Local area network what is
Local area network what is
local area network (LAN)
A local area network (LAN) is a group of computers and peripheral devices that share a common communications line or wireless link to a server within a distinct geographic area. A local area network may serve as few as two or three users in a home office or thousands of users in a corporation’s central office. Homeowners and information technology (IT) administrators set up LANs so that network nodes can communicate and share resources such as printers or network storage.
LAN networking requires Ethernet cables and Layer 2 switches along with devices that can connect and communicate using Ethernet. Larger LANs often include Layer 3 switches or routers to streamline traffic flows.
A LAN enables users to connect to internal servers, websites and other LANs that belong to the same wide area network (WAN). Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two primary ways to enable LAN connections. Ethernet is an Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) specification that enables computers to communicate with each other. Wi-Fi uses radio waves in the 2.4 gigahertz and 5 GHz spectrum to connect computers to the LAN.
Legacy LAN technologies, including token ring, Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) and Attached Resource Computer Network (ARCNET) have lost favor as Ethernet and Wi-Fi speeds increased and connectivity costs decreased.
There are two primary LAN types: wired LANs and wireless LANs (WLANs). A wired LAN uses switches and Ethernet cabling to connect endpoints, servers and internet of things (IoT) devices to the corporate network. For small businesses with only a handful of devices, a wired LAN can consist of a single unmanaged LAN switch with enough Ethernet ports to interconnect all devices. But larger LANs that connect thousands of devices require additional hardware, software and configuration steps to ensure the network is performing optimally. This is where the concept of virtual LANs (VLANs) comes into play.
Although virtual LANs can help reduce broadcast congestion issues, they create another problem. When devices on different VLANs need to talk to each other, a Layer 3 switch is required to transmit and receive traffic between the two LANs. This is known as inter-VLAN routing. Additionally, because large enterprise networks almost always are broken up into hundreds of VLANs, they require routers to be deployed throughout parts of the overall network. Today, vendors integrate Layer 3 routing capabilities into network switches to create a Layer 3 switch. Thus, a Layer 3 switch can perform both switching and inter-VLAN routing functions on a single appliance.
Wireless LANs use the IEEE 802.11 specification to transport data between end devices and the network using wireless spectrum. In many situations, a wireless LAN is preferable to a wired LAN connection because of its flexibility and cost savings, as it isn’t necessary to run cabling throughout a building. Companies assessing WLANs as a primary means of connectivity often have users who rely exclusively on smartphones, tablets and other mobile devices.
Operating systems (OSes), such as Microsoft Windows, Linux, Apple OS X, Android and iOS, have Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) and IPv6 networking capabilities incorporated into them. Additionally, personal computer (PC), tablet and smartphone hardware all come with an Ethernet port, Wi-Fi chip or both. This means that, as long as the network administrator has a relatively up-to-date laptop or desktop PC, it’s fairly straightforward to network machines together onto a wired or wireless LAN.
Setup of a simple wired LAN requires an administrator to connect the end device to a LAN switch using a twisted-pair Ethernet cable. Once connected, the devices can communicate with each other on the same physical LAN or VLAN.
To set up a wireless network, the administrator needs a wireless access point (WAP). The WAP can be configured to broadcast a network service set identifier (SSID) and require devices to authenticate to the network using one of several Wi-Fi authentication techniques. Popular authentication options include Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 pre-shared key and WPA2 Enterprise.
Local area networks enable devices to connect, transmit and receive information between them. The benefits of LAN technologies include the following:
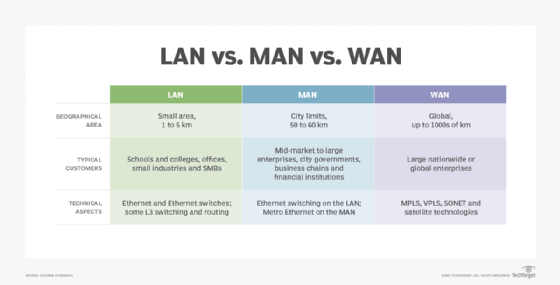
While LAN, WAN and MAN all are networking technologies, there are some distinct differences in terms of technologies, geographical sizes and management responsibilities.
MAN. Metropolitan area networks are most often used when an organization maintains multiple buildings or locations within a city or municipality. Buildings are typically connected using fiber optic cabling. In most cases, the organization partners with a telecommunications company to provide and manage the MAN service on the client’s behalf. Alternatively, the company can choose to lease dark fiber and own or manage the MAN equipment in-house. Modern MAN networks are built using Metro Ethernet, Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) and point-to-point or point-to-multipoint wireless technologies.
WAN. A wide area network connects business locations that are dispersed throughout a state, country or even globally. The organization purchases WAN services from a telecommunications provider that manages the operational status of each WAN link. In most cases, only network traffic that must be transported back and forth between business locations is moved over the WAN. Due to potential latency issues, geographically dispersed locations typically are built with their own internet connection. That way, internet-bound data can be directly sent to and from a branch office, instead of having it backhauled to a central office.
The technologies used to build WANs can include MPLS, Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS), Ethernet over Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) and satellite-based technologies. Since the carrier typically handles the underlying technologies, to the end customer, the WAN looks like a standard Ethernet connection between locations.
Once a network has been set up, it must be secured. This can be done through security settings in the L2/L3 switches and any existing routers. The use of administration authentication mechanisms, device logs and frequent software updates help to keep LAN equipment secure. Hardware-based security, such as fingerprint recognition, security tokens and full disk encryption, can also be used to enhance network security. Additional security packages for protecting and maintaining the network perimeter can be installed locally or purchased through a software-as-a-service (SaaS) delivery model.
Network topologies outline how devices in a LAN are connected, as well as how data is transmitted from one node to another. Popular topologies include the following:
Organizations have many options for implementing networking technologies. Whether they’re upgrading an existing business network or setting up a new one that incorporates the technologies examined here, the first step is to choose the right architecture and topology.
Related Terms
converged network adapter (CNA)
VLAN (virtual LAN)
An introduction to 8 types of network devices
Wireless access point vs. router: What’s the difference?
Zoom’s latest enhancements to IQ for Sales represent a product diversification strategy focused on delivering better intelligence.
Samsung aims the new Fold4 directly at the business market with optimized versions of Google and Microsoft productivity apps. The.
QR codes have many uses for organizations and their employees, but cybercriminals can take advantage of them, too. IT should keep.
Blockchain has been a significant contributor to the global chip shortage. Explore the role this rising technology has played.
From Infineon and Oxford Ionics’ partnership to Cambridge and Honeywell’s merger and QCI’s new Entropy Quantum Computing, explore.
A key index reports unexpected service sector growth, while digital services M&A could overtake 2021 deal volume and value levels.
Local Area Network
Local Area Network Definition
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a group of computers or other devices interconnected within a single, limited area, typically via Ethernet or Wi-Fi.
What is a Local Area Network?
A LAN is a computer network that consists of access points, cables, routers, and switches that enable devices to connect to web servers and internal servers within a single building, campus, or home network, and to other LANs via Wide Area Networks (WAN) or Metropolitan Area Network (MAN). Devices on a LAN, typically personal computers and workstations, can share files and be accessed by each other over a single Internet connection. В
A router assigns IP addresses to each device on the network and facilitates a shared Internet connection between all the connected devices. A network switch connects to the router and facilitates communication between connected devices, but does not handle Local Area Network IP configuration or sharing Internet connections. Switches are ideal tools for increasing the number of LAN ports available on the network.
What are the Basic Layouts of Local Area Networks
The Local Area Network layout, also known as Local Area Network topology, describes the physical and logical manner in which devices and network segments are interconnected. LANs are categorized by the physical signal transmission medium or the logical manner in which data travels through the network between devices, independent of the physical connection.
LANs generally consist of cables and switches, which can be connected to a router, cable modem, or ADSL modem for Internet access. LANs can also include such network devices as firewalls, load balancers, and network intrusion detection.
Logical network topology examples include twisted pair Ethernet, which is categorized as a logical bus topology, and token ring, which is categorized as a logical ring topology. Physical network topology examples include star, mesh, tree, ring, point-to-point, circular, hybrid, and bus topology networks, each consisting of different configurations of nodes and links.
How Does Local Area Network Work
The function of Local Area Networks is to link computers together and provide shared access to printers, files, and other services. Local area network architecture is categorized as either peer-to-peer or client-server. On a client-server local area network, multiple client-devices are connected to a central server, in which application access, device access, file storage, and network traffic are managed.В
Applications running on the Local Area Network server provide services such as database access, document sharing, email, and printing. Devices on a peer-to-peer local area network share data directly to a switch or router without the use of a central server.В
LANs can interconnect with other LANs via leased lines and services, or across the Internet using virtual, private network technologies. This system of connected LANs is classified as a Wide Local Area Network or a metropolitan area network. Local Area and Wide Area Networks differ in their range. An Emulated Local Area Network enables routing and data bridging an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) network, which facilitates the exchange of Ethernet and token ring network data.
How to Design a Local Area Network
The first step in Local Area Network design is determining network needs. Before building a Local Area Network, identify the number of devices, which determines the number of ports required. A switch can extend the number of ports as the number of devices increases.
In order to connect devices wirelessly, a router is required to broadcast a wireless LAN. A router is also required to establish an internet connection for devices on the network. The distance between hardware devices should be measured in order to determine the length of cables required. Switches can connect cables for very long distances.
The setup simply requires connecting the router to a power source, connecting the modem to the router, connecting the switch to the router (if using), and connecting the devices to the open LAN ports on the router via Ethernet. Next, set up one computer as a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol server by installing a third-party utility. This will enable all of the connected computers to easily obtain IP addresses. Turn on “Network Discovery” and “File and Printer Sharing” capabilities.
For wireless Local Area Network Installation, start by connecting the computer into one of the router’s LAN ports via Ethernet. Enter the router’s IP address into any Web Browser and log in with the network administrator account when prompted for a username and password. Open the “Wireless” section in the router settings and change the name of the network in the “SSID” field.
Enable “WPA-2 Personal” as the security or authentication option. Create a password under “»Pre-Shared Key,» ensure that the wireless network is “enabled,” save changes, restart the router, and connect wireless devices to the wireless network, which should appear on the available network list of devices within range.
Characteristics of wireless Local Area Network include: high capacity load balancing, scalability, network management system, role-based access control, indoor and outdoor coverage options, performance measuring abilities, mobile device management, web content and application filtering, roaming, redundancy, wireless Local Area Network Application prioritization, network switching, and network firewalls.
A common Local Area Network issue is a disabled Local Area Network adapter or adapter error, which can be caused by faulty network adapter settings or by VPN software. Typical solutions include: updating the network adapter driver, resetting the network connection, and checking WLAN AutoConfig dependency services.
How to Secure a Local Area Network
The majority of Local Area Network problems and solutions are concerned with the matter of security. There are a variety of strategies for designing a secure Local Area Network. A common approach is to install a firewall behind a single access point, such as a wireless router. Another valuable measure is to use security protocols such as WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) or WPA2 for password encryption on incoming Internet traffic.
Implementing specialized authentication policies enables network administrators to inspect and filter network traffic in order to prevent unauthorized access. Specific access points can be secured with the use of technologies such as VPNs. Internal Local Area Network security can be managed by installing antivirus or anti-malware software.
Virtual Local Area Network Definition
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a logical grouping of devices that can assemble together collections of devices on separate physical LANs, and is configured to communicate as if the devices were attached to the same wire. This enables network administrators to easily configure a single switched network to match the security and functional requirements of their systems without requiring any additional cables or significant changes to the current network infrastructure. VLANs are categorized as Protocol VLAN, Static VLAN, or Dynamic VLAN.
Importance of Local Area Network in an Organization
There are several advantages of Local Area Networks in business:
What Is a LAN?
A local area network (LAN) is a collection of devices connected together in one physical location, such as a building, office, or home. A LAN can be small or large, ranging from a home network with one user to an enterprise network with thousands of users and devices in an office or school.
Regardless of size, a LAN’s single defining characteristic is that it connects devices that are in a single, limited area. In contrast, a wide area network (WAN) or metropolitan area network (MAN) covers larger geographic areas. Some WANs and MANs connect many LANs together.
Contact Cisco
What’s in a LAN?
A LAN comprises cables, access points, switches, routers, and other components that enable devices to connect to internal servers, web servers, and other LANs via wide area networks.
The rise of virtualization has also fueled the development of virtual LANs, which enable network administrators to logically group network nodes and partition their networks without a need for major infrastructure changes.
For example, in an office with multiple departments, such as accounting, IT support, and administration, each department’s computers could be logically connected to the same switch but segmented to behave as if they are separate.
What are the benefits of a LAN?
The advantages of a LAN are the same as those for any group of devices networked together. The devices can use a single Internet connection, share files with one another, print to shared printers, and be accessed and even controlled by one another.
LANs were developed in the 1960s for use by colleges, universities, and research facilities (such as NASA), primarily to connect computers to other computers. It wasn’t until the development of Ethernet technology (1973, at Xerox PARC), its commercialization (1980), and its standardization (1983) that LANs started to be used widely.
While the benefits of having devices connected to a network have always been well understood, it wasn’t until the wide deployment of Wi-Fi technology that LANs became commonplace in nearly every type of environment. Today, not only do businesses and schools use LANs, but also restaurants, coffee shops, stores, and homes.
Wireless connectivity has also greatly expanded the types of devices that can be connected to a LAN. Now, nearly everything imaginable can be «connected,» from PCs, printers, and phones to smart TVs, stereos, speakers, lighting, thermostats, window shades, door locks, security cameras—and even coffeemakers, refrigerators, and toys.
What is LAN (Local Area Network)? Definition, Types, Advantages, Examples
What is LAN Network?
Definition of LAN– LAN stands for “Local Area Network“. LAN meaning that it works as privately network because LAN is a bunch of computer machines and other connected nodes, and they can transfer data in between entire network. Local area network is developed to operate over small region like as shopping mall, office, campus etc. Main objective of using of LAN is to share resources (printer, FAX machine, plotter etc) with multiple compute and swap data.
Diagram of LAN Network
Types of Local Area Network (LANs)
In the computer network industry, there are various types of LAN technologies. Such as –
There are two different types of LAN connections –
Client/Server LAN – In which, various types of different devices (Clients) are connected with centralized server machine, and this server can handle several activates such as data storage, printer and plotter access, and network traffic. The Clients and Server are linked each other with wired or wireless medium.
Peer-to-Peer LAN – In which, no need the centralized server machine, so it is not able to bear massive workload compare to Client/Server LAN. On this concept, each computer and other devices are connected with parallel nature.
LAN is most different from other networks on the behalf of these characteristics, such as
Topology – Topology is geometric representation of network system because on the behalf of this topology system, multiple computers are connected each other through wire or wireless medium. For examples are – Star topology, Bus topology, Ring topology, Mesh topology, Hybrid topology, and more.
Communication Medium – Two types of mediums are used in LAN to make link in between multiple devices, such as wire and wireless. In wire media, to use some cables like as twisted-pair wire, coaxial cables, or fiber optic.
Advantages of LAN (Local Area Network)
There are various benefits of LAN network, below explain each one –
Characteristics as well as Advantages of LAN
Resource Sharing – LAN offers to great facility resource sharing such as printer, modem, plotter, scanner, and more.
Software Program Sharing – LAN allows to use single software program with multiple computer that are linked in network. So, no need to buy separate licensed application program for every client machine.
Simple and Fast Communication – In Local Area Network (LAN), huge data and other types of messages can simply be shared with another linked computer terminal over network.
Cost-Effective – Local Area Network (LAN) is cheapest to setup and maintain compare to other like WAN and MAN, because in LAN system no need to large cabling and other infrastructure. Due to local nature of LAN, it gets easy troubleshooting and maintenance.
Centralized Storage – All data and messages are stored in the storage medium on centralized server machine. It allows to all users for accessing of those data on the network.
Data Protection – All data are saved on the local server computer machine, and it is not easy task to leak those data. So LAN is more protected.
Internet Sharing – Local Area Network (LAN) offers to great functionality to share internet connection with multiple LAN connected users.
Computer identification – Every computer machine has own MAC address that is stored in the switch or router during communication between multiple computers. With the help of these MAC addresses, each client machine can identify that where to send and receive all data.
What is Network LAN? A Guide About Local Area Network
Simply described, a Local Area Network (LAN) is a collection of computers and other devices that are all connected through a network and are all located in the same building, such as a house or business.In most cases, the local area network is owned by a single department or unit. It is simple to design, maintain, and grow, and it has a high level of system flexibility.
The idea of a Local Area Network was developed to find a better way of connectivity within a distinctive area. Later, it evolved as a powerful networking medium, and still, it has significant contributions in networking fields. In addition, LAN is unrivaled in some specific areas, although there many new technologies are available. It is convenient in terms of speed, management, costs, and availability.
What is LAN (Local Area Network)?
According to the fundamental local area network definition, a LAN is a group of devices confined in a small geographic area, such as a small building. But it seems complicated to define the exact points behind a local area network as the small-large concept is very relative and depends on perspective. Simply, devices use LAN to share resources within a specific location.
For example, a company with 10 computers in its office, local area network provides a centralized controlled network for those. The LAN ensures connectivity of all computers over one network.
Moreover, devices like printers and IP phones could be connected to the same local area network, and it can connect the devices through a single communication line or wireless link.
What is The History of LANs?
Universities and research labs first felt the need for a centralized sharing network in the late 1960s as the demand for computers increased. The local area network was not developed overnight; instead, it is an advanced manifestation of its prior network communication technologies.
The first installation of LAN connection was established in 1979 in the electronic voting system for the European Parliament. Earlier in 1970, Lawrence Radiation Laboratory reported the growth of a similar network named ‘Octopus’.
Later in 1974, Cambridge University developed Cambridge Ring LAN technology, and within these couple of years, Ethernet and Xerox PARC were developed. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) addressed the Xerox PARC as the standard of LAN communication at that time.
The rapid growth of personal computers using CP/M in the 1970s and later DOS-based systems has changed the networking scenario, and by the 1980s, LAN became the most popular among others.
What is LAN Used For?
At the early ages of LAN, it was only used for sharing storage and printers among connected devices. Later at pace with technological development, it expanded its uses to internet sharing, media streaming, multiplayer gaming, controlling smart devices, and more.
The local area network is used for a secure networking interface that allows password authorization for the different user groups. However, it is used primarily for sharing storage and applications among connected devices.
Storage type local area networks are used as a reliable source of communication for centralized backup systems. Moreover, firewalls and malware protection applications can avoid data comptonization from a local area network when connected to the internet.
Before going further discussion, let’s get into the network components and terminologies first-
How Does Local Area Network Work?
Local Area Networks work using the following network topologies. For different local area network setups, the network topology diagram is different. Here are the local area network topologies-
In a mesh topology, infrastructural nodes are interconnected with each other through a dedicated port-to-port link. As it is connected port-to-port, it is secure and doesn’t affect the whole network if one link stops working.
Figure 1. Mesh topology
Star Topology allows connecting all nodes to a central hub. It doesn’t allow direct connection between two devices. Instead, devices are needed to communicate through the hub.
Figure 2. Star topology
In Bus Topology, all devices are connected to the main media through drop lines. A simple utility called Network Tap connects the drop line to the main media.
Figure 3. Bus topology
In the Ring Topology, each node is connected with two nodes on either side of it. When three and more devices are connected, it forms a ring. When one node wants to transmit data to another node, it sends the data in one direction, and the repeater forwards the request until it is received.
Figure 4. Ring Topology
A combination of two or more topologies is known as hybrid topology. For example, bus topology and star topology together combine as a hybrid topology.
Figure 5. Hybrid Topology
What are The Advantages of a LAN?
The primary purpose of LAN was sharing data among the computers, but it has extended to many benefits. Here go 6 benefits of the local area network.
What are The Types of LAN?
Based on the distribution method, Local Area Networks are classified into four types. They are-
Ethernet
Ethernet is a type of LAN where the nodes are connected through the wire media. It can transmit data at a rate of more than 10 megabits per second.
Ethernet network protocol monitors the data transfer over a local area network. In such connectivity, when a device wants to communicate with other devices in the same network or the devices want to share, they first detect the data carrier media. After that, the carrier initiates transmitting data according to its availability.
Token Ring
In a Token Ring LAN connection, nodes are connected in a circular arrangement. It sends data in a specific direction using a token to avoid the collision of data.
IBM, in 1984, introduced the token ring local area network where a ring topology connects nodes.
Token Bus
Another IBM-developed network topology is the Token Bus. In this protocol, tokens are created to manage the access of communication. Any nodes that hold the token can transfer data.
Token Bus is similar to Token Ring topology. Still, in a token ring topology, the ends of the network do not meet each other, whereas the token bus topology allows transmitting data from both ends.
Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI)
In Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI), optical fiber is used as the data transmission medium. However, it is known as CDDI when copper cables are used to connect the nodes.
FDDI is used for long-distance high-volume data transmission. It can communicate up to 200 kilometers at 100 Mbps speed.
What are the Prices for Local Area Network Equipment?
What are the Examples of LAN?
There are many examples of local area networks available around us. Home wifi, small business networks are the most common examples of local area networks.
A home network allows connecting the devices in the home to the internet and sharing files from one device to another. Usually, a home network connects gaming systems, streaming devices, printers, mobile phones, etc.
An office network connects the devices needed for office purposes with or without cable. Usually, an office network connects computers, printers, shared storage, and other devices that give access to communicate, collaborate among the connected devices to the employee.
A personal network is used for a single user that connects multiple devices of the same owner. For example, many keep their home working network separate from the home network due to security reasons.
Storage network is used as a solid interface of storage across multiple devices. Offices where employees need to share a comparatively large amount of data, storage network allows them to store files in the server and share with others.
Public networks allow connecting devices to access data from a specific host network. Besides, it is used for sharing internet connectivity among people. Hotel and cafes wifi networks are the best examples of public local area networks.
What is the difference between a LAN and a WAN?
A Local Area Network exists in a small and confined area where the Wide Area Network (WAN) exists in many places far away from each other. Consider, you have two local area networks in different places, and a vast distance geographically separates both. Now you need the service provider to join these two local area networks. Here the functionality of WAN has begun.
Commonly, the internet is the one type of WAN but not the only one. Multiprotocol Label Switching is another type of WAN that is used to connect two or more local area networks.
Compared to the data transmission speed, LAN is faster than WAN. The bandwidth and data transfer rate of WAN is also lower than LAN.
LAN uses unshielded/shielded twisted-pair copper cable or fiber optic cable to connect the hardware, but WAN uses leased lines/fiber optic cables or satellites to connect the nodes. However, the LAN shows fewer transmission errors than WAN.
WAN is comparatively costly to set up and maintain, and LAN is more secure than WAN. Moreover, LAN uses peer-to-peer network topology, where WAN uses the client-server model to connect the devices.
The local area network requires hubs and switches to connect other devices into the network. But, the wide-area network needs a router and modem to access the network.
What is the difference between a LAN and a MAN?
Coverage
MAN stands for Metropolitan Area Network that is confined to a city, town, or metro area. It covers a higher distance from the local area network and a shorter distance from the wide-area network.
The primary difference between LAN and MAN is the size of area and distance they cover. A Metropolitan Area Network typically covers nearly 50 kilometers, where a Local Area Network covers around 1,000 meters.
Data Transmission
LAN uses ethernet cable to transmit data, and often the wireless network is used to connect the nodes among the network. MAN can also be connected through both ethernet and wireless networking media.
Speed
LAN is known for high-speed connectivity among devices. On the other hand, MAN is comparatively slow due to the congestion of the network.
Components
Apart from the computer, LAN needs some network components to establish the connection. Network adapter, cable, hubs, repeater, bridge, switch are some of the components that are used for local area networks.
On the contrary, a Metropolitan Area Network requires customers premises equipment (CPE) such as access links, routers to connect the network.
How to Setup a Local Area Network?
Setting up a local area network requires some basic equipment as well as a gradual workflow. It’s not necessary to have an internet connection in a local area network, but it is common in most cases. Let’s see how to set up a local area network.
Step 1: Gather and assemble the equipment
Before starting the installation, you thoroughly need a network switch or a router, ethernet cable, a computer, and other devices.
Additionally, you’ll require an internet connection, modem, and router if you want to connect to the internet.
Assemble all the equipment accordingly and follow the next step-
Step 2: First computer connection
Your network switch, internet connection need to be configured. Connect a computer and configure it with the credentials. It will be required once in the installation process.
For Windows users, go to the Network and Sharing Centre in the control panel. Then go for ‘Set up a new connection or network.’
On a Mac operating system, first, go to the System Preferences and then network. Select Built-In Ethernet and go for the advanced option.
Connect the computer following the setup process with the necessary details.
Step 3: Connect other devices.
After finishing the installation, connect other devices with the network. Set access rules and data distribution policy for the connected devices.
Step 4: Internet connection
As mentioned earlier, you’ll require internet connectivity from a service provider, a modem, and later a router to connect your network with the internet.
Just plug in this equipment, and you should be able to access the internet.
Step 5: Wifi setup
To connect other devices via wifi, you need to set up your router with your local area network. Connect your router to the network end through cable; this enables the network signal, which is now ready to configure.
Connect a device and go to the router login page (it depends on router variation. Manufacturers provide an IP or link for router administration).
Step 6: Sharing
To share data among the connected devices in a local area network, you need to set certain data forwarding and receiving roles. Most operating systems allow initial management, though you need manual configuration for a comparatively extensive local area network.
In the windows operating system, go to the Network and Internet option from the Control Panel, then Create a homegroup from the Homegroup menu.
Mac users can set their sharing environment from the Sharing preferences option in the System preferences menu.
What is a WLAN?
WLAN stands for Wireless LAN- a type of local area network that connects devices via radio transmission without using wires. Wireless local area networks give the users the ability to move within the area that covers the WLAN.
WLAN is used for reliable communication within a short distance. The connected devices with a wireless local area network can easily access data as well as hardware like IP phones, printers, and scanners. It saves time for installation. However, it reduces the costs of cable dropping and buying multiple hubs and switches.
Apart from these, a wireless local area network has some disadvantages too. Comparatively low data transfer speed is one of them. Reliability and security are great concerns for a WLAN.
What are General Local Area Network Problems and Solutions?
Regardless of how much effort you put into keeping the network running smoothly, problems might arise at any time. Take a look at some common local area network problems and see if they can help you fix the issues.
Duplicate IP Address
The duplicate IP address issue is the most common problem that occurs. When two devices attempt sharing a single IP, the ability to access the network can be interrupted for manual confirmation mistakes.
Why does it happen?
It can happen due to the default Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) configuration of the router. When the router attempts to assign an address for a new device, if another device already occupies the address, you may see ‘Address Already in Use.’
Also, this issue happens when a user may assign an IP address that is already being used by another device on the network manually.
Solution
Assigning a unique IP address could solve this problem. Moreover, you can take some actions to prevent IP conflicts. Assign DHCP addresses near the top end of the subnet and leave lower addresses available for devices that need static IPs.
IPv4 address exhaustion
IPv4 address exhaustion is the reduction of unallocated IPv4 addresses. When the IPv4 addressing structure fails to provide routable public addresses, you may see IPv4 address exhaustion issues.
Why does it happen?
This could happen when you are running out of the allowed IP addresses from your internet service provider. Or your physical network interface is unable to access the new IPs from ISP.
Solution
Purchasing a standalone router could solve the problem. Make sure your router is inoperational with NAT and DHCP. Both prevent IPv4 address exhaustion.
Network Interface Card Error
Network Interface Card (NIC) is another common error that could interrupt your network uses for the users. Usually, the physical network interface is responsible for this error.
Why does it happen?
NIC error could happen due to damaged components and installation errors. If the Network Interface Card is misplaced, you’ll not be able to access the network.
Solution
Check the Network Interface Card first. Examine the condition, whether it is good, damaged, displaced, or installed in the wrong way. After that, check the cable, hubs, and switches. Hopefully, you will be able to sort out the problem.
No Network Access Problem
Other most frequent and common issues are No Network Access and Limited Access.
Why does it happen?
Network access issues can come forward due to many reasons. Mostly, the failure of internet connection results in No Network Access. It can happen due to misconfiguration of any network components as well as for physical infrastructural errors.
Solution
First, check the router configuration and fix it if you find any issues. Then examine the physical network components carefully. Make sure that every component is connected properly. Furthermore, check the network hub, switches as well as router settings if anything goes wrong.












