What does preposition mean
What does preposition mean
SAT / ACT Prep Online Guides and Tips
What Is a Preposition? Definition, Meaning, and Examples
Prepositions are one of the eight parts of speech in the English language, and they’re pretty important. Prepositions allow us to create complex sentences and add in important details. They play a crucial role in helping sentences make sense, which is super important when you need to communicate clearly and effectively.
But if you have to sit down and give an accurate preposition definition, things can get a little tricky. You may know that prepositions are usually short words like at, for, in, on, or under, but what is a preposition as a part of speech? What do prepositions do, and how the heck do you identify a preposition in a sentence?
To help you become an expert on prepositions, we’re going to talk about the following in this article:
If there’s a specific type of preposition you want to know more about—like prepositions of space—you can find the information quickly by holding Command + F on your keyboard, then typing in the term you’re looking for.
Now without further ado, let’s get started!
What’s a Preposition? Preposition Meaning and Usage in Sentences
Grammar rules for the English language state that prepositions are defined based on their function in a sentence. So, here’s how a preposition functions to create meaning in a sentence: A preposition combines with a noun, noun phrase, or pronoun to demonstrate a relationship between the noun and another component of the sentence, often another noun and verb.
In other words, prepositions help readers understand the relationship between different nouns and verbs in a single sentence.
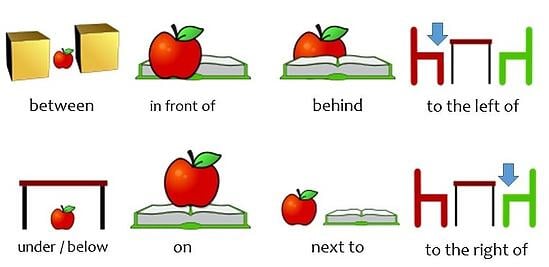
Now that you’ve got an answer to the question, “What’s a preposition?” you’re probably wondering what kind of relationships prepositions show. Prepositions can show relationships of time, space, or possession between a subject and an object in a sentence.
For example, in the following sentences, each preposition (in bold) helps us better understand the relationship between the cat and the table:
In the examples above, the prepositions on, under, beside, and at help clarify the nature of the relationship between the cat—the subject of the sentence—and the table—the object of the preposition. Notice that each sentence makes us visualize something different: a cat sitting on a table is not the same thing as a cat sitting under a table. And guess what? That’s what prepositions are designed to do!
Here’s a helpful list of prepositional phrases!
The Prepositional Phrase
The next thing you need to know about prepositions in sentences is that they almost always appear in a prepositional phrase. Prepositional phrases are important for communicating what types of actions and interactions occur between the subjects and objects of sentences.
A prepositional phrase consists of a preposition (or prepositions), the object of the preposition (a noun, noun phrase, or pronoun), and any other words that modify the object (an adjective or adverb). In the examples above involving the cat and the table, on the table, under the table, beside the table, and at the table are all prepositional phrases because they begin with a preposition that is followed by a noun (cat).
Quick note: if you’re not sure what things like nouns, adjectives, or adverbs are, don’t worry. We have a complete, expert guide to each part of speech that will teach you everything you need to know!
Keep in mind that prepositional phrases aren’t limited to a single preposition and a single object. Prepositional phrases can also contain modifiers of the object, which are usually adjectives and adverbs. Here’s an example of a prepositional phrase that also contains modifiers:
The cat sat under the dirty, decaying table.
In this example, under the dirty, decaying table is the entire prepositional phrase. It consists of the preposition (under), the object (the table), and the adjectives that modify the object (dirty, decaying). So while a prepositional phrase must contain at least one preposition and an object, it can also contain other types of words.
Now if someone asks you, “What is a preposition?” you have an answer! Next, we’ll break down the different types of prepositions for you so you’ll be a preposition expert.
2 Forms of Prepositions and Prepositional Phrases You Need to Know
Part of answering the question, “What is a preposition?” includes explaining the two different forms, or structures, that prepositions and prepositional phrases can take. Think of form like a formula: it’s a prescribed way that you can put different prepositional words together to make them work in a sentence!
Let’s look at the two forms of prepositions below.
#1: Simple Prepositions
Simple prepositions are the first type of preposition, and it’s one of the two types that Defining simple prepositions is, well, simple: simple prepositions are one-word prepositions that appear at the beginning of a prepositional phrase in front of an object or in front of an article and an object. In other words, simple prepositions look something like this:
We’ve been playing since noon.
They walked through the field.
In both of the examples above, the prepositional phrases begin with a simple preposition: since is the simple preposition in the first example, and through is the simple preposition in the second example. In both examples, the simple prepositions are followed by an object (noon in the first example) or an article plus an object (the field in the second example).
These examples also explain how this is a form of preposition. While both of these are simple prepositions, the words we used totally changed the meaning of the sentence. In the first sentence, using since helps us understand the amount of time the person has been playing. That’s because since is a preposition of time! But the simple preposition structure also works in the second sentence, even though we’re using a preposition of movement (through) instead.
So just like math, prepositional forms let you swap words in and out to create meaning.
And that’s the definition of a simple preposition! Simple prepositions are used very frequently in the English language, so you’ll probably start to see them everywhere now that you know what you’re looking for.
#2: Complex (or Compound, or Double) Prepositions
There’s a little disagreement out there about what to call this form of preposition: sometimes they’re called complex prepositions, compound prepositions, or double prepositions. Just know that all of these terms refer to the same thing.
Complex prepositions are a group of prepositions that function like a simple preposition. That means complex prepositions always consist of more than one preposition (unlike simple prepositions, which only have one). Here are two examples of complex prepositions in a sentence:
Get these chips away from me.
She laughed at his joke in spite of herself.
As you can tell from these examples, complex prepositions can appear in two-word units or three-word units. When a complex preposition appears in a two-word unit, it involves two prepositions in a row which are followed by an object. In the first example, away from is our complex preposition, and the object that follows it is me.
When a complex preposition appears in a three-word unit, it follows a different formula. In three-word units, the first preposition and second preposition are separated by a noun, then the object comes afterward. In the second example, in and of are prepositions, spite is the noun, and herself is the object!
Remember how we talked about forms of prepositions working like a mathematical formula? That’s definitely the case for complex prepositions! Though there are many complex prepositions (which you’ll see in our list below), the most commonly used formulas for a complex preposition in English are the following:
To help you pick out complex prepositions when they’re used in sentences, here’s a list of commonly used complex prepositions:
4 Types of Prepositions and Prepositional Phrases That Convey Meaning
These types of prepositions are used to convey meaning in a sentence. You can pop them into one of the forms we discussed above to help people better understand specific relationships between a subject and an object in a sentence. Specifically, these types of prepositions describe four different types of relationships: time, space, direction/movement, and agent/instrument.
These prepositions can be mixed and matched with the preposition forms we just talked about, so most prepositions fit into two categories: one for their form, and another for their meaning. Put another way, a preposition in a sentence can be both a simple/complex preposition and a preposition of time, space, direction/movement, or agent/instrument!
Now, let’s learn a little more about the four types of prepositions that help writers convey meaning.
#1: Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of time demonstrate relationships between things in terms of when something occurred. Prepositions of time can show the specific, exact time when something happened or will happen. It can also express a more general, extended period of time.
Take a look at the table below for a list of prepositions that are frequently used to demonstrate relationships in terms of time:
So how do prepositions express time, exactly? Let’s look at two examples:
Example #1: Sean will drop off the recycling after work.
In this first example, after is the preposition of time, and after work is the prepositional phrase. But how is after establishing a time-based relationship here? After establishes time by showing that Sean will perform a specific action—dropping off the recycling—only after he has finished with work. In this case, we can see how these two elements of the sentence relate to one another: one has to end before the other can happen.
It’s also worth noting that after is also part of a simple preposition. so it’s both a simple preposition and a preposition of time!
Now that you have a better understanding of how this works, here’s a second example of a preposition of time in a sentence:
Example #2: I’m going live at ten o’clock.
In this example, at is the preposition, and at ten o’clock is the prepositional phrase. More importantly, at is establishing a precise time. In this case, the person speaking is going to go live on television at an exact time. Thus, the preposition at establishes that the time-based relationship between the subject and the verb and the object is a precise one.
You use prepositions of time every day, even if you don’t realize it. Whether you’re giving directions, planning your day, or just telling a story, prepositions of time help us create chronological order.
#2: Prepositions of Space
Prepositions of space are used to show where a person, living creature, or other object or entity is located in space (as in, like, physical space in the everyday world, not outer space).
The words in the following list are classified as this type of preposition, meaning they show where things are located in space, including location in relation to other things, direction, and movement.
Now that we have a full list of prepositions of space, let’s look at an example of a preposition of space: one example that simply shows where something is located in space. Here we go:
There’s an owl in the chimney!
This example is pretty straightforward. Where is the owl? It’s located in the chimney. There’s a spatial relationship established between the owl and the chimney through the use of the preposition in.
Prepositions of direction and movement help readers understand movement. In this case, the dancer is lifting his partner off the ground!
#3: Prepositions of Direction/Movement
Prepositions of space are sometimes broken down into even smaller categories, and two of the categories you need to know about are prepositions of direction and movement. These types of prepositions show movement from one place to another. Because of this, prepositions of direction and movement are often used with verbs of motion.
Here’s a list of words that are classified as prepositions of direction and movement:
Prepositions of direction and movement connote that something is moving through space in relation to another object. Check out this example:
Sophia threw the dart at the bullseye.
In this example, the dart’s location in space is described in relation to the bullseye’s location in space through the use of the preposition at. We know that the dart is directed toward the bullseye, and since the dart has to move through space in order to actually hit the bullseye, we consider prepositions of direction/movement as falling into the bigger category of prepositions of space!
Here are a few more examples of prepositions that connote direction/movement:
They walked among the wildflowers.
The festival-goers twirled around the maypole.
Like the earlier example, both of these examples show that living beings are moving through space in relation to other objects. In the first example, they are moving through space in relation to some wildflowers. In the second example, the festival-goers are moving through space in relation to the maypole.
One way to recognize prepositions of space that connote direction/movement is to look for a verb right before the preposition, because prepositions of direction/movement often follow a verb in a sentence!
#4: Prepositions of Agent/Instrument
There are also prepositions that can be used to connote a different kind of relationship besides relationships of time or space. These prepositions are known as prepositions of agent/instrument, and they demonstrate a relationship in which one noun performs an action on or toward another noun in a sentence.
Here are the common prepositions of agent/instrument that you need to know:
Let’s have a look at an example of a preposition of agent/instrument in a sentence:
I think the movie was produced by Disney.
This example conveys a relationship of agency, or power, between a noun and a verb: the movie under discussion in this sentence was produced by Disney. This conveys a relationship in which a group of persons has caused something to occur. In this sentence, prepositions help us understand that Disney has control over the production of the movie. It’s also important to note that prepositions of agency are usually used in sentences that are constructed in the passive voice, like in the example above.
Now, here’s an example that shows a preposition of instrument. A preposition of instrument is used to describe machines, technologies, and devices. Basically, when you need to explain how a mechanical noun acts toward another noun, you use this type of preposition! Here’s an example:
She lit the candle with a match.
This sentence example uses the preposition meaning with to show a relationship between one noun—a match, which is an instrument—and another noun—the candle, which is also an instrument. In other words, the preposition with connotes a relationship in which the match acts upon the candle. Prepositions of instrument almost always describe use of devices, technologies, or other objects.
3 Top Tips for Identifying Prepositions in a Sentence
As you’ve probably guessed by now, prepositions can be a little bit sneaky in sentences. Sometimes words that are commonly used as prepositions are also used for other purposes, which can make identifying prepositions in a sentence a little bit confusing! We’ve come up with three top tips on preposition grammar to help you spot prepositions in a sentence correctly.
#1: Break Down the Word Itself
If you have trouble remembering where a preposition should appear in relation to the object that it modifies in a sentence, you can break down the actual word “preposition” as a memory hack. A preposition appears in front of its object, so you can think of it as being pre-positioned in front of the object.
Read the examples above one more time. In each one, the preposition comes before the object. And there’s an added bonus: when you can find the preposition in a sentence, you can also find its object, too!
#2: Remember That Prepositions Are “Anywhere a Cat Can Go”
We’ve already used cats in a couple of our example preposition sentences, but did you know that many people are taught in school that prepositions are anywhere a cat can go? Just think about it: how many videos have you watched of cats fitting themselves into bizarre places? They can go on, in, through, around, under, across, behind, between, through. pretty much any object (especially boxes). And as it turns out—all of those words are prepositions!
So If you’re looking for a way to remember prepositions of space, location, direction, and movement, just picture a cat playing with a box. If the word you’re using is somewhere the cat can go, then you’re probably dealing with a preposition.
#3: Watch Out for Verbs. and Look for the Prepositional Phrase
Something super important to know about words that are classified as prepositions is that they don’t necessarily function as prepositions every time they appear in a sentence.
This means that you can’t really just glance at a sentence and pick out a single word that is often used as a preposition and be sure that it’s working like a preposition in that particular sentence. You’ve got to look at the bigger picture of the sentence itself to determine whether the word is being used as a preposition!
So what do you look for to determine whether a word is being used as a preposition? Look at the words around the preposition to see if there’s a prepositional phrase. Remember: a word that is often used as a preposition must show a relationship between the noun and another part of the sentence in order to function as a preposition.
Additionally, preposition grammar rules indicate that when a word that looks like a preposition comes before a verb phrase instead of a noun phrase, that little word that looks like a preposition isn’t functioning as a preposition at all—it’s functioning as a particle instead. So, in addition to looking out for prepositional phrases, you can also look out for verbs. Here’s an example of what a particle looks like in a sentence:
We’re going to walk at the market.
In this example, the phrase to walk might look like a prepositional phrase at first glance, but walk is a verb, not a noun, noun phrase, or pronoun. So, in this case, to isn’t the beginning of a prepositional phrase and isn’t being used as a preposition. However, the phrase at the market at the end of the sentence is a prepositional phrase, since the market is a noun!
What’s Next?
Prepositions help make your writing clearer, which is incredibly important if you want to ace the writing portions of your standardized tests. Luckily for you, we have expert guides to help you ace your SAT and ACT essays! Click here to learn how to get a perfect 12 on your ACT essay. If you’re aiming to get a perfect 8 | 8 | 8 on the SAT essay, you’ll want to check out this article instead.
You’ll also have to write stellar admissions essays if you want to get into your dream school. Start by getting expert advice on how to tackle the Common App essay prompts, then check out our blog for school-specific tips. We have thorough guides about how to write essays for the top schools in the nation, including Harvard, Yale, Notre Dame, Michigan State, USC, and more!
If you’re interested in grammar because you love to write, you might consider majoring in creative writing. If this sounds like you, you should definitely check out this list of the best 12 creative writing programs in the United States.
Need more help with this topic? Check out Tutorbase!
Our vetted tutor database includes a range of experienced educators who can help you polish an essay for English or explain how derivatives work for Calculus. You can use dozens of filters and search criteria to find the perfect person for your needs.
Have friends who also need help with test prep? Share this article!
Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com, allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we’ll reply!
Preposition: Definition & Types
What is preposition
A preposition is a word that indicates the relationship between a noun and the other words of a sentence. They explain relationships of sequence, space, and logic between the object of the sentence and the rest of the sentence. They help us understand order, time connections, and positions.
Example:
There are a few interesting linguistic facts about prepositions.
First, they are a closed class of words which means no new preposition gets added to the language. We use a fixed set of prepositions.
Second, prepositions do not have any other form. They cannot be plural, possessive, inflection, or anything else.
Third, most of the prepositions have many different contextual and natural uses. So, it is easy to be confused about it.
Fourth, sometimes a preposition works as nouns, adjectives, and adverbs.
Prepositions can be of one, two, three, or even more words. Prepositions with two or more words are called phrasal prepositions.
There are some commonly used phrasal prepositions:
because of, in case of, instead of, by way of, on behalf of, on account of, in care of, in spite of, on the side of, etc.
Types of Preposition
Most of the prepositions have many uses. There are some prepositions which are common in every type of preposition as they function in a versatile way.
Simple Preposition
These are among the most common type of prepositions. The prepositions used to express the relationship the Nouns and Pronouns of a sentence have with the rest of the words in it are called Simple Prepositions. They are often used to join two clauses in terms of Complex Sentence and Compound Sentence.
| Most Popular Prepositions | |||||
| and | but | at | to | on | in |
| for | of | up | off | from | out |
| with | during | down | below | beside | over |
| by | near | behind | inside | among | along |
Double Preposition
Two Simple Prepositions joining together to form one which connects the Noun(s) or Pronoun(s) to the rest the words in a sentence.
Compound Preposition
Compound Prepositions are composed of prepositions as well as other words. Compound Prepositions are easily confused with Double Prepositions since they both require other prepositions or words to help with acting like a preposition.
Participle Preposition
| Present Participle Prepositions | Past Participles Prepositions |
| Assuming | Respected |
| Barring | Given |
| Considering | Gone |
| During | Barred |
| Notwithstanding | Provided |
| Regarding | Taken |
Participle Prepositions Used in Sentences:
Disguised Preposition
These prepositions are usually disguised as some other element in the English language. Often these prepositions are disguised as «a» and «o» in sentences.
Detached Preposition
A preposition that has been detached and sent to the very end of the sentence is called Detached Preposition. These prepositions are detached from the interrogative or relative pronouns and adverbs but get detached for the sake of the integrity of sentences.
Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of time show the relationship of time between the nouns to the other parts of a sentence.
On, at, in, from, to, for, since, ago, before, till/until, by, etc. are the most common preposition of time.
Example:
Prepositions of Place and Direction
Prepositions of place show the relationship of place between the nouns to the other parts of a sentence.
On, at, in, by, from, to, towards, up, down, across, between, among, through, in front of, behind, above, over, under, below, etc. are the most common prepositions of place/direction.
Example:
Prepositions of Agents or Things
Prepositions of agents or things indicate a causal relationship between nouns and other parts of the sentence.
Of, for, by, with, about, etc. are the most used and common prepositions of agents or things.
Example:
Phrasal Prepositions
A phrasal preposition is not a prepositional phrase, but they are a combination of two or more words that function as a preposition.
Along with, apart from, because of, by means of, according to, in front of, contrary to, in spite of, on account of, in reference to, in addition to, in regard to, instead of, on top of, out of, with regard to, etc. are the most common phrasal prepositions.
Example:
What is a Preposition? Definition, Examples, and List of Prepositions
Home » The Writer’s Dictionary » What is a Preposition? Definition, Examples, and List of Prepositions
Preposition definition: A preposition is a part of speech that shows the relation of a noun or pronoun to another word.
What is a Preposition?
What are prepositions? Prepositions show the relationship of a noun or pronoun to another word. These relationships include where, when, who, or what.
Examples of Prepositions:
Let’s look closer at a preposition example.
A preposition can be understood as anywhere a dog can be in relation to its doghouse.
Each of these prepositions describe the relation between the dog and its doghouse. The dog can be inside the doghouse, it can be around the doghouse, it can be near the doghouse, it can be on the doghouse, etc.
All of these preposition examples show where the dog is in relation to its doghouse.
What is the Role of a Preposition?

Most often prepositions are used to introduce prepositional phrases.
Prepositions serve to modify and generally function in prepositional phrases as adjectives or adverbs.
Examples of prepositions indicating where:
Examples of prepositions indicating when:
Examples of prepositions indicating who:
Examples of prepositions indicating what:
Preposition List

aboard
about
above
across
after
against
along
amid
among
anti
around
as
at
before
behind
below
beneath
beside
besides
between
beyond
but
by
concerning
considering
despite
down
during
except
excepting
excluding
following
for
from
in
inside
into
like
minus
near
of
off
on
onto
opposite
outside
over
past
per
plus
regarding
round
save
since
than
through
to
toward
towards
under
underneath
unlike
until
up
upon
versus
via
with
within
without
For a more full list of prepositions, see our full page on the subject. Prepositions list here.
Object of Prepositions

Some Prepositions Also Function as Subordinate Conjunctions

The prepositions that can function in subordinate conjunctions include: after, as, before, since, until.
Prepositions together within subordinate conjunctions function as adverbs.
Preposition Examples:
What are Prepositional Phrases?
What does prepositional phrase mean? Almost always a preposition will function in a prepositional phrase.
A prepositional phrase is any preposition and its object (a noun). A prepositional phrase may also include any modifiers in the phrase.
Prepositional phrases clarify the relationship of the preposition to other words.
Prepositional Phrase Examples:
Multiple prepositional phrases may exist within one larger prepositional phrase.
Prepositional Phrase Examples:
Summary: What are Prepositions?
Define preposition: To clarify, prepositions:
What Is a Preposition?
By Bizhan Romani
Introduction
When it comes to dealing with the English language, especially for non-English speakers, its numerous little rules can feel confusing to say the least. For example, many people struggle with prepositions. Despite being a crucial part of the language itself, English speaking people tend to have a very limited number of prepositions that they actually use.
Indeed, there are around 150 different prepositions in the English language, but it is unlikely that you will use all of them. You might, though, be intrigued to know that while many prepositions go unused for the majority of speakers, some are among the most popular and commonly used words in the whole language. For example, the words of, in, and to are all known as common examples of prepositions. In this article, we are going to help you work out the answers to the following questions:
What is a preposition?
So, a preposition is a part of the English language that is defined by Merriam-Webster as “a word, or group of words, that are used in conjunction with a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase to show direction, location, or time, or to introduce an object.”
So, prepositions are used to try and connect together otherwise terms that might be lacking in any kind of meaningful context to the recipient of the wording. Many times, we will look to use prepositions as a means of trying to connect nouns together to a particular subject or an idea.
For example, let us say that you were in conversation and they asked you why you were not home when they rang your doorbell. You might say something like, “Oh, I went to the shops.” – the “to” here is the preposition; it is connecting the context of the sentence. It tells people who is involved in the conversation (you), and in this context it tells the person you are speaking to where you have gone that day (the store).
However, there are many examples of more advanced prepositions being used – for the most part, though, it will come down to things like those shown already: in, to etc.
For example, let us say someone asks you where you have parked the car when you go to pick them up. You could respond something like: “I have parked the car in front of the trolley.” – this tells the person that you have parked somewhere, with “in front of” doing all of the work as the preposition in this point. Without that information, they might assume you have parked behind the trolleys, or to its side. By saying in front of, they know where to look and where to find you.
Why do prepositions matter?
Put simply, prepositions matter because they give people an opportunity to communicate with you in a way that makes a lot more contextual sense. Instead of just telling someone generic details like “I went out”, you give people more information. This is useful for creating more detailed conversation, for giving people the information they need, and for always making sure you are never needlessly vague and/or ambiguous.
As noted above, prepositions are useful because they allow us to clearly describe what we have been doing, where we are going, and other important factors in detailing our lives. Also, prepositions matter because they can offer clarity and turn an otherwise ambiguous statement into something that can be far more factual and easier to use as evidence, information, or even can help to improve education. With so many different prepositions, though, you might not be sure when you are using prepositions and what this actually means for you.
Some of the most common prepositions that you might use on any given day include terms like among and behind, beside and between, from and in/into to near or toward. Basically, if you want to give someone an indication of a location, a destination, or even a place in time then you might need to get used to working with prepositions as a common part of your day-to-day conversation.
In short, using prepositions allows for you to give people a bit more information about what you are doing, where you are going, and/or where you are.
What type of prepositions are there?
As mentioned above, though, there are more than just basic prepositions – you get more than one type of preposition. They are used in all manner of conversation and thus need to be split up based on the context of what they are actually doing in the first place. For example, it is important to be able to distinctly tell apart all prepositions – and that is why the development of types of prepositions can be so useful in the modern world. Now, you can make sure you use the right kind of preposition when it is called for, optimizing accuracy.
Complementary prepositions
One of the most common forms of preposition is known as a complementary preposition. These are very useful because they give you a very easy way to understand why a certain word might follow on from a particular preposition.
These are very important as the word that follows on from a preposition helps to closely determine the kind of preposition that is actually being used. Many do not realize just how important this can be when it comes to determining what would make a suitable preposition in any given situation.
Conjunctive prepositions
This has become a common form of preposition as it allows for you to provide a clause as part of the overall complement. As you will find out, many prepositions tend to be delivered with a complement to help add a bit more detail to the statement being made.
For example, you might wish to use something like “because” as a preposition. This would be known as a conjunctive preposition, with “because” acting as the qualifier before your explanation. So, you could say something like “He lived on his farm because it provided privacy and an opportunity to work.”
That would well as it allow for you to help offer a bit more detail on the statement made.
Complex prepositions
As the name implies, the use of complex prepositions can be a touch difficult. They tend to use more than one word to make the point they intend to. This is commonly used to help describe a qualifier before a statement, so it could be something like “Due to the recent weather, we’ve had to cancel the celebration…” or “In light of new evidence, the case will be re-opened.”
It could even include things like ‘in the middle of’ i.e. “I am in the middle of washing my hair, phone me back later!” or even something like “On behalf of my family, I would like to say thank you.”
As you can see, then, more complex prepositions tend to be quite packed with information and ideas that you need to try and get across in a very particular way. The main challenge when choosing a preposition is to make sure that the beginning of the sentence can only make sense by using the preposition in the middle to help join it all together.
These are commonly used as a qualifier to help describe a new piece of information or statement brought to light.
Transitive prepositions
Following on from the above, transitive prepositions are very important as they always make use of a complement alongside a preposition. So, for example, you could say something like “he lived among the animals on his farm.” – that would be a transitive preposition. The reason why this matter is that you couldn’t simply say “he lived among the farm” – you need to explain what he lives amongst.
It adds more detail and description for the reader/listener and can be very important for making sure you can detail something properly. The vast, vast majority of transitive prepositions tend to be based around describing facts in closer detail.
Intransitive prepositions
Another form of preposition that you need to get used to dealing with are intransitive prepositions. These are very important to note about because they do not use a complement – this is important as not all prepositions are built with that method.
For example, to build on the example above, you could simply say instead something like “he lived indoors.” Or “he lived inside.” – it does not need to come with an extra complement of information. While a little vague, intransitive preposition allows for you to answer with a clear statement of fact and often are not followed up with traditional grammars afterward.
Essentially, if your transitive prepositions must come with a complement, then intransitive prepositions have no reason to follow that same structure – they normally do not come with a qualifier.
What is a preposition versus a postposition?
While the above might sound somewhat confusing, you are about to find out about something very important: postpositions. So, a preposition is something that is used to help qualify a statement in the ways that we have shown you so far. However, sometimes, the position you might wish to take might be better done at the end as a conclusion as opposed to a link or a build-up discussion.
So, there is quite a difference between using prepositions and postpositions. While a preposition will always come before the complement or wider statement, a postposition will always come at the end of the complement. However, you might be shocked to find out that prepositions are far, far more common than using postpositions in the modern English language.
In fact, while most of us tend to use a small number of prepositions, we use an even more limited number of postpositions. In fact, it’s normally going to be built around basic statements of fact, such as “And that was a long time ago.” – for the most part, they tend to be used as a means of summing something up, adding a touch more context to a statement that needs extra adjustment, or simply is seen as part of the easiest way to finalize a sentence.
Common postpositions that you might find yourself using on a regular basis, though, include things like aside and apart as well as key terms like hence, on, and through as just a few small examples of the kind of issue that you might be dealing with.
You will be happy to know, though, that prepositions are far more common and generally far more useful. Even those who fluently speak English to an advanced level will find their use of prepositions to far outweigh the number of times they will reach out for a postposition. However, if you are trying to learn English, it might be a wise idea to spend some time mastering the rather confusing nature of prepositions and postpositions.
Once you get used to working with postpositions, though, you should find it a bit easier to start coming ahead with using these in the right time and the correct place.
When should you use prepositions?
While trying to balance your use of prepositions and postpositions takes work, once you get used to naturally reading/speaking the language it should become much easier in general. You will start to realize that, for the most part, the use of prepositions/postpositions simply offers a bit more detail and information. It could offer more context, for example telling people that you are in a specific room, sat at a particular table, or tell somewhere where to find something i.e. cards, ID, or even where to find a location i.e. “The shop is on the right-hand side.”
Remember that prepositions are typically built around showing where something is, or when something happened. So, you could normally look to use these to describe a time, place, or location as much as anything else. Once you get used to working with prepositions in this way, you can start to use them to your advantage.
Getting to grips with prepositions
The main challenge is getting used to making sure that your sentences and your phrases put the preposition first, not last. For example, instead of saying “Do you know where he is at?”, you could simply say “Do you know where he is?”
Many of us use prepositions incorrectly because it can bleed into our own informal slang and conversational usage. However, if you intend on doing any kind of serious writing, it does pay to get used to the various uses of prepositions. Once you understand they more or less always go prior to the complement outside of some very unique exceptions, you will find it easier to be more detailed in both asking questions and providing answers.
You also need to remember that not every preposition is going to need you to include something like an ‘at’ – for example, many times you can substitute a preposition like “at” or something like “like”. For example, you could say something like “You look just like your father!” – but you wouldn’t say “You look just like you are furious!” – this does not sound correct. Instead, you would say “You look furious.” – there is no need for the preposition in the second example, whereas the first would sound off without its usage.
You also need to think about how you end a sentence, too; for example, in the “You look just like your father!” example, you might wish to adjust it to say something like “you look just like your father does!”
However, in the context of a preposition, this more or less ‘translates’ to “You look similar to your father does,” and we both know that is not correct. So, you would need to look to swap out the use of “like” for something like “as” because, in the context of prepositions, this makes more sense.
Remember, too, that slang and informal text can mean that prepositions become even more confusing. For example, many of us substitute “of” for “have” and this can create sentences that, at least within prepositions, make no sense.
Mastering prepositions is a worthwhile exercise
The biggest challenge that you will likely face when it comes to writing and dealing with prepositions is getting to grips with all of the rules and subrules. For example, how you use terms like “into” and “in” can seem very similar, but within the context of prepositions would mean two entirely different things.
It can take some time to get your head around these factors, but it is by no means impossible. You just need to consider the various challenges that comes with how you use language. Once you get used to the little quirks that exist within prepositions, it does become much easier to use them effectively and accurately.
Preposition
Definition
Explanation
A preposition is one of the important parts of speech in English grammar. It is very essential while making a sentence as it provides additional and necessary details. Prepositions in English are words giving information to the readers such as where something takes place when something takes place, why something takes place, general descriptive information, etc. Prepositions work in groups of words (also called prepositional phrases) and do not stand alone.
List/Words
Some preposition words are like about, till, out, above, against, below, beneath, beside, besides, between, through, up, upon, within, during, except, for, from, in, off, on, onto, opposite, near, of, behind, inside, into, outside, around, before, among, to, along, at, toward, under, underneath, across, like, until, with, beyond, by, down, since, without, after, etc.
Types of Preposition
There are various types of prepositions described below with proper definition and examples:
Simple prepositions are used in the simple sentences. Some of the simple prepositions are in, on, at, to, from, with, by, about, over, under, off, of, for, etc.
Compound prepositions are used to join two nouns, pronouns or phrases. Some of the compound prepositions are about, across, among, beside, before, above, along, inside, between, around, behind, below, beneath, etc.
Prepositional phrases are groups of words having prepositions indicating relationships among various elements in the sentence. Some of the phrase prepositions are according to, an account of, in spite of, in front of, for the sake of, in order to, by means of, with reference to, in addition to, due to, etc.
A participle preposition is a participle (like an, ed, or ing verb) which acts as a preposition such as assuming, considering, barring, given, concerning, notwithstanding, pending, during, regarding, respected, provided, etc.
Double prepositions are words having two prepositions (joined together to make a whole new one) such as into, onto, outside of, out of, within, from behind, because of, etc.
Following are other types of prepositions:
Preposition of Place
Prepositions of place are used to show the place where something is located such as at, in, on, while, during, near, over, under, between, behind, etc.
Preposition of Time:
Prepositions of time are used to indicate time of an action or time relationship between nouns in the sentence. Such as at, to, in, etc.
I go to school daily at nine o’clock.
My result gets declared in March.
Preposition of Direction
Prepositions of direction are used to indicate direction of someone or something in the sentence such as over, under, to, on, into, in, onto, right, left, etc.