What does a singer does
What does a singer does
What does a singer do?
Would you make a good singer? Take our career test and find your match with over 800 careers.
What is a Singer?
A singer is someone who vocalizes musical sounds with tone and pitch, and uses his or her own voice to produce music. Singers may sing solo or in a group, and are oftentimes accompanied by instrumental music.
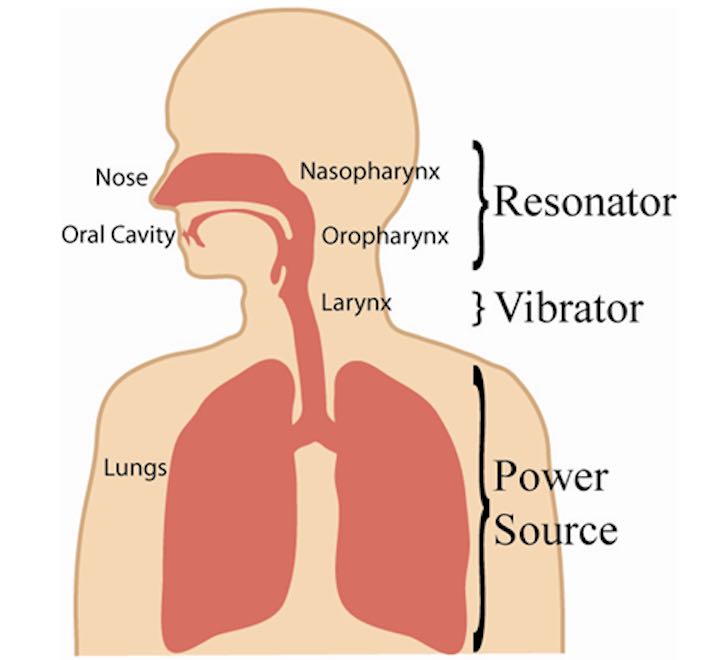
The physical act of singing occurs as air passes through the larynx, throat, and mouth, and it’s interesting to note that vocal resonation in singing involves seven areas of the human body: chest, tracheal tree, larynx, pharynx, oral cavity, nasal cavity, and the sinuses.
The history of singing goes back to the earliest recordings of mankind (as early as 800 B.C.), and songs are believed to have been used even before the development of modern languages. In western culture, singers were often restricted to only singing in churches until the fourteenth century. The rise of operas and performances thereafter laid the groundwork for today’s professional singers.
In this article:
What does a Singer do?
A singer is an artist or performer who crafts a vocal song using various techniques and training. Singers often practice daily and will hire professional voice coaches to help them hone their craft. Singers may write their own music or sing music written by others. In addition to singing, singers may work as music teachers or voice coaches.
Professional singers have typically had a lot of training, are highly talented, and have an excellent ear for identifying tone and pitch. They also possess a certain level of natural singing ability including a wide vocal range or pleasant vocal resonation. Singers often freelance and are contracted on a per job basis, either as a singer or as a consultant or judge in singing competitions.
Singing is an accepted art form that is taught in most public and private schools. It can also be a fun activity and be casual entertainment, such as karaoke.
Are you suited to be a singer?
Singers have distinct personalities. They tend to be artistic individuals, which means they’re creative, intuitive, sensitive, articulate, and expressive. They are unstructured, original, nonconforming, and innovative. Some of them are also enterprising, meaning they’re adventurous, ambitious, assertive, extroverted, energetic, enthusiastic, confident, and optimistic.
Does this sound like you? Take our free career test to find out if singer is one of your top career matches.
What is the workplace of a Singer like?
Professional singers may be employed by a record label that finances the development and recording of their music. Other singers may be employed by companies including radio advertising firms and variety show theatres. Special event singers often travel to perform at various venues including:
Theatrical singers are live performers who often perform nightly performances at a theatre. Opera singers are a specialization of theatrical singers that typically perform in a home theatre they are employed by. A theatrical singer in a main role will usually have their own dressing room and voice coach. Supporting or back-up singers will often share a common dressing area and receive less perks than a singer in a main role.
Professional recording singers exist outside of the entertainment industry in small numbers and are typically employed in marketing sectors for use in marketing jingles and advertisements. These singers will usually work as collaborators and writers of the pieces they sing and will work out of an office.
Professional singers in the music industry are the most noted public figures in the singing profession. Professional singers record their tracks in studios and often will spend hours in the editing booth with producers. Singers at this level are considered to be at the top of the profession and often have demanding travel and work schedules. Singers will be required to tour cities for months at a time performing on stage and promoting their music in stores and events, and will have tour buses to live out of while on the road.
Frequently Asked Questions
Steps to becoming a Singer
Most singers start humbly. The seemingly instant fame presented on televised national and international competitions is the exception, not the rule. This means that while the steps taken by those who want to make singing a career can certainly vary, the nonnegotiable constants are passion, dedication, and patience.
How long does it take to become a Singer?
There is absolutely no concrete answer to this question. Some now famous singers struck lightning in a bottle and were quickly discovered via social media. Others – the majority – spent years doing shows wherever they could, busking, posting their work online, and refining their talent before they got their break. It is also important to distinguish between having a singing career and having fame. With talent, and usually with some luck, the two may intersect. It is also true that they may not.
Many aspiring singers choose to take voice lessons. Some pursue a four-year Bachelor’s Degree in vocal performance. Some do both. And some do neither, relying solely on performing whenever and wherever they can. So, how long does it take to become a singer? It takes – as long as it takes.
Should I become a Singer?
Discipline, perseverance, a likeable personality, charisma, and stage presence. These qualities define most prosperous singers. Most also have stories of criticism and rejection and luck and serendipity. In deciding to pursue this career, it is essential to realize that worldwide fame and fortune are not the norm and not the only barometers of success. The profession is full of people who make a good living singing and who are not famous. With that important caveat in mind, let’s look at some facts about the career that may help you to determine if it’s for you.
The best singers do more than sing well.
They can write songs.
They are passionate about music and lyrics and have the discipline required to spend long days in studio and rehearsing.
They know how to network and market themselves.
They know that building a singing career is challenging and they are prepared to make sacrifices along the way. In the words of Katy Perry, ’It was five years of living in L.A. with no money, writing bad checks, selling my clothes to make rent, and borrowing money.’
They accept that singing is most certainly not a nine-to-five job.
They know that working as a singer can be as grueling as it can be exciting.
Are Singers happy?
Singers rank among the happiest careers. Overall they rank in the 99th percentile of careers for satisfaction. Please note that this number is derived from the data we have collected from our Sokanu members only.
This finding may be partially based in the fact that singing releases dopamine, serotonin, oxytocin, and endorphins in the brain. These hormones are responsible for happiness and mental health.
What are Singers like?
Based on our pool of users, Singers tend to be predominately artistic people. They are, in fact, creative and artistic by definition, whether they have a distinct and recognizable sound or mold their voice and overall sound to the song or genre they are singing.
Singers are also known as:
Vocalist Professional Singer Lead Vocalist Backing Vocalist Back Up Vocalist Backup Vocalist
THE PRESENT SIMPLE. – НАСТОЯЩЕЕ ПРОСТОЕ
Данное время употребляется для обозначения действия, относящегося к настоящему времени в широком смысле этого слова. Эта форма не указывает ни на длительность, ни на завершенность, ни на предшествование действия.
Настоящее простое образуется при помощи инфинитива (начальной формы) смыслового глагола без частицы to. Для образования вопросительной и отрицательной форм в настоящем простом используются вспомогательные глаголы do и does.
Таблица1
| Утверждение | Отрицание | Вопрос | |
| Единст. Число | I read He reads She reads It reads | I do not read He does not read She does not read It does not read | Do I read? Does he read? Does she read? Does it read? |
| Множ. Число | Wе read You read They read | We do not read You do not read They do not read | Do wе read? Do you read? Do they read? |
Настоящее простое употребляется для выражения следующих значений:
1) Обычные факты, повторяющиеся регулярно, практически каждый день
He visitshis grandparents every Sunday. – Он ездит к бабушке каждое воскресенье.
Usually I get up at 7 o’clock in the morning. – Обычно я встаю в 7 часов утра.
My friends like to travel by car. – Мои друзья любят путешествовать на машине.
2) Последовательные действия, происходящие в момент речи в настоящем времени
In the morning I get up, wash myself, dress myself, drink coffee and go to work. – Утром я встаю, умываюсь, одеваюсь, пью кофе и иду на работу.
3) Общеизвестные истины, пословицы, поговорки
The Sun rises in the east. – Солнце встает на востоке.
All roads lead to Rome. – Все дороги ведут в Рим.
4) Прошедшие дeйствия с глаголами to forget, to hear, to be told (passive)
I forgetyour address. – Я забыл твой адрес.
I hear you are doing well. – Я слышал, у тебя все хорошо.
Показатели, характеризующие Present Simple:
Usually – обычно, often – часто, seldom – редко, never – никогда, every day – каждый день (week – неделя, year – год), generally – в основном, sometimes – иногда, regularly – регулярно, as a rule – как правило, now and then – теперь и потом, from time to time – время от времени.
Ex. 1. Ответить на вопросы согласно модели:
Model: What does a driver do? – He drives.
What do drivers do? – They drive.
1. What does a singer do? 2. What does a runner do? 3. What do students do? 4. What does a dancer do? 5. What do cooks do? 6. What do dancers do? 7. What does a painter do? 8. What do teachers do? 9. What does a typist do? 10. What do writers do?
Ex. 2. Поставить подлежащее в предложениях в форму 3-го лица единственного числа. Правильно оформить глаголы:
Model: I write to parents. – He writes to parents.
They grow potato. – She grows potato.
1. I think I am ill. 2. They often visit their Granny. 3. We live in Leeds. 4. You usually speak too quickly. 5. Do you like boiled potatoes? 6. The boys box in the gymnasium on Fridays. 7. His dogs always attack the neighbours. 8. Heavy trucks make a lot of noise.
Ex. 3. Составить для каждого предложения вопрос и отрицание:
Model: She understands the rule. – She doesn’t understand the rule.
Does she understand the rule?
1. He usually has breakfast at 8 o’clock. 2. The lecture starts at 10.15. 3. The flowers look fresh. 4. They usually walk in the morning. 5. He has coffee in the evening. 6. He plays chess very well. 7. They feel very cold. 8. That train goes very fast. 9. We harvest grapes in March.
Ex. 4. Написать данные предложения еще раз, начав со слова, данного в скобках, и сделав все необходимые изменения.
Model: Some people begin work very early in the morning. (A postman). –
A postman begins work very early in the morning.
1. Those children help their mother. (Megan) 2. I get up at 7 every morning. (My father) 3. We like to go for a walk in the morning. (The old man) 4. They prefer coffee to tea. (Martin) 5. I spend a lot of money on books. (My brothers) 6. Some people do nothing during the holidays. (Eddie) 7. We finish the day’s work at 6 o’clock. (The clerk)
Ex. 5. Заполнить пропуски глаголом в отрицательной форме:
Model: She plays the piano, but she ….. it very well. – She plays the piano,
but she doesn’t play it well.
1. That shop sells office furniture, but it ….typewriters. 2. Scott smokes a lot, but he …..before breakfast. 3. We know Robert, but we ….his father. 4. His father gives him pocket-money, but he …..him much. 5. I feel tired, but I ….unwell. 6. English people eat a lot of potatoes, but they … much rice.
Ex. 6. Составить вопросы, начиная с вопросительного слова в скобках:
Model: Bob plays chess. (How often?) – How often does Bob play chess?
1. Felix watches birds every morning. (How often?) 2. I write to my parents twice a week. (How often?) 3. I have dinner at 7 o’clock in the evening. (What time / usually?) 4. She works at a hospital. (Where?) 5. She goes to the Zoo. (Who?) 6. People do stupid things. (Why?) 7. The motor breaks down. (What?)
Ex. 7. Перевести предложения на английский язык.
1.Растения хорошо растут в теплом климате. 2. Мне нравится читать детективы, а мой брат предпочитает научную фантастику. 3. Никто не знает, где он живет. 4. В Лондоне часто идет дождь. 5. Он никогда не пьет утром кофе. 6. Что он обычно ест на ужин? 7. У тебя есть последний фильм Тарантино? 8. Кто владеет этой фирмой?
Общие условия выбора системы дренажа: Система дренажа выбирается в зависимости от характера защищаемого.
Механическое удерживание земляных масс: Механическое удерживание земляных масс на склоне обеспечивают контрфорсными сооружениями различных конструкций.
 | Из за большого объема этот материал размещен на нескольких страницах: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
Упражнение 5. Переведите предложения. Поставьте их в отрицательную форму. Задайте общий вопрос к каждому предложению.
1. Tim does his morning exercises every day. 2. Emma gets up early. 3. Ann always gets up late. 4. His grandmother always wakes him up. 5. The Wilsons normally have breakfast at 7 o’clock. 6. My uncle usually watches TV in the evening. 7. It often rains in England. 8. It seldom snows in Spain. 9. We usually do the shopping on Thursday. 10. The children help mother to do the washing-up.
Упражнение 6. Используя вопросительные слова в скобках, задайте к предложениям специальные вопросы.
1. Не always smokes before lunch. (When?) 2. The Pearsons like to work in the garden. (Where?) 3. Amanda always wears too much make up. (Who?) 4. Kate works at a nursery school. (Where?) 5. Charles goes to the disco every Saturday. (How often?) 6. I sometimes spend the weekend in the country. (Why?) 7. She takes a shower in the morning. (When?) 8. I get to the pool by bus. (How?) 9. My sister visits her friends on Saturday evenings. (What?) 10. Our father takes medicine three times a day. (How often?) 11. They usually speak English. (What language?) 12. Everybody has a good time every Saturday. (Who?) 13. My name is Tom. (What?)
Упражнение 7. Ответьте на вопросы, используя фразы, данные в скобках.
1. What does a singer do? 2. What does a shoemaker do? 3. What does a housewife do? 4. What does an artist do? 5. What does a doctor do? 6. What does a hairdresser do? 7. What does a broker do? 8. What does a law student do? 9. What does a laundress do? 10. What does a sportsman do? 11. What does a baker do?
(to go in for sports, to study law, to cut and dress the hair, to paint pictures, to mend boots and shoes, to sing songs, to do the housework, to practice medicine, to buy and sell shares, to wash linen, to make bread.)
Упражнение 8. Исправьте предложения по образцу:
1. The American President lives in Rome.
2. The American President doesn’t live in Rome.
3. The American President lives in Washington.
1. Insects catch birds. 2. Elephants eat animals. 3. The River Volga
flows into the Baltic Sea. 4. The sun sets in the East. 5. Dentists look after nose.
Упражнение 9. Прочтите предложения и ответьте на вопросы.
I The students of your group like to go for walks in the woods in summer.
1. Do the students like to go for walks?
2. Where do they like to go for walks?
3. When do they like to go for walks?
4. What students like to go for walks?
5. What do they like to do?
6. Who likes to go for walks in the woods?
II Kostya helps his mother to look after his small brother.
1. What does Kostya help his mother to do?
2. Whom does Kostya help his mother to look after?
3. What does Kostya do?
4. Whom does Kostya help?
5. Who helps his mother?
6. Kostya helps his mother, doesn’t he?
Упражнение 10. Задайте вопросы к предложениям, опираясь на упражнение 9.
1. On Saturday we finish our lessons at 12 o’clock.
2. The girl gets off the bus at the stop in Pushkin Square.
Упражнение 11. Tell the group what you usually do,
— when your teacher comes to the workshop;
— when you come home from the college;
— when your mother asks you to help her;
— when you have session;
— when you stay at the library;
— when you go to the canteen.
Упражнение 12. Tell each other some words about Omsk Aviation College using the Present Simple Tense.
The Past Simple Tense
Прошедшее неопределённое (простое) время
для выражения действий повторяющихся, происходивших последовательно и имевших место в прошлом и не связанных с настоящим моментом.
Yesterday I went to the theatre.
С формой Past Indefinite часто употребляются слова и словосочетания: yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week (month, year),, days ago, in 1990 и т. д.
с помощью прибавления окончания – ed у правильных глаголов; у неправильных глаголов – II колонка
б) Глаголы, оканчивающиеся на у с предшествующей согласной, меняют у на i:
Did I (he, she, it, we, you, they) work? I (he, she, it, we, you, they) did not work.
Упражнение 1. Напишите форму прошедшего времени глаголов:
to go, to have, to see, to take, to give, to put, to stand, to put on, to sit, to understand.
Упражнение 2. Перепишите предложения. Глаголы напишите в Past Simple.
1. The children sometimes work on a collective farm in summer. 2. We play football and other interesting games at the camp. 3. Mike goes to his circle early. 4. It always snows in winter. 5. The Ninth Form pupils clean the street in front of the school. 6. We often ski and skate in the park. 7. She always answers questions well.
1. Yesterday (to be) the third of October. 2. It (to be) warm, and we (to play) ball in our yard. 3. Our dog (to be) with us too. 4. It (to like) the game. 5. He (to jump) and (to jump). 6. We (to have) five lessons yesterday. 7. After the lessons the pupils on duty (to water) the flowers and (to clean) the blackboard and other things. 8. When everything in the classroom (to look) clean, they (to go) home. 9. It (to be) half past three and they (to be) very hungry.
Упражнение 3. Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в форме Present или Past Simple.
1. I (to watch) television at seven o’clock every evening.
2. I (to watch) television yesterday.
3. She (to comb) her hair every morning.
4. Yesterday she (to comb) her hair.
5. They (not to rest) yesterday.
6. I usually (to walk) to my school but yesterday I (to take) a tram.
7. Yesterday he (to have) a holiday. He (not to go) to the office. He (to get) up at eleven o’clock, (to wash) his face, (to have) breakfast and (to go) for a walk.
8. As a rule my mother (to cook) dinner. But yesterday she (to decide) not to cook. She (to invite) us to the restaurant.
9. He (not to like) coffee. But yesterday he (to drink) a cup of coffee as he (to be) very tired.
Не gets up at seven o’clock. He washes his face, cleans his teeth and combs. He goes to the kitchen and has his breakfast. For breakfast he has a cup of coffee and cheese. When the breakfast is over, he goes to the office. He takes a bus to get to his work.
At the office he works till two o’clock. At two o’clock he has dinner. He finishes his work at seven o’clock in the evening. He decides to walk a little after his working day. He returns home at nine. He doesn’t want have supper, he only drinks tea. Suddenly he remembers that he has to phone his friend. He dials the numbers that he has to phone his friend. He dials the number but nobody answers. His friend is not at home. He goes to his room and decides to watch TV. When the TV program is over, he sleeps.
The weather is bad. There is no sun in the sky. Beth wakes up late in the morning. She doesn’t want to leave the bed. She stays in her bed for some time. But Beth is hungry. She wants something to eat. She makes herself to get up, and goes to the bathroom. She washes and cleans her teeth. Beth goes to the kitchen and has her breakfast. After breakfast she thinks how to spend her day. Suddenly the telephone rings. Her friend Tom phones. Tom says he has two tickets to the theatre and he invites her to go and see the play. Beth thanks him and agrees to go to the theatre. The play begins at twelve. She has only two hours to dress and to get to the theatre. Beth doesn’t know what to put on in such bad weather. She thinks for some minutes and chooses her new beautiful dress! The weather is bad but she is in a good mood.
Упражнение 5. Complete the sentences.
Example: He has dinner at three o’clock every day, but yesterday he had dinner at four.
Упражнение plete the sentences and make a story. Use the verbs in the Past Simple Tense.
My favourite song … « I saw…».
Упражнение 7. Do and say what you did
I. 1. Take your bag.
3. Take your exercise-book.
4. Put it on the desk.
2. Go to the teacher’s desk.
3. Take a picture.
4. Hang it on the blackboard.
III. 1. Go to the door.
2. Open the door.
4. Shut the door.
2. Turn to the middle of the classroom.
4. Count the lamps.
Упражнение 8. Answer the questions (see Exercise 7).
I. 1. Did he (she) take his (her) bag?
2. What did he (she) open?
3. What did he (she) do then?
4. Where did he (she) put the exercise-book?
II. 1. Did a girl or a boy stand up?
2. Whose desk did she (he) go to?
3. What did she (he) take?
4. Where did she (he) hang the picture?
III. 1. Who went to the door?
2. Did he (she) open the door or shut it?
3. What did he (she) do then?
4. What did he (she) shut?
IV. 1. Did a girl or a boy stand up?
2. Where did he (she) turn?
3. He (she) looked up, didn’t he (she)?
4. How many lamps did he (she) count?
Упражнение 9. Answer the questions.
1. You listened to the radio yesterday, didn’t you?
2. What mark did you get yesterday?
3. When did you have your dinner yesterday?
4. Did you write a dictation on Saturday?
5. Where did you go after the lessons on Monday?
6. Did you come home from college late?
Упражнение 10. a) Say who you saw this morning (yesterday) on the way to the college.
Example: I saw our doctor on my way to the college this morning.
b) Tell the group what sport games you played last summer (winter).
Example: I often played chess in summer.
How does the voice work?
Why do singers need to learn anatomy of the voice?
Knowing about the voice and then knowing how to use it are not the same thing. Yet the first is crucial in order to effectively do the other.
Why do singers need to know about other body parts?
So let’s learn about those parts which we need to either engage or relax, so that we can sing without straining and avoid getting hoarse. There are a few articles on the website advising on how to work with your body for singing, such as yoga poses to sing in.
Trust voice teachers: to an extent
You will be shocked how many voice teachers hardly understand vocal anatomy. We are voice teachers, not scientists, right?! Voice teachers were first trained as singers, some of them did NOT train as teachers. They know what they have been taught by their teachers, maybe what they learned in college. Not enough. Most teachers will not be familiar with the laryngeal muscles, with the different parts of the resonances and respiratory system, and in general have a vague idea of how the voice works, sadly. Personally, I have learned most of what I know through my own research.
Even the experts can be wrong
I have learned recently that one of the most esteemed voice experts, Jo Estill, who developed an internationally renowned teaching method, has gotten something wrong. She thought you can tilt the larynx for belting (find resource on what is tilting below at “advanced laryngeal function”), when this is actually impossible. You can watch a clip of a student of hers explaining the problem with tilt for belting.
That’s OK. Science is work in progress. We might not know everything, but we know plenty already. And it is our responsibility as singing students to be well-versed in the vocal anatomy and mechanism, because probably no one will do it for us.
So how does the voice work?
First, let’s look at what the instrument looks like on the inside:
How the air travels
As you make a sound, the air comes up from the lungs, passes through the vocal cords, which are located inside the larynx and leaves via the mouth/nose.
The vocal cords are separated/open as we inhale and exhale, and come together/close when we make sound.
When air goes through the closed vocal cords they vibrate and create the initial sound, which is then amplified by the pharynx (back of the throat, all the way from behind the nose down to behind the larynx). It is the main resonator of our instrument.
The resonance is then reinforced by more resonances in the nasal cavity, oral cavity, the chest cavity, and some more 🙂
What is necessary for singing?
It’s necessary to allow for the rather simple mechanism of the vocal cords coming together and the air passing between them.
That is: without any tension which compromises the resonating spaces and the airway!
PRESENT SIMPLE AND PROGRESSIVE.
1. АNSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS ACCORDING TO THE MODEL :
Model: What does a driver do? – He drives.
What do drivers do? – They drive.
1. What does a singer do? 2. What does a runner do? 3. What do students do? 4. What does a dancer do? 5. What do cooks do? 6. What does a painter do? 7. What do teachers do? 8. What does a typist do? 9. What do writers do? 10. What does a pilot do? 11. What do actors do? 12. What does a postman do? 13. What do musicians do? 14. What does a conductor do? 15. What does a receptionist do?
2. WRITE THE FOLLOWING SENTENCES IN THE 3 RD PERSON SINGULAR:
1.I think I am ill. 2. They often visit their parents. 3. We live in Voronezh. 4. You usually speak too quickly. 5. Do you like chocolate? 6. Cats eat mice. 7. Sometimes we go to the cinema. 8. Our teachers of English are very good. 9. They work in the hospital. 10. Big engines make a lot of noise. 11. Women always spend much money on make-up. 12. Sometimes I read books in English. 13. We write final tests every term. 14. Englishmen usually drink tea with milk. 15. They seldom walk to work, they normally travel by bus.
3. WRITE THESE SENTENCES IN THE INTERROGATIVE AND NEGATIVE :
1. She understands this rule. 2. He usually has breakfast at 8 o’clock. 3. The lecture starts at 11.50. 4. Those houses look modern. 5. I often walk in the morning. 6. She remembers them well. 7. He plays chess very well. 8. She leaves home at 10 a.m. every day. 9. Students sometimes miss classes. 10. Concord flies very fast. 11. The train comes to London at 17.25. 12. Teachers know their subjects perfectly. 13. I enjoy watching historical films. 14. We always spend our holidays on the seaside. 15. Mother often cooks meal in our family.
4. PUT THE VERBS IN THE BRACKETS INTO CORRECT FORM :
1. I (live) in Lipetsk, which (be) my native town. 2. He (work) in this factory? 3. How many languages you (speak)? 4. My brother (know) everything about cars. 5. She (not use) make-up very often. 6. I (play) the guitar, but I (not play) it well. 7. How much coffee you (drink) a day? 8. The Sun (set) in the West. 9. She often (go) to work by tram? 10. He (study) at our Academy? 11. You often (visit) your granny? 12. We usually (not spend) much time for lunch. 13. They (meet) every day. 14. How she usually (celebrate) her birthday? 15. Who (teach) you English in the Academy?
5. CONTINUE IN THE NEGATIVE :
Example: Mother is talking on the phone. (sleep) She isn’t sleeping.
1. John is reading. (write)
2. Father is mending our car. (watch TV)
3. The boys are playing. (fight)
4. He are translating the text. (retell)
5. They are speaking. (shout)
6. Mary is running. (walk)
7. I am eating. (drink)
8. The teacher is explaining a new rule. (check our tests)
9. He is working this summer. (have a rest)
10. She is doing her homework. (listen to music)
11. I am hurrying to work. (go home)
12. Dad is smoking on the terrace. (read a newspaper)
13. Mother is washing up. (cook)
14. They are shopping. (clean the house)
15. We are skating. (ski)
6. ANSWER THE QUESTIONS USING THE WORDS IN BRACKETS :
Example: Are you drawing? (write a story) No, I am writing a story.
Is Greg busy now? (type a report) Yes, he is typing a report.
1. Is Susan busy now? (have breakfast) 2. Are you watching TV? (study) 3. There are you going? ( see the professor) 4. Is Holly busy today? (go to the library) 5. Are they busy after lunch? (stay at home) 6. Are you busy today? (shop) 7. Is she talking on the phone? (listen to the radio) 8. Is he working now? (relax) 9. Are they going to the cinema tonight? (visit their granny) 10. Are the Browns busy today? (have a holiday) 11. Why is she leaving so soon? (hurry to a concert) 12. What are you doing today? (attend lectures) 13. Is she traveling by train? (drive) 14. Is he busy after classes? (do his homework) 15. What are you doing here? (buy textbooks)
7. PUT THE VERB INTO THE CORRECT FORM :
1. Please be quiet. I (try) to sleep. 2. Sue wants to lose weight. She (not eat) sweets now. 3. We (not go) to school this week. We are on holiday. 4. Why you (wear) your best dress today? 5. Why you (look) at me like that? Am I green or something? 6. You (make) a lot of noise. Can you be quieter? 7. Can you hear? The child (cry) again. 8. The prices for food (rise) at the moment. 9. The weather (change) every moment: now cold, now hot. 10. Can you help me, please? I (look) for a phone box. 11. Look! It (rain) again! 12. My English (improve) slowly. 13. We (do) exercise 7 now and our teacher (listen) to us. 14. You (enjoy) your new job in the factory? 15. Where he (go) in the evening? – He (visit) his parents.
8. OPEN THE BRACKETS USING PRESENT SIMPLE OR PROGRESSIVE :
1. John often (stay) in a hotel when he (come) to town, but tonight he (stay) with us. 2. Modern trains (go) very fast. 3. “I must go now.”- “Where you (go)? 4. It (be) the early bird that (catch) the worm. 5. “Why you (laugh)?- Because you (talk) nonsense. 6. He (laugh) best, who (laugh) last. 7. Actions (speak) louder than words. 8. Vasya (speak) to the dean and they both (smile). 9. The students (be) in cafeteria. They (have) their lunch. 10. Where (be) Andrew?- He (smoke) on the terrace.- I (think) he (smoke) too much. 11. What (be) this music?- It (be) Ann. She (play) the piano. 12. Mike (come) tonight?- No, he (work) hard at present. – What he (do)? – He (study) for his exams. 13. Petya (make) at least ten spelling mistakes in every composition. 14. I always (go) to the seaside on holiday. 15. My brother (live) in Belgorod. And where your brother (live)? 16. That bag (not belong) to me. 17. Look! He (come). I (want) to speak to him. 18. You can take my pen, I (not need) it now. 19. I (not believe) you! 20. Usually I (enjoy) music, but I (not enjoy) this record very much. 21. She (work) in Voronezh, but unfortunately (not have) a place to live, so she (look) for something now. 22. He (not feel) well at the moment. He (cough) and (sneeze). 23. Mother always (help) her children. 24. I (know) it often (rain) in England. 25. How often you (visit) your grandparents? – I (visit) them every weekend, and, by the way, I (see) them tonight.
9. REACT TO THE QUESTIONS AFTER YOU READ SITUATIONS :