What does aids stand for
What does aids stand for
What does AIDS stand for?
What does AIDS mean? This page is about the various possible meanings of the acronym, abbreviation, shorthand or slang term: AIDS.
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome
Almost Ideal Demand System
As If Doing Something
Anally Injected Death Sentence
American Invention to Discourage Sex
Army Inventory of Data Systems
Acquired Insanity Due to Studies
All In Dead Silence
ADCOM (Aerospace Defense COMmand) Information Display System
Air Improvement Disruption Syndrome
Automated Infantry Data System
American Invention to Disrupt Sex
Acquiring Information Destroying Stereotypes
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes
American Invention to Demonize Sex
Another Illegal Disease Spotted
Autism Is Deadly Son
As I Die Slowly
A**hole Infected; Dead Soon
σύνδροο επίκτητης ανοσοποιητικής ανεπάρκειας
Alcohol Induced Dizzy Spells
Accretive Industrial Development Syndrome
Accident/Incident Data System
All Individuals Deserve Support
Aircraft Integrated Data System
What does AIDS mean?
Popularity rank for the AIDS initials by frequency of use:
Couldn’t find the full form or full meaning of AIDS?
Maybe you were looking for one of these abbreviations:
Discuss these AIDS abbreviations with the community:
Report Comment
We’re doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we’ll take care of it shortly.
What does HIV/AIDS stand for? Different Names for AIDS
HIV is the acronym for human immunodeficiency virus which is responsible for the development of AIDS after prolonged HIV infection.
AIDS is Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome which develops in the latter stages of HIV infection.
HIV & Immunity
HIV is the virus, which is transmitted from person to person and is the causative microbe responsible for HIV infection. The virus targets the body’s immune cells. AIDS is the syndrome that results once the immune system has been significantly compromised and is unable to maintain adequate functioning.
Immunity in the human body is a complex system comprised of cells and chemicals. In conditions like HIV/AIDS, the virus targets a specific type of immune cell known as the CD4 T-lymphocyte. The virus enters and replicates within the cell and exits the immune cell thereby destroying it. As the disease progresses, the body’s immune functioning is hampered due to the decreasing immune cell population (test : CD4 count) in relation to the increasing viral population (test : viral load) and the patient is considered to be immunocompromised.
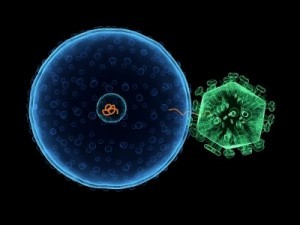
Picture of Virus Infecting Cell
HIV infection does not indicate the onset of AIDS. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome is determined by the presence of AIDS defining illnesses or a CD4 count less than 200 cells/mm.
Common Names for HIV/AIDS
There are many common names for HIV/AIDS which varies among different cultures, languages and regions in the world. Example : isandulela ngculazi is the Zulu word for AIDS, widely used in South Africa which has the highest HIV/AIDS adult prevalence rate. HIV/AIDS is a global problem affecting every sector of the human population and the disease is perceived differently based on ignorance, misconceptions and cultural and religious beliefs.
The most common names for HIV/AIDS refers to the wasting (cachexia) which typically occurs in the latter stages of the disease. This is often referred to as the ‘thins‘ or ‘slim’s disease‘, a term very often used in Africa in the native tongue. Less politically correct names had emerged in the 1980s and early 1990’s at a time when the disease was only associated with gay men and homosexual behavior. These misconceptions have been allayed in recent years as HIV is more often spread in heterosexual couples.
AIDS: Definition, Causes, Symptoms & Preventive Measures
AIDS stands for Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. AIDS is a life-threatening disease caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). AIDS was first reported in the United States (US) in June 19811981. AIDS damages our body’s immune system. In the last 2525 years or so, AIDS has spread all over the world, killing more than 2525 million people. This article will discuss all the details related to AIDS.
AIDS is an important topic in the chapter “Human Health and Diseases” in NCERT Biology books for Class 12. NCERT books are structured in a way that makes it easier for the students to understand the concepts related to the topic better. Embibe offers a range of study materials that includes PDF of NCERT books, previous year question papers and solution sets. Students can follow these study materials to enhance their preparations significantly.
AIDS: Details
AIDS is an immunodeficiency disease, the last stage of HIV infection is referred to as AIDS. It occurs when the immune system of the body is damaged because of the virus that interferes with the ability of the body to fight against the infections.
AIDS is acquired at any phase during the lifetime of an individual, indicating that it is not a congenital disease (a disease that is present at or before birth). The word ‘syndrome’ in AIDS meaning ‘a group of symptoms’.
What is HIV?
AIDS: Symptoms
People infected with the HIV virus remain apparently well even after the infection. They may not show any physical symptoms of illness for a long time which may vary from a few months to several years (\(5 – 10\)years). But after some time, the body may respond in many ways:
AIDS: Causes
The ways by which AIDS disease is spread are as follows:
Important Fact!
Although the AIDS virus has been found in tears and saliva, no instance of transmission from these body fluids has been reported. So, there is no danger of infection with the AIDS virus by casual social contact or by sharing cups, towels, or food. Also, there are no known cases of AIDS transmission by insects like mosquitoes or pests.
HIV Infection: Progression
Without treatment, HIV infection advances in stages, getting worse over time. There are three stages of HIV infection:
Acute HIV Infection
It is the earlier stage of HIV infection, which generally develops within \(2 – 4\) weeks after infection with HIV. In this stage, HIV multiplies rapidly and spreads throughout the body. HIV attacks and destroys the T-lymphocytes of the immune system. The level of HIV in the blood is very high, which greatly increases the risk of HIV transmission. A person may experience significant health benefits if they start taking HIV medicines during this stage.
Chronic HIV Infection
It is the second stage of HIV infection (also called asymptomatic HIV infection or clinical latency). During this stage, the rate of multiplication of HIV is very low. The person may not have any HIV-related symptoms, but it is possible to transmit HIV to others during this stage. The transmission can be prevented by taking HIV medicines. Without medicines, this infection usually advances to AIDS in 10 years or longer.
Is AIDS the last stage?
AIDS is the final, most severe stage of HIV infection. At this stage, HIV would have severely damaged the immune system due to which the body can’t fight against opportunistic infections like pneumonia, tuberculosis, cancer, etc. A person with AIDS has a high HIV load and can transmit HIV to others very easily. Without treatment, people with AIDS typically survive about \(3\) years.
Which Group of People are at High-risk of Getting Infected with HIV?
The high-risk groups who become infected with HIV are as follows:
Diagnostic Test for AIDS
When HIV enters the bloodstream, it begins to attack the white blood cells (T- Lymphocytes). In response to these viruses, substances called antibodies are produced in the body. These antibodies can be detected by a specific blood test called ELISA, usually two weeks to three months after infection. However, Western blotting provides the most accurate results.
Detection of AIDS by ELISA Test
The Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) test is the most widely used method for detecting the presence of HIV antibodies. In \(1984\), ELISA was developed to determine whether an individual is carrying HIV or not.
Western Blot Assay
Western blot assay is conducted for confirmation of cases that show positive ELISA test. This process helps to detect specific HIV proteins (antigens) for which antibodies are present in the serum of ELISA-positive patients.
Process of Infection by HIV
The process of infection by HIV are as follows:
AIDS: Preventive Measures
AIDS is a progressive disease and there is no cure to it as of yet. However, medical science has evolved to the point where the progression of the disease can be slowed down significantly. There is no vaccine invented to prevent AIDS. Most individuals with severe infection die within a few years from other infections. However, it is preventable. People can be educated on the following things so as to help ignorant people from becoming victims.
However, by taking HIV medicines called Anti Retro-viral Therapy (ART), people with HIV can live long and lead healthy lives and prevent transmission to their sexual partners. National AIDS Control Organisation (NACO) and other Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs) are doing a lot to educate people about AIDS.
Summary
AIDS is considered to be one of the challenging public health issues. But there is a global commitment to stop new HIV infections and ensure that everyone with AIDS has access to HIV treatment. New global efforts have been undertaken to fight against this disease, particularly in the last decade. The number of people with new HIV infections has reduced over time. \(1\)st December is declared as World AIDS Day since \(1988\). It is an international day dedicated to raising awareness for the AIDS pandemic.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on AIDS
Frequently asked questions related to AIDS is listed as follows:
Q.1. Which cells are killed by the AIDS virus?
Ans: T-lymphocytes or specifically known as T-helper cells or CD\(4\) cells, are killed by the AIDS virus.
Q.2. Can someone die from AIDS?
Ans: AIDS is a life-threatening disease that can kill a person. But, with an early diagnosis and proper treatment, the life expectancy of the HIV-positive patient can be increased.
Q.3. How is AIDS caused?
Ans: AIDS is caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). This virus can be transmitted in the following ways:
1. By sexual contact with an infected person.
2. By sharing infected needles, blades, or razors.
3. By blood-to-blood contact as in blood transfusion.
4. From an infected mother to a foetus through the placenta.
Q.4. What are the three stages of HIV infection?
Ans: The three stages of HIV infection are:
1. Acute HIV Infection
2. Chronic HIV infection
3. AIDS
Q.5. How does the AIDS virus work?
Ans: The AIDS virus or HIV attacks and destroys the white blood cells (specifically T-lymphocytes also called CD 4 cells) of a person’s immune system, which helps in producing the antibodies against the attacking pathogen.
Now that you have a detailed article on AIDS, we hope you do your preparation well. If you face any issue regarding the same, do let us know about it in the comments section below and we will get back to you soon.
Методическая разработка по английскому языку на тему «СПИД/ВИЧ»
МИНИСТЕРСТВО ЗДРАВООХРАНЕНИЯ РЕСПУБЛИКИ КРЫМ
Государственное автономное образовательное учреждение
среднего профессионального образования Республики Крым
«Керченский медицинский колледж имени Г.К. Петровой»
по дисциплине «Иностранный язык»
по теме: СПИД/ВИЧ
Для специальности: 31.02.02 Акушерское дело,
31.02.01 Лечебное дело
Методическая разработка комбинированного занятия составлена в соответствии с ФГОС СПО по специальности 31.02.02 Акушерское дело, 31.02.01 Лечебное дело
Организация-разработчик: ГАОУ СПО РК «Керченский медколледж им. Г.К.Петровой»
Мамбетова Л.Э. – преподаватель первой категории, преподаватель дисциплины Иностранный язык ГАОУ СПО РК «Керченский медколледж им. Г.К.Петровой»
Методическая разработка рассмотрена на заседании предметной (цикловой) комиссии общего гуманитарного и социально-экономического цикла ГАОУ СПО РК «Керченский медколледж им. Г.К.Петровой», протокол № ____ от _____
Председатель предметной (цикловой) комиссии __________/ Т.И.Ломаева
I . Методический блок
Методическая разработка занятия
Специальность: 31.02.02 Акушерское дело,
31.02.01 Лечебное дело
Дисциплина: Иностранный язык
Вид занятия: комбинированное
лексический минимум, необходимый для чтения и перевода профессионально ориентированных текстов по теме «СПИД»;
грамматический материал по теме «The Present Simple/Continuous Tense»;
читать, писать, переводить терминологию по теме;
читать и переводить тексты по теме «СПИД»;
использовать изученную лексику, речевые обороты в устной и письменной речи;
выполнять лексико-грамматические упражнения;
отвечать на вопросы по данной теме.
2. Воспитательные цели:
воспитывать сострадание, гуманизм, милосердие;
воспитывать самостоятельность в преодолении затруднений в понимании иностранного текста;
воспитывать умение осмысливать и анализировать;
воспитывать желание и умение использовать уже имеющиеся знания;
воспитывать интерес к поиску новой информации
3. Развивающие цели:
развитие творческих способностей студентов;
развитие навыков диалогической и монологической речи по теме;
развитие навыков чтения текста для получения различных видов информации;
развитие навыков понимания иноязычной речи;
развитие логического мышления, внимания, памяти, языковой догадки;
ПК 4.6. Проводить мероприятия по сохранению и укреплению здоровья различных возрастных групп
ОК 1. Понимать сущность и социальную значимость будущей профессии, проявлять к ней устойчивый интерес.
ОК 2. Организовывать собственную деятельность, выбирать типовые методы и способы выполнения профессиональных задач, оценивать их эффективность и качество.
ОК 3. Принимать решения в стандартных и нестандартных ситуациях, нести за них ответственность.
ОК 4. Осуществлять поиск и использование информации, необходимой для эффективного выполнения профессиональных задач, профессионального и личностного развития.
ОК 5. Использовать информационно-коммуникационные технологии в профессиональной деятельности.
ОК 6. Работать в коллективе и команде, эффективно общаться
с коллегами, руководством, потребителями.
ОК 11. Быть готовым брать на себя нравственные обязательства по отношению к природе, обществу и человеку.
4. Оборудование и оснащение занятия:
1.Лексика и речевые обороты по теме «СПИД»
2.Тексты по теме
3.Упражнения и задания:
Задания на понимание содержания текста
Учебные пособия и материалы:
2.С.А. Тылкина, Н. А.Темчина «Пособие по английскому языку для медицинских училищ», Москва,
3. Голицынский Ю.Б. «Грамматика. Сборник упражнений» изд. 9 С-Пб «Каро»
4.Англо-русские и русско-английские словари
5. Межпредметные связи: основы безопасной жизнедеятельности, основы сестринского дела, введение в специальность, латинский язык, психология общения
Приветствие, контроль явки студентов
1)Greeting 1 мин
T: Good morning, dear students, I’m very glad to see you. Sit down, please. Prepare all necessary things for the lesson. I hope, you are ready for our English lesson.
Answer my questions, please: What date is it today?
Who is absent today? Why? (T – P1,P2) 4 мин
Let’s check you home task
Revision of the Matereal Covered at the Previous Period ( Проверка домашнего задания )
Let’s check your homework. What was your home assignment?
S: Our home assignment was to learn new words by heart and to retell the text. 10 мин
1) Lead in (введение к новой теме, мотивация):
Our theme for today is „ HIV and AIDS ”. You are future doctors’ assistants/midwives, so you should know that AIDS (Acquired immune deficiency syndrome or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) is a disease caused by a virus called HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus). The illness alters the immune system, making people much more vulnerable to infections and diseases. This susceptibility worsens as the disease progresses. 5 мин
Exercise 1. Read and learn the following words:
W
HIV ( Human Immunodeficiency Virus ) [‘ hjuim ə n i ‘ mju : n ə di ‘ fi ∫ə nsi ‘ vai ə r ə s ] ВИЧ (вирус иммунодефицита человека)
AIDS ( Acquired Immunodeficiency syndrome ) [ə’ kwai ə d i ‘ mju : n ə di ‘ fi ∫ə nsi ‘ sindr ə mi :] СПИД (синдром приобретенного иммунодефицита)
transmit [ tr æ nz ‘ mit ] передавать, переносить
contaminated [ k ə n ‘ t æ mineitid ] зараженный
properly [‘рrорəli] должным образом
opportunistic infections [‘ op ə tju : nistic ] оппортунистические (условно-приобретенные) инфекции
chickenpox [‘t∫ikə n poks ] ветряная оспа
insure [ in ‘∫ u ə] страховать
afford [ə’ fo : d ] позволять себе
prejudice f ‘ pred udis ] предубеждение; настраивать против
ignorance [‘ ign ə r ən s ] невежество, незнание
educate [‘ edju : keit ] воспитывать, обучать
3) а) Pre-reading activity (Дотекстовые упражнения).
What is the difference between HIV and AIDS?
HIV is the virus which attacks the T-cells in the immune system.
AIDS is the syndrome which appears in advanced stages of HIV infection.
AIDS is a medical condition.
Exercise 2. Match the word combinations with their Russian variants
white blood cell
effective antiretroviral treatment
белые кровяные тельца
возможные побочные эффекты
эффективная антиретровирусная терапия
b) Reading and translation of the text (Чтение и перевод текста )
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) was discovered in 1983. It is a retrovirus that primarily infects vital components of the human immune system. It also directly and indirectly destroys cells required for the proper functioning of the immune system. The immune system functions poorly leading to the syndrome known as AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). AIDS is transmitted in body fluids through sexual contact, sharing of contaminated needles (by IV drug abusers), contact with contaminated blood or transfusion of contaminated blood or blood products.
AIDS occurs when HIV has damaged the patient’s immune system. The patient’s lymphocytes cannot fight infection properly. Bacteria and viruses, which cause mild illnesses in healthy people, cause severe life-threatening diseases in patient with AIDS. These diseases are called opportunistic infections. Patients with AIDS can die of chickenpox which is usually a very mild disease of children.
There is no cure of AIDS but some drugs can slow the progress of the disease. Antibiotics and antiviral drugs can often cure opportunistic infections but they are very expensive. In many countries people die from opportunistic infections because they are not insured and cannot afford treatment.
Many people are prejudiced against those who are HIV-positive. This prejudice is sometimes caused by ignorance. Some people think that they can catch AIDS by shaking hands with an HIV-positive person, eating at the same table or even talking to him on the telephone! That is why patients who are HIV-positive are under severe psychological stress.
Thus the task of the physician is not only to search for a cure for AIDS but also to teach his patients to prevent it and to educate the public in order to reduce prejudice and discrimination against HIV-positive people 15 мин
c ) Post-reading activities (Упражнения, которые выполняются после прочтения текста).
Exercise 4 Translate following words and word combinations
Жизненноважній компонент, иммунная система, прямо или косвено, должное функционирование, известный как, зараженная игла, бактерии и вирусы, здоровые люди, болезни опасные для жизни, ветрянная оспа, детская болезнь, некоторые лекарства, замедлять процесс, через рукопожатие, разговаривать по телефону, психологический стресс, задание врача, уменьшие предубеждение, дискриминация против.
Exercise 5 Answer the questions:
When was HIV discovered?
What do the abbreviations HIV (AIDS) stand for?
How is AIDS transmitted?
What are opportunistic infections?
Can patients with AIDS die of chickenpox?
Is it possible to catch AIDS by shaking hands with an HIV-positive person?
What is the role of the physician while treating a patient with AIDS?
Exercise 6 Is the sentence true or false. Correct false statement
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) was discovered in 1993.
HIV directly and indirectly creates cells required for the proper functioning of the immune system.
AIDS is transmitted by shaking hands with an HIV-positive person, eating at the same table or even talking to him on the telephone.
AIDS occurs when HIV has damaged the patient’s urinary system.
HIV-positive patient’s lymphocytes cannot fight infection appropriately.
Bacteria and viruses cause severe life-threatening sickness in patient with AIDS.
Antibiotics and antiviral drugs can often treat opportunistic infections but they are high-priced.
Thus the tasks of the doctor is not only to search for a cure for AIDS but also to teach his patients to prevent it.
Exercise 7 Guess the word(word combination) using its definition
A disease, caused by the HIV virusand transmittedin body fluids, which breaks down the sufferer’s natural defences against infection.
A submicroscopic organism which can cause disease.
The basic structural and functional unit of living organisms.
Any combination of signs and symptoms that are indicative of a particular disease or disorder.
A red that is pumped by the heart through the arteries and veins, supplies tissues with nutrients, oxygen, etc., and removes waste products.
A person who is receiving medical care
1. Подведение итогов занятия
2. Home task ( Задание на дом ) : to learn new words by heart and to read additional text.
How did you feel about the lesson in general?
Did you have any particular difficulties?
Give some brief ideas of follow-up work you would do for this lesson.
Any other comments you would like to add.
Работа с дополнительным текстом:
Прочитайте и переведите текст с помощью словаря:
Entering 2003, HIV is the deadliest and most massive epidemic of infectious disease in medical history, with close to 65 million people living, dying, or dead with HIV.
What is HIV/AIDS?
• AIDS stands for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
• HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus
• A positive HIV test result does not mean that a person has AIDS. A diagnosis of AIDS is made by a physician using certain clinical criteria (e.g., AIDS indicator illnesses).
• Infection with HIV can weaken the immune system to the point that it has difficulty fighting off certain infections. These types of infections are known as «opportunistic» infections because they take the opportunity a weakened immune system gives to cause illness.
• Many of the infections that cause problems or may be life-threatening for people with AIDS are usually controlled by a healthy immune system. The immune system of a person with AIDS is weakened to the point that medical intervention may be necessary to prevent or treat serious illness.
The HIV-AIDS Connection
• AIDS was first recognized in 1981 and has since become a major worldwide pandemic.
Abundant evidence indicates that AIDS is caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which was discovered in 1983. By leading to the destruction and/or functional impairment of cells of the immune system, notably CD4+ T cells, HIV progressively destroys the body’s ability to fight infections and certain cancers
How long does it take for HIV to cause AIDS?
• Since 1992, scientists have estimated that about half the people with HIV develop AIDS within 10 years after becoming infected. This time varies greatly from person to person and can depend on many factors, including a person’s health status and their healthrelated behaviors.
• Today there are medical treatments that can slow down the rate at which HIV weakens the immune system. There are other treatments that can prevent or cure some of the illnesses associated with AIDS, though the treatments do not cure AIDS itself. As with other diseases, early detection offers more options for treatment and preventative health care.
How is HIV passed from one person to another?
HIV transmission can occur when blood, semen (including pre-seminal fluid, or «pre-cum»), vaginal fluid, or breast milk from an infected person enters the body of an uninfected person.
HIV can enter the body through a vein (e.g., injection drug use), the anus or rectum, the vagina, the penis, the mouth, other mucous membranes (e.g., eyes or inside of the nose), or cuts and sores. Intact, healthy skin is an excellent barrier against HIV and other viruses and bacteria.
These are the most common ways that HIV is transmitted from one person to another:
• By having sexual intercourse (anal, vaginal, or oral sex) with an HIV-infected person
• By sharing needles or injection equipment with an injection drug user who is infected with HIV
• From HIV-infected women to babies before or during birth, or through breast-feeding.
These body fluids have been proven to spread HIV:
What does AID stand for?
What does AID mean? This page is about the various possible meanings of the acronym, abbreviation, shorthand or slang term: AID.
Agency for International Development
Activation-Induced cytidine Deaminase
Acute Infectious Disease
Artificial Insemination by Donor
Association for India’s Development
Angel In Disguise
Accident Investigation Division
Autodin Interface Device
Assistance In Distress
Also Includes Drugs
Alien In Disguise
Association of India’s Development
Amputee Identity Disorder
Adapted To Include Drugs
ASARS (Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar System) Interface Device
Asociación Internacional del Desarrollo
Autonet Information Director
American Idol Divas
Automated Intelligence Discovery
Association for Individual Development
Artificial Insemination Donor
Arkansas Insurance Department
What does AID mean?
Popularity rank for the AID initials by frequency of use:
Couldn’t find the full form or full meaning of AID?
Maybe you were looking for one of these abbreviations:
Discuss these AID abbreviations with the community:
Report Comment
We’re doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we’ll take care of it shortly.