Journalists have reported that the president is ill
Journalists have reported that the president is ill
Помогиите! Пожайлуста! People expect him to win
Journalists have reported that the President is away in France.
The President has been reported to be away in France.
It has been reported that the President is away in France.
Everyone knows that the statement was untrue.
The statement is known to have been untrue.
It is known that the statement was untrue.
Many people believe that the climate is changing.
The climate is believed to be changing.
It is believed that the climate is changing.
Everyone knows that he has been in a serious car accident.
He is known to have been in a serious car accident.
It is known that he has been in a serious car accident.
Many people say that the new prices are too high.
The new prices are said to be too high.
It is said that the new prices are too high.
They claim that this diamond is the largest in the world.
This diamond is claimed to be the largest in the world.
It is claimed that this diamond is the largest in the world.
—————
I remember being taken to the circus.
I like being given with presents.
I love being invited to the parties.
—————
Jam _is made_ from fruit.
A young girl _was rescued_ by a firefighter yesterday.
This email should _be sent_ right away.
Life _hasn’t been found_ on other planets yet.
The boy _was taken_ to hospital by an ambulance.
I don’t like _being told_ what to do.
A new shopping centre _is being built_ outside the city centre.
The new library _is going to be opened_ by the mayor next week.
The animals at the zoo _are fed_ twice a day.
Passive structures
Note these passive structures. They are mostly rather formal:
The verbs believe, expect, feel, hope, know, report, say, think etc can be used in the following passive patterns:
People say she is rich.
1. It + passive + that-clause It is said that she is rich.
2. Subject (person) + passive + to-infinitive She is said to be rich.
3. Active object complement → passive subject complement
e.g. The Queen considered him a genius. → He was considered a genius.
e.g. They elected Mrs Robins President. → Mrs Robins was elected President.
e.g. The others call him stupid. → He is called stupid by the others.
e.g. You’ve made me very happy. → I have been made very happy.
e.g. There are thought to be fewer than twenty people still living in the village.
e.g. There were said to be ghosts in the house, but I never heard anything.
3.1 Make these sentences passive, using one of the above structures:
1. People think the government will fall.
2. We appointed Mr Evans secretary.
3. The villagers called her a witch.
4. People believed that fresh air was bad for sick people.
5. Some people say that there are wolves in the mountains.
6. Police think the man holding the hostages is heavily armed.
7. They say he is in an agitated state.
8. Everybody considered her strange.
9. We expect that the rate of inflation will rise.
10. They say he is somewhere in Germany.
3.2 Write these sentences in another way, beginning as shown. Use the underlined word in your sentence:
1. It is expected that the strike will end soon. – The strike is expected to end soon.
2. It is expected that the weather will be good tomorrow. – The weather is ____.
3. It is believed that the thieves got in through the kitchen window. – The thieves ____.
4. It is reported that many people are homeless after the floods. – Many people ____.
5. It is thought that the prisoner escaped by climbing over a wall. – The prisoner ____.
6. It is alleged that the man drove through the town at 90 miles an hour. – The man is ____.
7. It is reported that the building has been badly damaged by fire. – The building ____.
8. a) It is said that the company is losing a lot of money. – The company ____.
b) It is believed that the company lost a lot of money last year. – The company ____.
c) It is expected that the company will lose money this year. – The company ____.
3.3 Turn the following into the Passive as in the example:
1. People expect him to win.
He is expected to win. It is expected that he will win.
2. Journalists have reported that the President is ill.
The President _________________________________
3. Everyone knows that the statement was untrue.
The statement _________________________________
4. Many people believe that the climate is changing.
The climate ___________________________________
5. Everyone knows that he has been in prison.
6. Many people say that the new prices are too high.
The new prices ________________________________
7. They claim that this diamond is the largest in the world.
This diamond _________________________________
It _____________________________________________
(be) supposed to
Sometimes (be) supposed to = it is said to:
e.g. Let’s go and see that film. It is supposed to be very good. (= it is said to be very good)
e.g. “Why was he arrested?” “He is supposed to have kicked a policeman.” (= he is aid to have kicked a policeman)
3.4 People say a lot of things about Arthur. Nobody knows for sure whether these things are true or not. Write sentences about Arthur using (be) supposed to:
1. Arthur eats spiders. – Arthur is supposed to eat spiders.
2. He has 12 children.
3. He is very rich.
4. He robbed a bank a long rime ago.
5. He writes poetry.
But sometimes (be) supposed to has a different meaning. “Something is supposed to” = it is planned, arranged or expected. Often this is different from what really happens:
e.g. I’d better hurry. It’s nearly 8 o’clock and I’m supposed to be meeting Ann at 8.15. (= I have arranged to meet Ann, I said I would meet her)
e.g. You were supposed to clean the windows. Why didn’t you do it?
“You are not supposed to do something” = it is not allowed or advisable for you to do it:
e.g. You are not supposed to park your car here. It’s private parking only.
3.5 Now you have to use (be) supposed to with its other meaning. In each example what happens is different from what is supposed to happen. Use (be) supposed to +one of these verbs:
arrive, be, block, come, park, phone, start
Some of the sentences are negative (like the first example):
You are not supposed to park here. It’s private parking only.
The train was supposed to arriveat 11.30, but it was an hour late.
What are the children doing at home? They __________ at school at this time.
We __________ work at 8.15, but we rarely do anything before 8.30.
This door is a fire exit. You __________ it.
Oh dear! I __________ Ann but I completely forgot.
They arrived very early – at 2 o’clock. They __________ until 3.30.
Get
Sometimes you can use get instead of be in the passive:
e.g. There was a fight at the party but nobody got hurt. (= nobody was hurt)
e.g. I don’t often get invited to parties. (= I’m not often invited)
You can use get to say that something happens to somebody or something, especially if this is unplanned or unexpected:
e.g. Our dog got run over by a car.
You can use getonly when things happen or change. For example, You can not use get in these sentences:
e.g. Jil is liked by everybody. (not “gets liked” – this is not a happening)
e.g. He was a mystery man. Nothing was known about him. (not “got known”)
We use get mainly in informal spoken English. You can use be in all situations.
We also use get in the following expressions (which are not passive in meaning): get married, get divorced, get dressed, get changed.
3.6 Complete the sentences using get/got + one of these verbs (in the correct form):
ask, break, damage, hurt, pay, steal, sting, stop, use
1. There was a fight at the party but nobody got hurt.
2. Ted _____ _____ by a bee while he was sitting in the garden.
3. How did that window _____ _____?
4. These tennis courts don’t _____ _____ very often. Not many people want to play.
5. I used to have a bicycle but it _____ _____.
6. Last night I _____ _____ by the police as I was driving home.
7. How much did you _____ _____ last month?
8. Please pack these things very carefully. I don’t want them to _____ _____.
9. People often want to know what my job is. I often _____ _____ that question.
Дата добавления: 2015-09-12 ; просмотров: 57 | Нарушение авторских прав
Доступные файлы (8):
| Business English Курс лекций.doc | 1497kb. | 11.06.2006 20:48 |  скачать скачать |
| Improve Your Speaking Skills in English.doc | 1104kb. | 05.10.2005 14:31 |  скачать скачать |
| D0_ar_engl_Bibliography.doc | 31kb. | 19.07.2004 15:11 |  скачать скачать |
| D0_ar_engl_gr1.doc | 489kb. | 19.07.2004 15:11 |  скачать скачать |
| D0_ar_engl_gr2.doc | 460kb. | 19.07.2004 15:11 |  скачать скачать |
| D0_ar_engl_gr3.doc | 447kb. | 19.07.2004 15:11 |  скачать скачать |
| Практическая грамматика английского языка 1.doc | 1812kb. | 05.10.2005 14:31 |  скачать скачать |
| Практическая грамматика английского языка 2.doc | 2643kb. | 05.10.2005 14:31 |  скачать скачать |
Практическая грамматика английского языка 2.doc
А
при Президенте Республики Беларусь
Система открытого образования
английского языка
для среднего и продвинутого
уровней обучения
Часть II
Учебное пособие для студентов гуманитарных специальностей
высших учебных заведений
2-е издание, исправленное
Серия основана в 2001 году
Рекомендовано к изданию Комиссией по приемке и аттестации электронных версий учебных и учебно-методических материалов Академии управления при Президенте Республики Беларусь.
Печатается по решению редакционно-издательского совета Академии управления при Президенте Республики Беларусь.
Рецензенты:
доктор филологических наук, профессор кафедры грамматики английского языка Минского государственного лингвистического университета Д.Г.Богушевич;
П-69 ^ Практическая грамматика английского языка ( для среднего и продвинутого уровней обучения): учебное пособие для студентов гуманитарных специальностей высших учебных заведений / На англ. яз.= English Grammar Review; под общ. ред. д.филол.н., профессора Л.М.Лещевой. Часть II. – 2-е изд., испр. – Мн.: Акад. упр. при Президенте Респ. Беларусь, 2005. – 391с.
ISBN 985-457-473-3
Учебное пособие является второй частью «Практической грамматики английского языка», состоит из 7 разделов и посвящено английскому глаголу. В разделе 1 представлена общая информация о глаголе; в разделах 2-5 рассматриваются времена групп Indefinite, Perfect, Continuous и Perfect Continuous; раздел 6 носит обзорный характер, и времена в нем рассматриваются в сравнительно-сопоставительном плане; в разделе 7 анализируется система английского залога. Каждый раздел включает вводный и заключительные тесты и содержит описание формообразования времен и залогов, их значения и употребления, а также тренировочные и обзорные упражнения.
Предназначается студентам гуманитарных специальностей неязыковых вузов, а также всем, кого интересует грамматический строй и функционирование английского языка.
| ISBN 985-457-473-3(ч.II) | © Володька С.М., Лещева Л.М., Кипкаева В.С., и др., 2003 |
| ISBN 985-457-471-7 | © Академия управления при Президенте Республики Беларусь, 2003 |
Chapter 7 V E R B S
Unit 1 GENERAL INFORMATION
1. Identify the verbs as simple (S), derived (D) or composite (C) as in the model. Start with the second verb.
^
Model: 1) work – S (simple)
1) work 2) stand up 3) milk 4) reread 5) give in 6) stay up 7) disagree
8) overcook 9) uncover 10) compute
2. Identify the verbs as derived by prefixation (P), suffixation (S) or by conversion (C). Start with the second verb.
^
Model: 1) lengthen – S (by suffix -en )
1) lengthen 2) water 3) dust 4) falsify 5) undercook 6) unload
7) misunderstand 8) enrich 9) patronize 10) fish
3. Say which of the following words are verbs or may be used as verbs:
1) feed 2) loss 3) blood 4) short 5) strike 6) sing 7) economize 8) law 9) belief 10) advise 11) arrival 12) slowly 13) strength 14) blacken
15) election 16) bite 17) ride 18) fill 19) live 20) pay
4. Derive new verbs from the following verbs, nouns and adjectives by means of the prefixes: re-, mis-, be-, un-, de-, dis-, over-, en-. Use each prefix only once.
1. Identify the verbs in the following sentences as auxiliary (A) or main (M) as in the model. Start with the second sentence.
^
Model: 1) did – A (auxiliary), like – M (main)
2. Identify transitive (T) and intransitive verbs (I) in the following sentences as in the model. Start with the second sentence.
^
Model: 1) took – T (transitive)
1. Identify the tense form of the verbs in the following sentences as in the model. Start with the second sentence.
Unit 8. Active and Passive Voice
A. Formation and Basic Meanings
B. Changing from Active into Passive
Exercise1. Turn the sentences from Active into Passive. Do it to the following scheme:



 |
1. Muslims celebrate Ramadan.
2. An expert is restoring the antique car.
3. Steven Spielberg has directed a lot of successful films.
5. A famous designer is going to redecorate the President’s house.
6. Van Gogh painted “Sunflowers”.
7. Astronauts are exploring space.
8. The company gave her the first rise in April.
9. Mr Layton carried out an interesting experiment.
10. His colleagues started to respect Tom.
Exercise 2. Look at the signs, notices, headlines, etc. and make the sentences using the full form of the Passive.
 |
Sample: Rare birds found in remote countryside. – A rare bird has been found in the countryside.
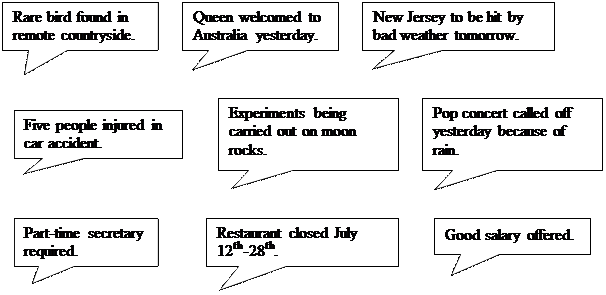 |
Exercise 3. Change each of the following sentences from the Active into the Passive Voice.
1. Someone typed the report last week.
2. Someone has sent all the letters today.
3. Someone was writing the information during the meeting.
4. Someone will write down the client’s telephone number.
5. Someone is repairing the computer.
Exercise 4. Do the General Knowledge Quiz “Guess Who?” asking and answering questions as in the example.
 |

 |
| Penicillin The “Mona Lisa” The radio The pyramids America The telephone The song “Imagine” Mickey Mouse “Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland” The electric bulb The revolver The Pacific Ocean The television Paper Radioactivity dynamite | Discover Paint Invent Build Discover Invent Write Create Write Invent Invent Discover Invent Invent Discover Invent | Leonardo da Vinci Lewis Carol The Ancient Egyptians Walt Disney John Lennon Marconi Alexander Fleming Alexander Graham Bell Thomas Edison Christopher Columbus Vasco Nunez de Balboa Samuel Colt The Chinese John L. Baird Alfred Nobel Becquerel |
 |
Exercise 5. Use “by or “with”. Justify your choice.
 |
1. The window was broken…a hammer.
2. He was knocked down…a car.
3. The lion was shot…a rifle.
4. That novel was written…D.H. Lawrence.
5. The garden was dug…a spade.
6. The city was attacked…the enemy.
7. The pudding was made…fruit and chocolate.
8. He was hit…a handbag.
9. The picture was painted…Jackson Pollack.
10. The house was built…wood and bricks.
11. The busy shopping street was crowded…people.
12. All through January the fields were covered…snow.
13. The island was inhabited…people of mainly Chinese origin.
14. The emergency exit was concealed…a red curtain.
15. The room was crammed…furniture of all descriptions.
Exercise 6. Turn the following into the Passive in two ways. Do it to the following scheme:

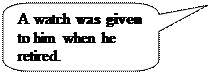

1. They gave him a watch when he retired.
2. They have offered him a job.
3. She will send you a fax.
4. They are going to show me a new technique.
5. Someone gave her a book.
6. They give the students extra lessons.
7. They have shown her the plans for the house.
8. They should have sent you a receipt.
9. The secretary told me a lot of lies.
10. Mrs Lee teaches us French.
12. My dad has lent me a car for the week.
13. The manager promised us a full explanation.
14. The referee gave Mary the first prize.
15. The controller will give you another ticket.
Exercise 7. Make the following active sentences passive. Remember that the postposition or preposition should follow the verb immediately.
 |
1. We are dealing with your complaint.
2. They gave up the search after three hours.
3. No one brought up that question at the meeting.
4. Someone should look into the matter.
5. We had to put off our visit until later.
6. I was shocked to hear that someone had broken into your house.
7. Don’t speak until someone speaks to you.
8. You must account for every penny you spent.
9. Someone hasn’t stuck this lamp on very firmly.
10. No one can rely on him.
11. You should look after the children better.
12. They will deal with the matter as soon as possible.
13. They have done away with many dangerous diseases.
14. All the ministers will see him off at the airport.
15. Nobody objected to his proposal.
Exercise 8. Use passive constructions with “get” where possible. Comment on your choice.
 |
Example: The plants (damage)…by the cold weather. – The plants got damaged by the cold weather. (“Get” is used here to emphasize an unfortunate action that happened unexpectedly.)
1. I never found the book we were looking for. It (lose)…when we were moving.
2. After the way he behaved last time he never (ask)…to their house again.
3. I phoned to explain what had happened but I (cut off)…before I could finish.
4. The book (tear)…when the children started fighting over who should read it first.
5. She was quite friendly at first, then she (promote)…and now she doesn’t care about us any more.
6. They were only married a year before they (divorce)…
7. There isn’t any cheese left; I’m afraid, it (eat)…in the morning.
8. Without a map we soon (loose)…
9. He was a well-known expert on animal diseases and his opinion (respect)…greatly.
10. He (kill)…in a plane crash.
 |
 |
Exercise 9. Make the following active sentences passive where appropriate. Justify its use.




1. Nobody has used this room for ages.
2. We have to give the books back.
3. John enjoyed seeing his native town.
4. Martin is writing the company report this year.
5. They put fresh flowers in the hotel rooms every day.
6. Glass breaks easily.
7. Bad weather may delay your flight.
8. She washed herself and combed her hair.
9. The advertisement reads that the swimming-pool is free.
10. I hate people staring at me.
Exercise 10. Which sentences can be changed with the verb underlined in the Passive Voice?
 |
Example: What happened to your team yesterday? = Cannot be changed.
1. Johnson scored the first goal in the second half.
2. The team refused to obey the referee’s decision.
3. Three competitors complained that Smith had taken a short cut.
4. The judges awarded the first prize to Denise Long.
5. She couldn’t run because her new shoes didn’t fit properly.
6. I really love the excitement involved in basketball.
7. The BBC broadcast the whole match live last season.
8. Both teams arrived late at the stadium.
Exercise 11. Change the words underlined. Use the passive voice, and make any other necessary changes.
 |
Nobody really knows how people invented the game of basketball. People say that some ancient Greek vases show the game and people playing it. People generally think, however, that the game began in the United States quite recently. Somebody thought of the game in a YMCA club. Nobody can prove this of course, so perhaps it did begin earlier. Wherever people first played the game, basketball is now very popular, and many thousands of people play it, as people can play it outdoors and indoors. Personally, I wish nobody had ever invented it, because people keep me awake when a big game is on TV. The noise is terrible.
Exercise 12. Read the information about a town, and complete the guidebook entry underneath it.
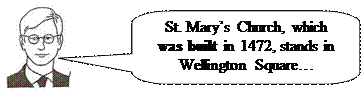 |
| Railway station – closed (to be demolished, site to become sports centre). Dobson Gallery bought from Major Dobson (1923). Many gifts of paintings from private collectors. 4,000 visitors (double this expected this year). Local traders hold market on Tues. Town Hall (called by the Great Britain Guide a fine example of late Victorian architecture). St. Mary’s Church (1472), restored to original condition. |
Exercise 13. Complete the following dialogues that might be used in the conversation between workmates. Use the verbs to give, to fire and to type by making them correspond to the passive forms. Then make your own dialogues using different passive forms.
· Have you heard about John?
· No, I haven’t. What happened?
· He … a raise last week.
· That’s great! That’s the second time he … a raise this year.
· Have you heard about Mary?
· No, I haven’t. What happened?
· What a shame! That’s the second time she … this year.
· 
· I’m calling about my report. Has it … yet?
· Not yet. It’s … right now.
· When can I pick it up?
· 
Exercise 14. Turn the following into the Passive using the constructions “It + Passive + that-clause” and “Subject (person) + Passive + to-infinitive”.




1. People expect him to win.
2. The newspapers expect that prices will fall in the spring.
3. Scientists have proved that smoking has some relation to lung cancer.
4. An official spokesman announced that 150 people had lost their lives in the disaster.
5. Journalists have reported that the President is ill.
6. Everyone knows that the statement was untrue.
7. Many people believe that the climate is changing.
8. Everyone knows that he has been in prison.
9. Many people say that the new prices are too high.
10. They claim that this diamond is the largest in the world.
Exercise 15. Answer the following questions using the passive form of the verbs in brackets.
Модуль 2. The Passive Voice
The Passive Voice
Цель: Повторить употребление пассивного залога
1. Проверьте домашнее задание по листку контроля и оцените свою работу.
2. Формирование навыков распознавания активного и пассивного залогов.
Выполните упражнение 1 и оцените свою работу.
Упражнение 1. Раскройте скобки, употребляя глагол в нужной форме.
1) Although the cheetah is the fastest animal in the world, it is in danger of becoming extinct if it continues . tо be killed. (kill) for its skin.
2) The children. (frighten) by the story. It was about ghosts, witches and evil spirits.
3) Derek crashed his mother’s car, and now they can’t go on holiday. It. (cannot/repair) quickly, because the front end. (knock) into the wheel, making it unmovable.
4) Yesterday we had a surprise party for Albert’s birthday. While Mary. (take) him to a show, we. (gather) at his apartment When they. (return) home, Albert was surprised to see us all there.
5) The scandal is certain. (report) in all the newspapers. The president. (have) a difficult year.
6) Joan is an example of someone who can beat the odds. In 1980, she. (tell) she had six months to live because she had cancer. After exercise, dieting and positive thinking she. (recently/inform) that she. (beat) the disease.
7) This newspaper. (publish) by an Italian company. It. (always/have) interesting stories.
8) Rice. (grow) in this area for hundreds of years, but now the government. (try) to find an alternative crop because rice. (not/make) much profit last year.
9) My shoes. (make) in Italy, but I. (buy) them in France last May.
10) The Queen. (not/see) since last July. The newspapers. (say) that she is sick, but most people. (not/believe) it.
3. Формирование навыков перевода предложений из активного залога в пассивный.
Выполните упражнение 2 и оцените свою работу.
Упражнение 2.Перепишите текст в пассивном залоге.
The Government made an important decision last night. They will ban all cars from the centre of town as pollution is seriously affecting people’s health. They will allow only bicycles and buses to enter the town centre. They are making plans for a new environmental police force. After all, they must do something before it’s too late.
4. Формирование навыков перевода с английского языка на русский.
Выполните упражнение 3 и оцените свою работу.
1) When was the new building of Moscow University completed? 2) The new building of the university was being built when I entered the History Faculty. 3) Will another building of the university be built in the near future? 4) A lot of beautiful buildings have been built in Moscow lately.
5. Формирование навыков перевода с русского языка на английский.
Выполните упражнение 4 и оцените свою работу.
1)Все телеграммы отправлены? – Половина телеграмм отправлена вчера. Остальные, кроме трех напечатаны. Последние сейчас печатают. Их напечатают минут через двадцать. 2) Не входите в комнату. Сейчас экзаменуют студентов. Их экзаменуют уже 20 минут. 3) Студентов попросили выучить правило самостоятельно, так как оно было уже объяснено.
6. Подведите итоги своей работы.
1) Почему над ним всегда смеются? – Why is he always laughed at?
2) Нам рассказали длинную историю. – We were told a long story.
3) Он легко переведет эту статью. – He will translate the article easily.
4) Его попросили зайти попозже. – He was asked to come later.
5) Нам велели прийти в пять. – We were told to come at five.
6) Эта популярная программа часто показывается по телевидению. – This popular programme is often shown on TV.
7) О нем всегда много говорят. – He is always much spoken about.
8) Его никогда не слушали. – He was never listened to.
9) Ему объяснили правила? – Was he explained the rules? / Were the rules explained to him?
10) Вы можете написать сочинение на эту тему. – An essay on this topic can be written.
11) Мне вчера дали много интересных книг. – I was given a lot interesting books yesterday.
12) Его всегда приглашают на вечеринки. – He is always invited to parties.
2. were frightened 3. be repaired, was knocked 4. took, gathered, returned 5. to be reported, has had ( to have been reported, had) 6. was told, has been informed, has beaten 7. is published, has 8. has been grown, is trying, didn’t make 9.were made (have been made), bought 10. has not been seen, say, do not believe
An important decision was made by the government last night. All cars will be banned from the centre as people’s health is being seriously affected. Only bicycles and buses will be allowed to enter the town centre. Plans for a new environmental police force are being made. After all, something must be done before it’s too late.
1. Когда было построено новое здание МГУ? 2. Новое здание МГУ строили, когда я поступила на исторический факультет. 3. Будет ли построено еще одно здание университета в ближайшем будущем? 4. Много прекрасных зданий выстроили в Москве за последнее время.
1. Have all the telegrammes been sent off? – Half of the telegrammes were sent off yesterday. The rest of them, except three, have been typed. The last ones are being typed now. 2. Don’t enter the room. The students are being examined now. They have been examined for twenty minutes. 3. The students were asked to learn the rule themselves as it had already been explained.





