providers’ (MSPs’) essential duties—for hundreds or even thousands of different customers across multiple networks.
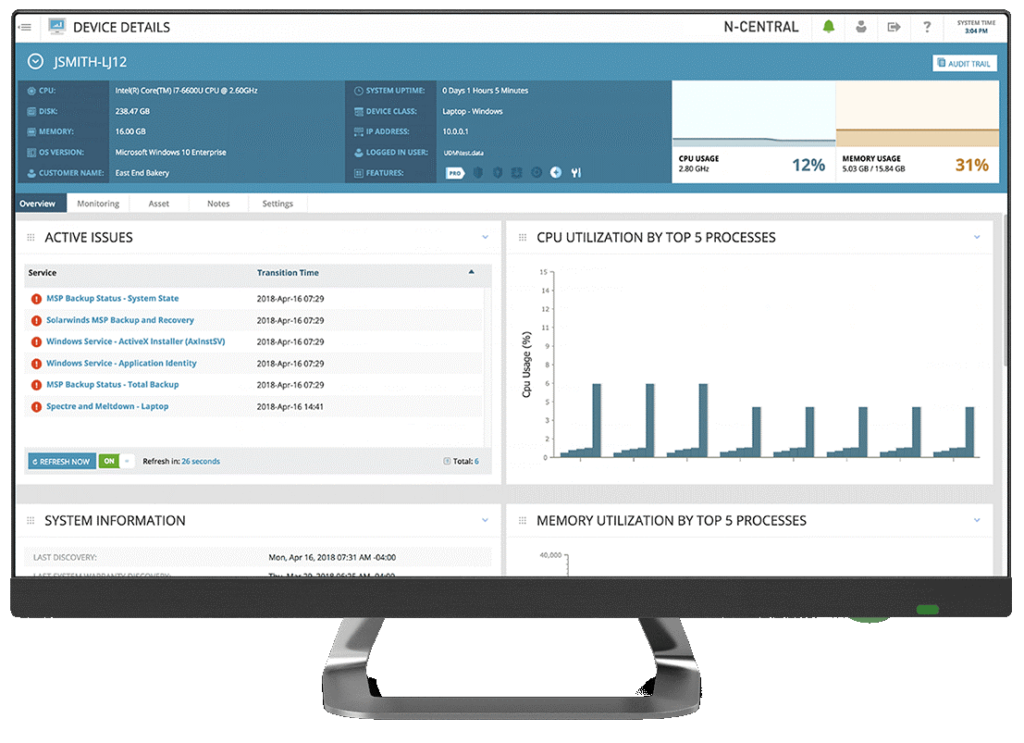
The N-central network topology mapping solution enables you to perform in-depth assessments of the networks you manage. You can perform on-demand and scheduled scans, as well as get access to detailed data represented in a clear, visual way.
What to Know About Network Topology Today
The best advice I can give regarding network topology is that you should be deeply familiar with the needs and usage requirements of your network. The total number of nodes on the network is one of the primary considerations to account for, as this will dictate whether it’s feasible to use a simpler topology, or whether you’ll have to make the investment in a more complicated network structure.
As I mentioned earlier, no one topology is “best.” Each offers its own set of perks and drawbacks, depending on the network environment you’re working with or attempting to set up. For this reason, I would avoid jumping to immediate conclusions about any of the network topologies based solely on the descriptions here. Before deciding, try using a network topology mapping tool to sketch the layout you’re thinking about using. Network Topology Mapper, my personal favorite, lets you plot the entire structure of your network in a way that’s both easy to use and easy to parse, and it offers a 14-day free trial.
Network Topologies for Large Businesses
Related Articles
When designing a network’s architecture, best practices focus on the need to build scaleability into network topology. Topology provides a map of the network, including network connection devices like switches and routers. Principles of scaleability have as their foundation an understanding that as technology advances and your business grows, your network must adapt to these changes and continue to perform in a manner that meets your business’s needs.
Build the Network for Expansion
An important goal in building a network infrastructure is to design it with expansion in mind. As your business grows, a poorly designed network can present difficulties as the number of computers and demands for bandwidth increase. Planning for expansion should also include the possibility of incorporating future technologies into your network. Closely monitor technology trends to determine new technologies that are likely to become standard network products, such as the trend of allowing users to “bring your own device,” or BYOD, and use it on the corporate network.
Interoperability
Network Security
As businesses move towards a structure that includes the utilization of electronic records, data security has become a key concern. This concern has been elevated by legislation that imposes stiff fines on a business where personal identifiable information, or PII, is leaked as a direct consequence of the business not implementing effective security measures.
Network security segmentation is commonly achieved in large business networks through the utilization of virtual local area networks, or VLANs, which provide separate logical networks operating on the same physical infrastructure. Encryption technologies like AES are becoming a standard means for data storage protection and data transmission, and multifactor authentication techniques utilizing biometrics like iris scans and facial recognition are being implemented in high-security environments.
Moving Business Networks to the Cloud
With the widespread adoption by businesses of server virtualization tools provided by companies like Microsoft, Citrix and VMware, businesses are beginning to consider a virtualized approach that moves their network infrastructure to the “cloud.” Placing network services in the cloud provides some clear advantages, including improved network reliability and availability in the event of a disaster by utilizing a cloud provider that includes redundancy in its service model.
While there are obvious security concerns relating to data access and storage in an environment a business doesn’t own, security safeguards that include advanced authentication and encryption techniques, providing network access through virtual private networks, or VPNs, have reduced potential risks to a point where many businesses use a cost vs. benefit approach to decide whether to move IT services to the cloud.
Steve Linthicum is a professor at Sierra College in Rocklin, Cal., and also serves as an adjunct professor at Lesley University in Cambridge, Mass. Linthicum holds a Bachelor of Science in engineering from Arizona State University and a Juris Doctorate from University of Pacific. Writing professionally since 1999, he has written two textbooks on Windows security and numerious articles for information technology magazines.
All About Network Topology—Types and Diagrams
By Staff Contributor on September 24, 2021
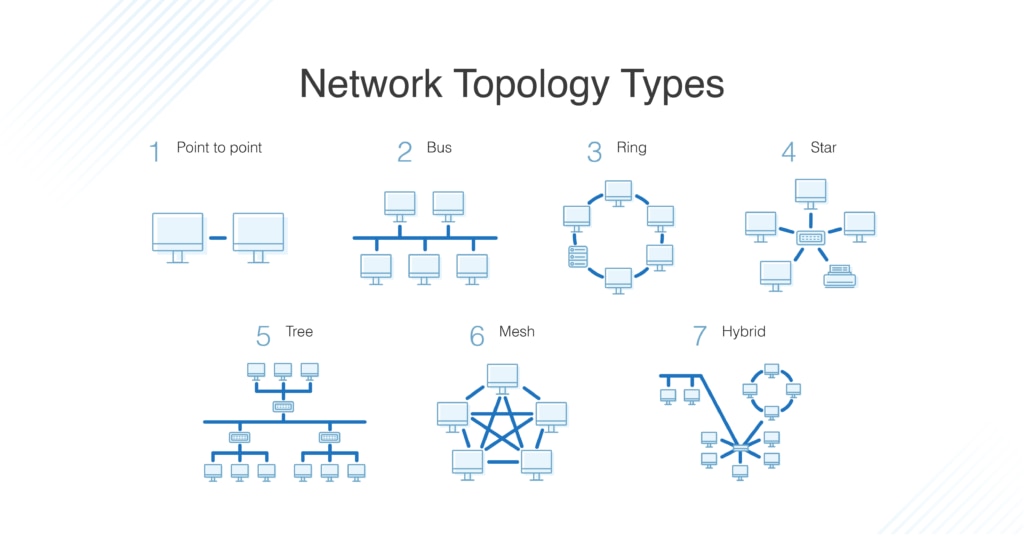
Every network has a specific collection of nodes and links that connect them. The arrangement of those nodes and links, or the network topology, informs performance, maintenance costs, and more. You should know the network topology models in use today when designing or managing a network, including the ring, mesh, bus, star, and tree topologies. To effectively manage your network topology, it’s essential to stay on top of your network’s configurations, visually map your network, and monitor its performance.
While it’s possible to perform manual topology mapping, you get more for your time with an automated tool. I recommend SolarWinds ® Network Topology Mapper (NTM), which offers automated device discovery and can generate detailed and easily digestible network topology maps, allowing you to view and understand your network more quickly and clearly.
What Is Network Topology?
A network’s topology details how the devices within it connect with one another and how data moves between its nodes. It can also be defined simply as a schematic description of a network’s elements’ arrangement.
While a logical network topology illustrates how data flows between your network’s devices, a physical network topology illustrates the physical connections within your network, such as its computers and cables. Visual diagrams can be used to represent logical and physical topologies, depending on your needs—either can be useful for understanding your network and its layout.
Why Is Network Topology Important?
Your network’s configuration, or topology, will affect its function and performance, so selecting the right topology for your organization is crucial. By choosing the topology best suited for your organization, its resources, and its needs, you can reduce operational costs, improve performance, and optimize resource allocation.
Using diagrams to understand your organization’s logical and physical network topologies will enable you to visualize how your network’s devices connect, helping you troubleshoot network slowdowns and connectivity issues quickly.
Types of Network Topology
There are several types of network topologies, each with advantages and disadvantages, so there’s no one-size-fits-all network topology solution. Understanding each topology’s strengths and weaknesses will enable you to make an informed decision and find a network topology that will better serve your organization in the long run.
Star Network Topology
As the name suggests, each device in this common topology connects to a central switch with coaxial cables, twisted pair cables, or optical fiber cables. Non-central nodes are also indirectly connected with one another through the central switch, or hub, which can serve as a repeater.
Advantages of Star Network Topology
Star topologies are easy to set up because each device only needs a single cable to connect to the central hub, so this topology requires fewer cables than others. Star topologies can also simplify the process of troubleshooting network performance problems. Since every network device connects to a single switch, this topology is easy to manage. You can easily add or remove nodes from the central switch without taking the entire network offline. Additionally, if a cable fails, only one device will be affected, offering these topologies protection against failures.
Disadvantages of Star Network Topology
Star network topologies rely on the central switch’s health and performance; when the central switch goes down, the rest of the network will follow. As a result, monitoring and managing the central switch is essential.
While it’s easy to add new devices to star topologies, it’s important to remember the central switch will have a limited number of ports, putting a fixed cap on the network’s size.
This topology requires fewer cables than other topologies, but you’ll still need to invest in the central switch, which can drive up installation costs.
Bus Network Topology
Within a bus network topology (also known as backbone network topology), the network’s nodes, or computer and network devices, are connected via drop lines to the common cable. Bus topologies are simple and allow for unidirectional data transmittance. A bus topology with two endpoints is called a linear bus topology.
Advantages of Bus Network Topology
Bus topology is the easiest and cheapest type of topology to install. With a one-to-one ratio of devices to drop lines, this topology requires less cable than other topologies, reducing the installation time and expenses. Adding new devices to the network is also straightforward. Just connect the new device to the central cable with a new drop line.
Given their simple layout, bus topologies aren’t usually used for office networks anymore and are, instead, best suited for small networks or consumer products.
Disadvantages of Bus Network Topology
While having a single cable makes bus topologies incredibly cost-effective, it also introduces several potential problems, including increased collisions, increased congestion, and low security. As a result, bus topologies are best for networks with low traffic volumes.
With a single point of failure, this topology isn’t very robust. If the common cable fails, then your entire network will crash. Additionally, as a half-duplex, data can only be transmitted in one direction along the cable at any given time, making congestion a common problem. As more network nodes begin to rely on the main cable, data transmission rates will slow.
Mesh Network Topology
Ideal for high-value, small to mid-sized networks, mesh topology consists of interconnected nodes, making it a fast and secure choice. In a full mesh network topology, each node is connected to all the other nodes via direct link, creating point-to-point connections. In a partial mesh topology, most nodes are interconnected, but some nodes only connect with a few others via point-to-point links.
Data transmitted within a mesh topology is sent through routing or flooding. With routing, the nodes determine the shortest distance to the packet’s destination using routing logic, while flooding involves sending the data to every node within the network.
Advantages of Mesh Network Topology
Mesh topology is quick, durable, and secure, thanks to the nodes’ interconnectivity. The mesh of nodes increases data transmission speed and ensures the network doesn’t have a single point of failure, increasing security and redundancy.
Disadvantages of Mesh Network Topology
As you might expect, it takes several cables to connect each node to all the other nodes, which means installing mesh topology can get expensive quickly, takes a considerable amount of time to set up, and requires a lot of configuration. Consequently, this topology is difficult to administer and costly to maintain. Your network’s size will also be limited by how many cables your computers can accommodate.
Ring Network Topology
As its name implies, ring topology consists of a ring of devices connected to two adjacent devices via point-to-point links, with the first and last nodes linking the loop. You can conveniently monitor your devices and configure the network through one node. Ring topologies are half-duplex, so data can only be sent in one direction at a time, and data will pass through each network node on its way to its target device.
In a ring topology, the node possessing the token is the only node capable of transmitting data, reducing the possibility of a collision. With early token release, the node releases the token as soon as it transmits the data, while with delayed token release, the node holds onto the token until it receives an acknowledgment from the receiver that the data has been received.
Advantages of Ring Network Topology
Thanks to its low installation costs, high data transmission rates, and low incidences of collision, many small businesses use a ring topology. It’s easy to manage, install, and expand, and it uses token-based protocols, which reduces the risk of packet collisions. Dual ring topologies are particularly redundant, providing continuity for the network.
Disadvantages of Ring Network Topology
This topology is vulnerable to failure, as if just one node fails, the entire network will go down. As a result, you’ll have to constantly monitor your ring topology network to ensure every node is functioning correctly, and you’ll have to shut the entire network down to add new nodes or alter any existing ones.
Since all your network’s devices will share bandwidth, it can be difficult to scale your network beyond a certain point without encountering performance issues. You’ll need to monitor the number of devices added to your network to ensure your bandwidth isn’t stretched too thin, causing communication delays.
Dual Ring Topology
Dual ring topologies function in the same manner as ring topologies with one key difference: they can send data in both directions, making them full-duplex and more efficient. Each node has two connections on both sides, enabling the transmission of data in both directions.
In addition to all the benefits ring topology offers, dual ring topology is redundant, thanks to the second ring, which can send data if the other ring fails.
Tree Network Topology
Named for its tree-like shape, the tree network topology has a hierarchical layout with at least three different levels. The tree topology consists of the central hub, secondary hubs, and devices. Data will flow from the central hub to a secondary hub to a device or from a device to a secondary hub to the central hub. The central hub serves as the sole mutual connection between the secondary hubs and their devices, creating parent-child dependencies.
Advantages of Tree Network Topology
Since the tree topology combines the bus and star topologies, it’s used in wide area networks (WANs) to support physically distanced devices. It’s also easy to manage and expand as your organization continues to grow. The tree topology’s hierarchical structure simplifies the troubleshooting process by allowing you to systematically check for performance issues within the network.
Disadvantages of Tree Network Topology
Between the monitoring software and the large amount of cabling needed, tree topology can get expensive. It’s also not very robust; if the central hub is compromised, the whole network may fail as the subtrees become partitioned. Therefore, it’s essential to invest in monitoring software if you have a large network.
This complicated network topology is difficult to manage and only becomes increasingly difficult to administer as more nodes are added. Consequently, this topology is better suited for networking experts.
Hybrid Network Topology
A hybrid topology combines two or more standard network topologies. A larger enterprise might opt to use a hybrid topology to allow various departments to employ different network topologies.
Advantages of Hybrid Network Topology
Though each hybrid topology’s advantages will be determined by which topologies are implemented, using a hybrid topology will generally give your organization flexibility and scalability. Therefore, they’re optimal for larger networks.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Network Topology
Again, each hybrid topology’s disadvantages will be determined by the topologies being employed. However, hybrid topologies are often complex and require professional management and monitoring software.
Which Topology Is Best for Your Network?
When considering which topology to use, you may be wondering What is the most common network topology? While other topologies were used more commonly in the past, these days the star topology is the most common.
However, it might not be the best topology for your network. Every organization’s networking needs will differ according to its size, budget, expertise, and needs. When trying to determine which topology is best for your network, consider your organization’s size, future expansion plans, goals, and budget.
Consider each topology’s scalability, cable length, and cable type. For example, the bus or ring topology might be best if you have a limited budget because they require fewer cables to install. If you’d prefer to have a more durable and secure topology, the mesh topology with its point-to-point connections might be a better fit. Ultimately, you should carefully compare your organization’s needs, plans, and resources with each topology’s requirements, advantages, and disadvantages.
What Tools Can Help Manage Network Topology?
Regardless of which network topology your organization uses, monitoring, managing, and mapping your topology is essential. Manually creating a network topology diagram can be a time-consuming and complicated process. I recommend using a tool for this.
With Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, LibreOffice Draw, and more on the market, there are plenty of tools for network monitoring, mapping, and managing to choose from. However, my favorite topology mapping tool is the comprehensive SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper.
SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper (Free Trial)
With automated device discovery and mapping SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper (NTM) is a useful tool designed to make creating comprehensive network topology maps simple. You can easily manage, share, encrypt, and print maps with this intuitive network diagram software.
NTM was built to automatically plot your network using ICMP, SNMP, WMI, or CDP, and works with VMware and Microsoft Hyper-V, but users can also manually connect network devices and edit node details. NTM’s automatic scans and automated reports help ensure you’ll have current information about your network and its devices. With an up-to-date network diagram, your organization can better meet compliance requirements for SOX, PIC, HIPAA, and FIPS 140-2.
Start Mapping Your Network Topology Today
Given the way network performance is affected by its topology, it’s important to find the right topology for your organization’s needs—but the work doesn’t end there. By frequently scanning and mapping your network, you can perform inventory management of hardware assets and quickly detect topological changes.
The best way to map your network topology is with a convenient and thorough solution like NTM. Download a 14-day free trial of SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper today to gain a clear view of your network’s topology.
A Comprehensive Guide on Network Topology, Types, and Tools
Networking plays a crucial role in every organization’s daily activities. It helps exchange sensitive data between nodes (computer systems and network devices) over a shared medium. However, building a network and arrangement of networking devices is challenging. Organizations need to plan out specific models, follow crucial guidelines, and create physical and logical layouts of a network or a configuration map to achieve optimal network performance. Various topology tools can help create and understand the layout of a computer network and the physical and virtual connections of the components, so it’s easier to identify and troubleshoot errors.
What Is Network Topology?
Network topology aligns a network setup so each node is interconnected with network links or connecting lines. It helps organizations in device monitoring, network visualizations, and network issue diagnosis.
While there are several ways of arranging a network, each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Depending on the degree of connectivity and security the organization needs, IT teams may develop a network topology map.
Importance of Network Topology
Network topology is used to define the layout of a network, its structure, and its shape, both physically and logically. A network can have one physical topology and multiple logical topologies simultaneously.
Physical network layout refers to the physical connections of the devices such as wires, cables, and more. Tasks like provisioning, setup, and maintenance require insights into the physical layout. The logical network layout, on the other hand, is a conceptual representation of how various devices operate at different layers of abstraction. It provides information about the interconnection of multiple nodes, how the data is transmitted, and the medium of transmission. Cloud and virtual resources come under the logical network layout.
Choosing the right topology helps organizations locate faults, troubleshoot errors, and allocate resources across the network. With a better understanding of networking concepts, teams can maximize the effective utilization of resources and networking components. Having a well-managed and streamlined network topology reduces maintenance and operational costs up.
Types of Network Topology
Organizations can choose different types of network topologies depending on the suitability of various operations, overall network size, and business objectives.
Bus Topology
Bus topology is sometimes also referred to as line or backbone topology. In this network setup, every device is connected to a single cable running throughout the network. Teams can connect as many nodes as they need; however, it may affect network performance. One of the connected nodes acts as a server and transmits data in a single direction from one end to the other. Smaller networks using this type of topology often use a coaxial or RJ45 cable to link devices together.
Advantages
Bus topology works well for smaller networks and keeps the layout extremely simple and easy to understand. It’s reliable, flexible, and expandable. In a bus topology, it’s easier to connect and remove devices without affecting the others in the network. And, it’s cost effective, as it uses a single cable for data transmission.
Disadvantages
Bus topologies are highly vulnerable to network failures and slowdowns. One of the major disadvantages of this topology is it uses a single cable for data transmission, which can lead to various issues. If the cable fails to work, the entire network goes down, which is time consuming to fix and expensive to restore. During high traffic, the network performance decreases as the data travels through one cable. These limitations make this topology suitable for smaller networks. Moreover, bus topology is half-duplex, which means data cannot be transmitted in opposite directions simultaneously—a drawback for organizations with an extensive network where high-level data transmission is a regular practice.
Ring Topology
In ring topology, devices are connected in a loop forming a ring. The data packets circulate from one computer to another in a single direction to reach their destination. Ring topology is also known as half duplex for this reason. Ring topology can be converted into dual ring topology or full duplex, meaning the data can flow both clockwise and anticlockwise with the help of two concentric rings or cables connected to each node. Dual ring topology is used as a backup if the primary ring fails.
Ring topology follows the token passing principal. The tokens are passed from one computer to another based on which way the data is transmitted. Once the computer receives the token, it transmits data and sends the token back with an acknowledgment signal. Within the topology, one node is chosen to configure the network and monitor other devices in the loop. This type of network configuration is mostly used in small businesses and schools.
Advantages
The circular flow of data and the token-based protocols minimize the chance of packet collision. The unidirectional nature of ring topology provides high speed. Ring topology is capable of handling high volumes of nodes in a network and heavy traffic compared to bus topology. Troubleshooting errors like cable faults in the ring network is easier and more convenient. It provides excellent communication over a long distance and is cost effective compared to other topologies such as mesh, hybrid, and tree. Dual ring topology offers an extra layer of data security as it’s more resistant to failures due to its dual network connection. If one network fails, the other takes over.
Disadvantages
The failure of one node can take down the entire network. The nodes in ring topology need to be continuously monitored to ensure they’re in good health. Transmission line failure is another drawback of ring topology. This type of network configuration also raises scalability issues. The addition or removal of network devices can lead to communication delays.
Star Topology
A star topology is the most commonly used network configuration. In this type of topology, nodes are connected to a central device like a switch or a hub with the help of coaxial cable, optical fiber, or twisted pair cable. The node layout in star topology is done such that the central device acts as a server and the peripheral devices are treated as clients. The central device is responsible for data transmission across the entire network and performs its job repeatedly.
Advantages
Star topology has several advantages that make it the most-used network configuration. The use of a central server greatly reduces the chances of network failure and data loss. If a node stops functioning, it doesn’t impact others in the network. Unlike ring topology, new computers and devices can be added, removed, and modified in star topology without taking the entire network offline. Moreover, this type of topology is simple to set up and manage and requires fewer cables to connect the nodes with the central device.
Disadvantages
In star topology, if the central device fails to operate, the entire network goes down at once. Administrators need to monitor and maintain the central device carefully to avoid errors. The performance of the entire network solely depends on the central device’s configurations, speed, and performance.
Mesh Topology
Mesh topology is a point-to-point connection in which infrastructure nodes are connected directly, non-hierarchically, and dynamically to as many nodes as possible to transmit data. The web-like structure of the network configuration offers two methods for data transmission: routing and flooding. Routing refers to the way nodes use a routing logic to find the shortest distance to the destination of the packet. Flooding refers to the way the data is transmitted to nodes within the network. It doesn’t require a routing logic.
Types of Mesh Topology
Partial Mesh Topology
In a fully interconnected mesh network, when some nodes are connected to one or two nodes (peripheral nodes), the setup is known as partial mesh. If the network or primary nodes fail, the rest of the nodes remain unaffected.
Full Mesh Topology
When every node within a network is interconnected, the set-up is known as full mesh. To calculate the number of connections in the network, the following formula can be used:
(n is the number of computers in the network)
Advantages:
Mesh topologies are extremely reliable. They can manage high amounts of traffic as multiple nodes can transmit data simultaneously. The strong interconnections make the topology resistant to failures. Additional devices don’t burden the network or disrupt data transmission.
Disadvantages:
Mesh topology is time consuming, expensive, and sometimes gives redundant connections. The mesh layout is hugely complex and is difficult to set up, manage, and maintain.
Tree Topology
Tree topology is a network structure in which a root node is connected to other nodes arranged in a parent-child hierarchy. Tree topologies need to have at least three levels of hierarchy in which only one mutual connection exists between two connected nodes. The topology is a combination of the star (nodes connected to the central server) and bus (linear) topologies. Due to the flexible and scalable nature of this topology, it’s often used for a wide area network to sustain spread-out devices.
Advantages
It’s easier to add more nodes in this type of topology as it follows a parent-child hierarchy. The hierarchy and the alignment of nodes make it easier for IT teams to find and troubleshoot errors.
Disadvantages
The only point of concern in tree topology is its root node. If it fails to function, it affects all the nodes connected to its branches. Maintaining the network is challenging because when adding nodes, it becomes difficult to manage the entire network and each node in it. Moreover, tree topology requires a considerable amount of cables to connect nodes throughout the hierarchy, which makes the layout more complex.
Hybrid Topology
A hybrid topology is a mix of two or more topologies highlighted above. It’s most commonly used by large enterprises where individual departments have personalized network topologies to suit their network usage requirements. The capabilities and vulnerabilities highly depend on the type of topologies coupled together. The combination of star-bus and star-ring network configurations are the most common examples of the hybrid network topology.
Advantages
Hybrid topologies offer flexibility, reliability, and scalability by combining the strongest aspects of different topologies in a single hybrid setup. Hybrid topologies can be modified according to an organization’s needs.
Disadvantages
Hybrid topologies are highly complex. Each type of technology has its own drawbacks. Therefore, administrators need to manage each topology involved in a hybrid setup as per its unique requirements.
Which Topology to Consider?
Choosing a topology depends on a range of factors such as length of the cable, cable type, cost of setting up, and scalability. If a business’s priority is keeping the setup simple, bus topology is the most lightweight and easy-to-install network configuration, in terms of cable needs. All topologies generally use three types of cables: twisted pairs, coaxial cables, and optical fiber cables. The cost of installing the network configuration is also an important consideration. The more complex topology the organization chooses, the more it has to pay for the resources and the time invested in creating their setup.
If the organization plans to upscale the network infrastructure later, teams should consider choosing a scalable topology unaffected by adding devices. Star topology is an ideal choice for this requirement as it shows minimal disruption when adding nodes.
Top 5 Network Topology Software
Due to variations in network topology and its behavior, including pressure points, unique security issues, and management challenges, it’s crucial to automate configurations and management tasks using a reliable and efficient network topology software. Topology software uses various methodologies and integrations to locate connected devices. It helps IT administrators identify network inefficiencies and bottlenecks and conduct root cause analyses of network problems.
1. SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper
SolarWinds ® Network Topology Mapper offers automated mapping and on-demand device discovery. The tool helps teams automatically scan new devices and the entire organizational network using SNMP, ICMP (Ping and Traceroute) protocols, and scheduled scanning to ensure an accurate, up-to-date record of your network. Based on the data collected, the tool generates comprehensive reports and topology maps, saving valuable resources, bandwidth, and time. These maps can be exported into Microsoft Office Visio, PDF, and PNG formats for distribution purposes. The tool is FIPS 140-2 compliant and meets compliance requirements for PCI, SOX, and HIPAA.
Teams can use robust reporting tools to get an automated report of inventory and device management. The report helps keep track of inventory and network information, saves time, and increases productivity. Moreover, teams can store topology maps and set auto-discovery features to get real-time information about the new devices added to the network. The tool offers a 14-day free trial with all the standard features.
2. Intermapper
Intermapper is a powerful network monitoring tool for Mac, Windows, and Linux. It includes an automated mapping and discovery feature to help teams plan and create their own network topology from scratch. Live and dynamic maps display real-time network health of the organization. The auto-discovery feature helps to assimilate visual representation of all IP-enabled devices such as switches, workstations, laptops, routers, and PCs. It also sends alerts to respective teams to spot and fix errors in the network. The tool also offers several network monitoring functions. It helps in capacity planning, network performance scanning, and SLA compliance reporting. Intermapper is easy to install, deploy, and use. It features simple, predictable device-based pricing models, allowing it to scale with changing environments. The tool offers a 30-day free trial, which can monitor up to 10 devices.
3. Lucidchart
Lucidchart is a web-based, user-friendly flow chart or a diagramming application loaded with multiple features to create and share professional diagrams. It helps create flow diagrams, organization charts, wireframes and UML, and more. It has specialized icon libraries for various industries and software, including network topology. Although the tool doesn’t offer an auto-discovery feature, maps can be exported in a range of formats, including Visio, to create a network from scratch. The tool works well with business systems and popular web applications, including Google Apps, Google Drive, Jive, and Atlassian. The tool offers a free version and a 7-day free trial of the paid versions. However, the free version doesn’t include import and export features. To use premium features, teams can choose subscription-based models. Pricing plans are per user account. For larger teams, the team plan lowers the cost of the entire system. The software can be installed on Linux, macOS, Windows, Chrome OS, iOS, and Android.
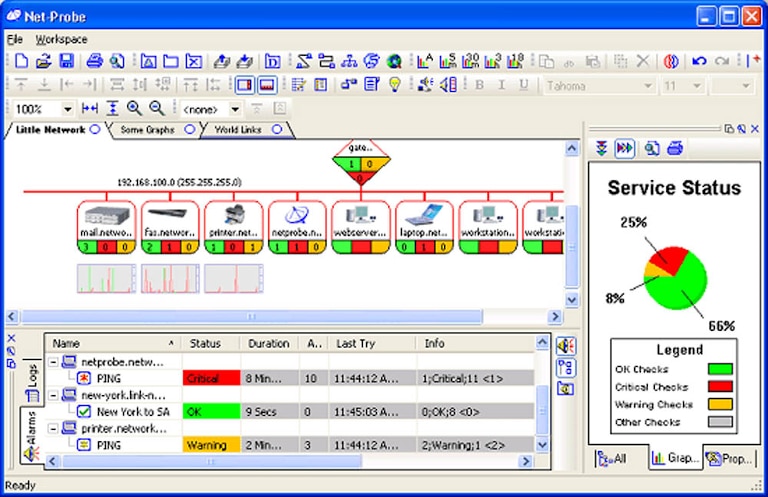
4. Net-Probe
Net-Probe is a network monitoring solution deployed at each node for its management. Net-Probe uses plugins to collect network data and network maps to troubleshoot faults. The tool offers an auto-discovery feature to help compile hardware inventory and customize network organization. Live maps display real-time device status on equipment icons and send alerts on a separate screen. The software runs on Windows with a free standard version, which can monitor up to eight devices. However, the free version doesn’t include tools such as Ping, Traceroute, and network scanning. The paid versions can monitor between 20 to 400 devices, depending on the plan you choose (Pro, Deluxe, and Enterprise).
5. Spiceworks Network Mapping Tool
Spiceworks Network Mapping Tool compiles inventory data of the connected devices in a network and generates easy-to-understand topology maps. The design editor tool can be used to edit and modify the generated map. The tool automatically updates the network maps on a schedule. Therefore, it’s essential to turn off this feature when generating customized network maps, as the changes might be deleted. Moreover, the automatic updates display network bandwidth usage of each device, which helps identify bottlenecks in the organizational network. It also gathers information about each existing and new device, including its model number, operating system, and capacity. This free tool can be installed on Debian, Linux, Ubuntu, Windows, and Mac OS.
Which Is the Best Network Topology Tool?
All the above-highlighted tools are exceptionally reliable and scalable for small, medium, and large enterprises. Along with these tools, organizations can also use network configuration tools to automate repetitive tasks and network performance tools to monitor real-time network outages and performance issues. Network configuration management tools help organizations understand the various networking layers. The tools also auto-detect new nodes added to the network, so IT teams can deploy standard configurations required for compliance. They empower teams to secure the entire network by highlighting vulnerabilities. Network performance management tools, on the other hand, send alerts at times of network slowdowns, so teams can efficiently identify and troubleshoot issues. With complex topologies, it’s difficult to determine which part of the network is having issues. NPM and NCM offer standard functionalities to make it easier to identify such issues. Both these tools can be used along with network topology mappers for extended functionalities.
If organizations are looking for network topology tools with specific, reliable, and advanced features, I recommend SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper. It’s specifically designed to create maps, auto-discover devices, and identify network issues while fulfilling regulatory compliance requirements.
6 Types of Network Topology | Advantages and Disadvantages
There are 6 types of network topology – Bus topology, Ring topology, Star topology, Mesh topology, Tree topology and Hybrid topology.
Table of Contents
Full Tutorials : Complete Computer Network (Free)
What is Network Topology?
Network Topology refers to the logical arrangement or layout of a network and a description of how various nodes(sender/receiver) are connected and communicate with each other.
Different Types of Network Topology
Bus Topology
Bus topology is a network, in which all the computer nodes and network system are connected to a single transmission channel.
Linear Bus topology: when it has exactly two endpoints.
Distributed bus topology: when it has more than two endpoints.
Features of Bus topology
Bus network topology advantages and disadvantages are mentioned below:
Advantages of Bus topology
Disadvantages of Bus topology
Ring Topology
In a Ring topology, the device forms the ring shape, in which each device is connected exactly to its neighbour on both sides through point to point connection and the first and last nodes are connected to each other.
The functionality of Ring topology:
Features of Ring topology
Ring network topology advantages and disadvantages are mentioned below:
Advantages of Ring Topology
Disadvantages of Ring topology
Star Topology
In star topology, all the computers are connected to a single central node called a hub through a cable. All the transmission of data is through the hub.
Features of Star Topology
Star network topology advantages and disadvantages are mentioned below:
Advantages of Star Topology
Disadvantages of Star Topology
Mesh Topology
In a mesh topology, every computer is connected to each other computer via dedicated channels.
Features of Mesh Topology
The total number of ports that are required by each device is N-1. (if 5 devices are connected then 4 port are required) The total number of dedicated links required to connect them is N(N-1)/2. i.e, if there are 5 computers connected to it then required dedicated link will be 5*4/2 = 10.
It can be divided into two kinds:
1. Fully connected mesh topology: all the nodes connected to every other node. 2. Partially connected mesh topology: It does not have all the nodes connected to each other.
Mesh network topology advantages and disadvantages are mentioned below:
Advantages of Mesh Topology
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
Tree Topology
Tr ee topology has a root node and other two nodes are connected to the root node. There is only one connection between any two connected nodes. It has a parent-child hierarchy.
It is also known as hybrid topology that combines characteristics of linear bus and star topologies. It includes at least three specific levels.
Examples of Tree topology
Features of Tree Topology
1. Usually implemented in WAN
Tree network topology advantages and disadvantages are mentioned below:
Advantages of Tree Topology
Disadvantages of Tree Topology
Hybrid Topology
A hybrid topology is a combination of two or more types of network topology.
This types of network topology are usually implemented by the organisation
Examples of Hybrid Topology
Features of Hybrid Topology
1. Collection of two or more topology.
Hybrid network topology advantages and disadvantages are mentioned below:
Advantages of Hybrid Topology
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on 6 Types of Network Topology | Advantages and Disadvantages in the comments section.