In what place does the climate differ
In what place does the climate differ
In what place does the climate differ
Задание №11851.
Чтение. ОГЭ по английскому
Вы проводите информационный поиск в ходе выполнения проектной работы. Определите, в каком из текстов A — F содержатся ответы на интересующие Вас вопросы 1 — 7. Один из вопросов останется без ответа.
1. What natural resource do Icelanders use as an alternative to central heating?
2. What should you take with you when going to Iceland?
3. What are thenational characteristics of the local people?
4. In what seasons can you see snow in Iceland?
5. What extreme excursions can the country offer?
6. What does a traditional Icelandic house look like?
7. Why are these animals widely used in tourist business?
A. In spite of its hard northern climate, Iceland is very attractive to tourists. Many people who have visited the country once want to go there again and again. The country turns skeptics into poets and optimists. It’s not only because of the views but also because of the local people. Icelanders are friendly and hospitable and welcome guests. It really compensates for the cold harsh climate!
B. An adventurous traveller would never mistake Iceland’s scenery for any other because of the boiling water fountains and the steam coming from the earth. Smoking volcanoes attract the bravest tourists. Iceland is the only place in the world where you can hike up a volcano and even go inside. There are guided walks to the glaciers, large masses of slowly moving ice, too.
C. Icelandic weather is unpredictable throughout the year. Bright sunshine can easily change to cold and miserable weather within a few hours. In the summer, rain is typical in Iceland. From September to May, when the temperature falls, it often snows, especially on the south and west coasts.
D. Till nowadays Icelanders cannot do without horses. And horses are very important not only for farming. From the Viking Age, horses have become a part of Iceland’s culture. They look like My Little Pony toys but they are exceptionally strong, so they can do heavy work and survive cold winters. The horses are good-natured, which is perfect for new riders. Guesthouses and travel companies across the country offer horse rides and tours.
E. If you decide to visit Iceland, you’ll never regret your decision. The only thing that can spoil your trip is the weather. That’s why it’s very important to get a reliable weather forecast whatever season it is. If you wear appropriate clothes and have some smart heating devices, neither rain nor snow can ruin your trip.
F. Hengill, a place near Reykjavik, is a famous landmark of the country. It is a field of more than 7 thousand hot springs. The water from the springs is used to warm the houses and to fill the open pools in the capital of Iceland. The water comes from below the earth where the temperature is about seven thousand degrees.
| Текст | A | B | C | D | E | F |
| Вопрос |
Решение:
В тексте A содержится ответ на вопрос 3 (What are the national characteristics of the local people? — Каковы национальные особенности местного населения?): «Icelanders are friendly and hospitable and welcome guests.»
В тексте C содержится ответ на вопрос 4 (In what seasons can you see snow in Iceland? — В какие сезоны можно увидеть снег в Исландии?): «From September to May, when the temperature falls, it often snows. »
В тексте D содержится ответ на вопрос 7 (Why are these animals widely used in tourist business? — Почему эти животные широко используются в туристическом бизнесе?): «From the Viking Age, horses have become a part of Iceland’s culture.»
В тексте E содержится ответ на вопрос 2 (What should you take with you when going to Iceland? — Что взять с собой в Исландию?): «If you wear appropriate clothes and have some smart heating devices, neither rain nor snow can ruin your trip.»
В тексте F содержится ответ на вопрос 1 (What natural resource do Icelanders use as an alternative to central heating? — Какие природные ресурсы исландцы используют в качестве альтернативы центральному отоплению?): «The water from the springs is used to warm the houses and to fill the open pools in the capital of Iceland.»
Показать ответ
354721
Источник: ФИПИ. Открытый банк тестовых заданий
Сообщить об ошибке
АНГЛИЙСКИЙ, СООТНЕСТИ ЗАГОЛОВКИ С ТЕКСТАМИ
1.What natural resource do Icelanders use as an alternative to central heating?
2.
What should you take with you when going to Iceland?
3.
What are the national characteristics of the local people?
4.
In what seasons can you see snow in Iceland?
5.
What extreme excursions can the country offer?
6.
What does a traditional Icelandic house look like?
7.
Why are these animals widely used in tourist business?
A.
In spite of its hard northern climate, Iceland is very attractive to tourists. Many people who
have visited the country once want to go there again and again. The country turns skeptics
into poets and optimists. It’s not only because of the views but also because of the local
people. Icelanders are friendly and hospitable and welcome guests. It really compensates for
the cold harsh climate!
B.
An adventurous traveller would never mistake Iceland’s scenery for any other because of the
boiling water fountains and the steam coming from the earth. Smoking volcanoes attract the
bravest tourists. Iceland is the only place in the world where you can hike up a volcano and
even go inside. There are guided walks to the glaciers, large masses of slowly moving ice,
too.
C.
Icelandic weather is unpredictable throughout the year. Bright sunshine can easily change to
cold and miserable weather within a few hours. In the summer, rain is typical in Iceland.
From September to May, when the temperature falls, it often snows, especially on the south
and west coasts.
D.
Till nowadays Icelanders cannot do without horses. And horses are very important not only
for farming. From the Viking Age, horses have become a part of Iceland’s culture. They
look like My Little Pony toys but they are exceptionally strong, so they can do heavy work
and survive cold winters. The horses are good-natured, which is perfect for new riders.
Guesthouses and travel companies across the country offer horse rides and tours.
E.
If you decide to visit Iceland, you’ll never regret your decision. The only thing that can spoil
your trip is the weather. That’s why it’s very important to get a reliable weather forecast
whatever season it is. If you wear appropriate clothes and have some smart heating devices,
neither rain nor snow can ruin your trip.
F.
Hengill, a place near Reykjavik, is a famous landmark of the country. It is a field of more
than 7 thousand hot springs. The water from the springs is used to warm the houses and to
fill the open pools in the capital of Iceland. The water comes from below the earth where the
temperature is about seven thousand degrees.
What are the different climate zones? A simple explainer
Climatic differences are produced by numerous factors, including differences in radiation, geology, and lattitude.
As the name implies, climate zones are areas with distinct climates. They are roughly spread in an east-west direction around the Earth and can be classified using different climatic parameters.
Of course, different areas can have localized climates, with unique distribution and characteristics. Here, we will only look at the major climate zones, the one that form belt-shape areas around the world.
What’s the climate, anyway?
Climate is essentially the average weather conditions in a place over a long period of time — 30 years or more. And as you probably already know, there are lots of different types of climates on Earth.
Typically, the hottest regions are closest to the equator. This happens because the Sun’s light is most directly overhead at the equator. At the poles, light falls at an extreme angle, and only a part of its energy and warmth reaches the ground.
That’s why, in general, climate areas tend to be warmer towards the equator and cooler towards the poles. This varies with lattitude.
How has it changed over time?
Over the past two million years, Earth’s climate continuously changed — usually very slowly. Long, cold periods called ice ages, or glacial, have been interspersed with warmer periods. The last ice age ended about 10,000 years ago. At its height, all of northern Europe and parts of North America, Siberia, New Zealand, Tasmania, and the southernmost tip of South America were covered by ice sheets up to 3,300 ft (1,000 m) thick.
As a result, we are currently living a warm interglacial era that began about 11,000 years ago. We do have some ice at the poles, but it is still fairly warm compared to glacial eras.
These geological changes are common in the Earth’s history, but they are very different from the type of climate change we are observing nowadays. As opposed to a natural change, this is a man-made shift caused by the emission of greenhouse gases. Among the effects of this climate change, warmer areas will expand and move, and ice will melt in the polar areas, raising water levels.
What are the influences on climate?
Mountains play a crucial role in our planet’s climate.
In the strictest sense, climate is controlled by the energy absorbed and reflected from the Sun, as well as the heat generated inside the Earth through radioactive reactions.
However, considering this energy budget, climate is also controlled by wind, oceans, and mountains. For instance, winds bring moisture from seas to land, producing typically wet climates. North and south of the Equator, the trade winds blow from the northeast and southeast, respectively. These winds converge in the tropics, forcing air to rise. This produces thunderstorms, humidity, and monsoons — characteristics of some climates.
North and south of the trade winds, about 30° from the Equator, there is relatively little wind, and therefore little moisture blowing inland from the oceans. Also, dry air is sinking back to the surface, warming in the process. This is why many of the world’s great desert regions — the Sahara, the Persian Gulf region, and chunks of Mexico — lie at the same latitude. A similar band of deserts lies to the south in Australia, South America, and southern Africa.
Mountains force wind to rise as it crosses over them. This cools the air, causing moisture to condense in clouds and rain. This produces a wet climate on the upwind side of the mountains and an arid “rain shadow” on the downwind side. Oceans provide moisture that fuels rainstorms. They also buffer the temperature of coastal regions, regardless of latitude.
How were the climate zones established?
Forests are also key actors in the climatic scene. Image credits: Larissa Rodrigues.
There’s no clear delimitation, but most scientists agree on a few rough climate areas.
In the early 1900s, climatologist Wladimir Köppen divided the world into five major climate groups. Moist, tropical climates are hot and humid, Köppen wrote. Steppes and deserts are dry, with large temperature variations. Plentiful lakes, rivers, or nearby oceans give humid, mid-latitude climates cool, damp winters, but they have hot, dry summers. Some of these climates are also called the Mediterranean. Continental climates occur in the centers of large continents.
Mountain ranges (or sheer distance) block off sources of moisture, creating dry regions with large seasonal variations in temperature. Much of southern Canada, Russia, and parts of central Asia would fall into this category. Cold, or polar, climates round out Köppen’s list. A sixth region, high elevations, was later added to the classification system.
To this day, Köppen’s general classification endured. Again, this is only a rough demarcation, and should only be considered as a simple climate classification.
What are the features of each zone?
White-peaked volcanos rise from the plains of the Atacama Desert under deep blue skies. The Atacama is the driest desert in the world.
Will climate zones change in the future?
Some scientists believe that Earth will enter another ice age in a few thousand years. However, almost all scientists believe that pollution caused by human activities is slowly causing the planet to grow warmer — a phenomenon called global warming, which can alter the climate zones. The temperature has already increased 1ºC compared to pre-industrial levels, and shows no sign of stopping.
Marina Ventura’s Climate Explorers
Discovering the different climates all around the world!
What are the major climate zones of the world?
Plus, what are local climates and what affects these?
Climate is all about patterns of weather. We find out more about the different climates on our planet and what causes them to be different from each other.
When you hear the words “weather” and “climate” you might think they mean the same thing – but they’re quite different!
It might be rainy today or it might be sunny – that’s the weather. But climate is the pattern of weather in a place over a much longer time.
Different parts of the world have very different patterns of weather. The Earth’s climate is driven by energy from the sun which arrives in the form of heat. Half of this energy travels through our atmosphere and reaches the Earth’s surface.
More to click.
The other half is either absorbed by the atmosphere or reflected back into space. Because the Earth is a sphere, the sun’s rays reach the earth’s surface in polar regions at a much more slanted angle than at equator. So straight away, we know that the Poles are colder than the Equator.
When things aren’t in balance, nature likes to even things out. So the extra energy at the Equator needs to be spread across the planet and it’s this that creates different climate zones across the world.
Warm air rises at the equator and moves toward the poles. Where warm, wet air rises, we get thunderstorms and tropical rainforests. Where air sinks, it stops clouds from forming – so it rains less, even making deserts.
How many climate zones are there and how do they differ?
1. Tropical
Around the Equator we have tropical climates which are hot and humid, this is where you’ll find the world’s rainforests.
2. Arid
Then there are arid or dry climates – like you’d find in deserts.
3. Mediterranean
Next is Mediterranean with hot dry summers, and cooler wetter winters.
4. Temperate
Then there are temperate climates. That’s what we have in the UK, where summers are mild and winters aren’t too cold.
5. Continental
In areas that are a very long way from the sea, the climate is continental with long, cold winters and short, hot summers.
6. Polar
Finally, there’s polar climates which experience long periods of extreme cold.
Local climates
You might have been to countries like France and Italy, in the Mediterranean, where they have lots of snow in winter – and some of their mountains are even snow covered all year round.
But they also have beautiful beaches – great fun during the hot and dry summers. So if you’ve got both snow covered mountains and hot beaches, does that mean they don’t have a Mediterranean climate?
No, it just means that local climates in a country can be different to the region’s climate. This can be for lots of reasons – high places like mountains tend to be colder because the air is cooler the higher you go.
What else can affect local climates?
Vegetation can also affect the local climate we experience. In equatorial rainforests, dense vegetation blocking the wind combined with high temperatures and rainfall means it’s a very humid place to be! Where there’s no vegetation, the air can be much drier and the wind can blow.
In busy cities, the air temperature is often warmer than the surrounding countryside, particularly at night-time. This is due to buildings and roads absorbing heat during the day, and giving it off at night.
Another thing that can affect a local climate is the wind! It might be that part of a country frequently catches wind from another region – this is called a prevailing wind. If it’s coming from a hotter place, this might raise temperatures, or if it’s from a colder area, it’ll cause the local temperature to drop.
The oceans also have a part to play in influencing our weather and climate.
But just because a place has one climate doesn’t mean it won’t change.
Climate scientists take measurements over long periods of time to track patterns in temperature and rainfall. These help us know what to expect today and in the future but are also a great way to see what changes have happened in the past.
It’s amazing to think that 20,000 years ago the UK would have been in the Ice Age, and our climate here would have been similar to the Polar climates that we see today! Cold enough to have a pet polar bear!
You can hear Marina Ventura’s Climate Explorers weekdays from 11.30am on Fun Kids!
Get the series on your phone or tablet and listen whenever you like – at home or in the car!
…or you can listen here:
Marina Ventura: Kids Guide to Our Planet
The podcast exploring the environment, ecology, oceans and climates on our planet Earth.
MOBILE: Marina Ventura: Kids Guide to Our Planet
The podcast exploring the environment, ecology, oceans and climates on our planet Earth.
What Are the Different Climate Types?
Climate is the average weather conditions in a place over a long period of time—30 years or more. And as you probably already know, there are lots of different types of climates on Earth.
For example, hot regions are normally closest to the equator. The climate is hotter there because the Sun’s light is most directly overhead at the equator. And the North and South Poles are cold because the Sun’s light and heat are least direct there.
The snow-covered peaks of the Chigmit Range during winter. Credit: NPS/M. Cahill 2015
Using this information, in the late 1800s and early 1900s a German climate scientist named Wladimir Koppen divided the world’s climates into categories. His categories were based on the temperature, the amount of precipitation, and the times of year when precipitation occurs. The categories were also influenced by a region’s latitude—the imaginary lines used to measure our Earth from north to south from the equator.
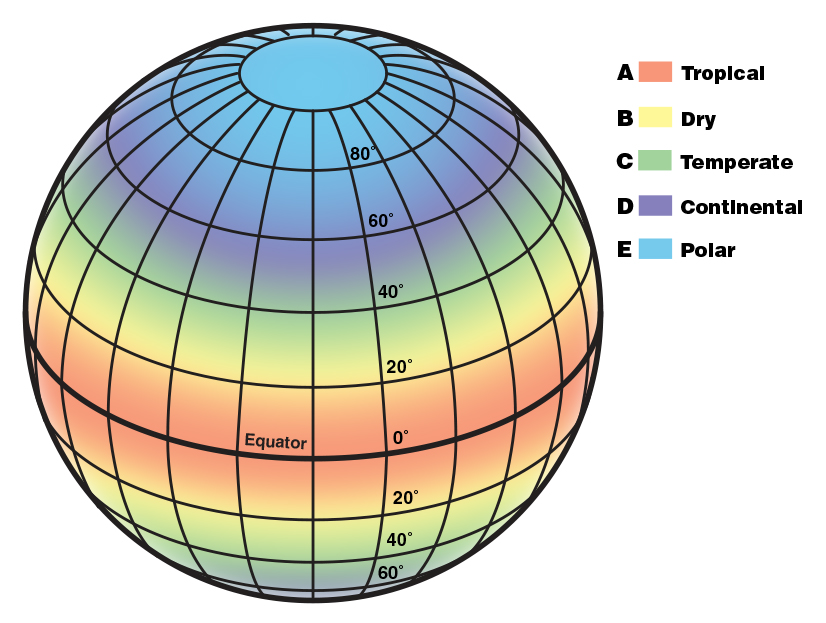
Today, climate scientists split the Earth into approximately five main types of climates. They are:
A: Tropical. In this hot and humid zone, the average temperatures are greater than 64°F (18°C) year-round and there is more than 59 inches of precipitation each year.
B: Dry. These climate zones are so dry because moisture is rapidly evaporated from the air and there is very little precipitation.
C: Temperate. In this zone, there are typically warm and humid summers with thunderstorms and mild winters.
E: Polar. In the polar climate zones, it’s extremely cold. Even in summer, the temperatures here never go higher than 50°F (10°C)!
This is roughly where those climate zones appear on a globe:
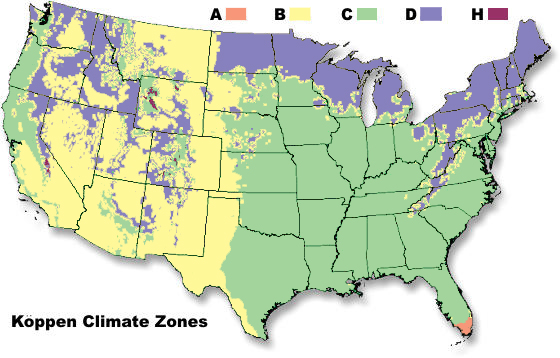
What does a map of climate zones really look like?
Distance to the equator is only one part of an area’s climate. Things like the movement of the oceans and Earth’s tilt and rotation also affect how weather patterns move around the globe.
If you classify the United States into climate zones using all of this information, it actually looks something like this:
This is an illustration of the climate zones within the United States. The extra climate zone, labeled «H» on this map, is a special zone called the highlands. The highlands climate zone is characterized by weather that differs from the surrounding area because of mountains. Credit: NOAA (modified)
How can information about climate zones be used?
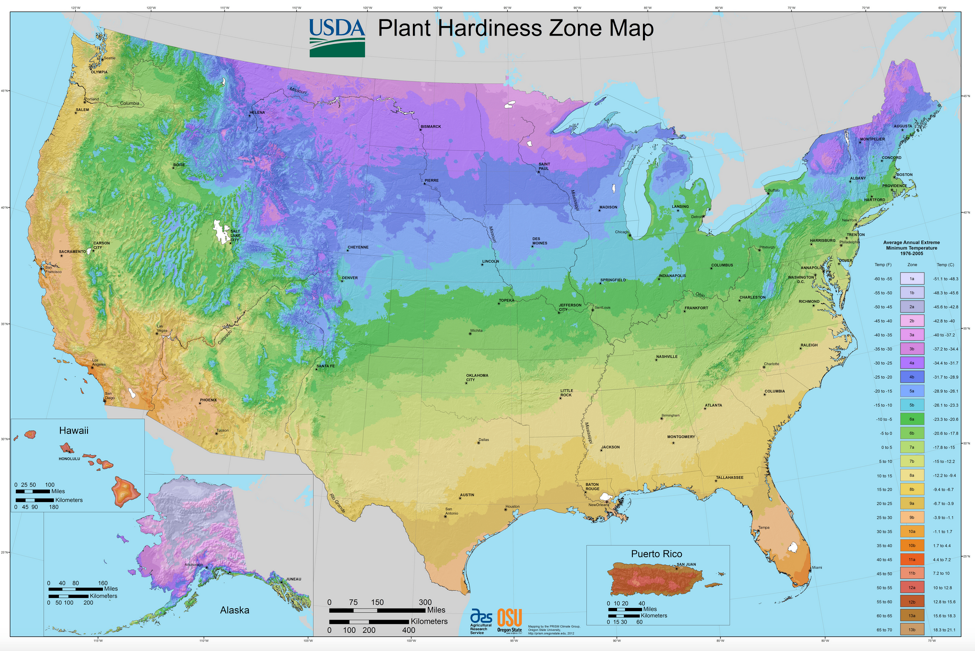
Climate zones can be useful for gardening and farming. Plants grow best in the climate conditions that are found in their native ecosystem. For example, if you want to plant an apple orchard in your backyard, you should first check to see which varieties of apples are a good match for your region’s climate.
This is called a Plant Hardiness Zone map. It’s a specific type of climate zone map that can help you figure out what kinds of plants will survive in your back yard. Image credit: USDA/Agricultural Research Service/Oregon State University
How do weather satellites play a role?
Weather satellites mostly help with tracking conditions that are happening right now and forecasting weather in the near future. However, they also collect information that helps us monitor a region’s climate over time.
For example, satellites in the GOES-R series—short for Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-R—can monitor the sea surface temperature and the Gulf Stream, a powerful current in the Atlantic Ocean. Both of these things can influence a region’s climate.
In addition, the temperature of the land becomes cooler at night, and there are changes in the amount of clouds. The GOES-R series satellites monitor cloudiness and land surface temperature—information that helps scientists to understand how the differences between day and night can affect a region’s climate.
Satellites in the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) can also provide information on differences between day and night. For example, JPSS orbits Earth twice a day in what’s called an afternoon orbit. As the satellite orbits from North Pole to South Pole, it captures observations in the afternoon on one side of Earth and observations of the early morning on the other side of the planet.
While JPSS orbits, the satellites provide global observations of many other variables that influence climate such as atmospheric temperature and water vapor, snow and ice cover, vegetation, sea and land surface temperature, precipitation and more. These add important information to our records of regional differences in Earth’s climate.