What is a publication source
What is a publication source
Whats a publication source?
Asked by: Miss Juanita Christiansen
Publication Source. Publication Source is a single line text field used to display the official title of the journal, book, or other medium in which the document was published.
How do you find the source of a publication?
The page immediately following the title page is often called the copyright page. This is where you find the remaining copyright information for the book. Here is where the publication or copyright date is typically printed.
What is a publication source example?
journals, letters and diaries. speeches. scrapbooks. published books, newspapers and magazine clippings published at the time.
What are examples of publications?
What are the three types of publication?
How to Evaluate Sources
41 related questions found
What is a popular publication?
A popular publication will contain language easily understood by a general audience. They are usually written by journalists or freelance writers and do not undergo a formal review by experts before release. Popular publications generally do not have full citations for information used to write the piece.
What is a scholarly source example?
Books, conference publications, and academic journal articles, regardless of whether they are print-based or electronic, are common types of scholarly materials, which share the following characteristics: The authors are scholars or researchers with known affiliations and educational/research credentials.
What are the two types of sources?
There are two kinds of sources: primary and secondary. The main difference between a primary and a secondary source is when they were made.
What is the title of publication?
What is the year of publication?
Date published can most usually be found on the copyright page of a book. That page will tell you when the work was copyrighted – and if the book is a first edition, the copyright date will be the same as the date published. If it is a later edition, the date will be different.
What type of source is a newspaper?
Newspaper articles can be examples of both primary and secondary sources.
What is the difference between journal name and title?
The article title is followed by the name of the journal, which is italicized. Omit any introductory articles (e.g. A, An, The) from the journal name. Journal names are usually given in full, since it is not incorrect to spell out a journal name.
What does publication name mean?
A human readable textual identifier of the publication. (
What is the purpose of publication?
The purpose of publication is to disseminate information.
What are the two main sources of history?
There are two main types of sources of history- primary and secondary sources.
What are types of sources?
What are the literary sources?
Literary sources are the information which is in written form and their sources are journals, letters, books, reports, documents etc. Complete answer: History primarily can be traced by two kinds of sources namely, archaeological sources and literary sources.
What makes something a scholarly source?
Government documents and government websites are generally considered authoritative, credible sources of information. Many are scholarly, and some are even peer-reviewed!
How do you identify a scholarly source?
What is a professional publication?
A professional magazine or journal is one produced by a professional organization and tailored to the interests of its members. Professional magazines present news and analysis, editorial comment, and book reviews of interest to the association’s members and often take the form of newsletters.
How do you write a publication?
Which is an example of a trade publication?
Examples of trade journals include Police Chief, Education Digest, Energy Weekly News, Aviation Week and Space Technology, Engineering News Record, Design News, and Traffic World.
Is article a publication?
Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. An article or piece is a written work published in a print or electronic medium. It may be for the purpose of propagating news, research results, academic analysis, or debate.
What is the difference between publication name and publisher?
As nouns the difference between publication and publisher
is that publication is the act of publishing printed or other matter while publisher is one who publishes, especially books.
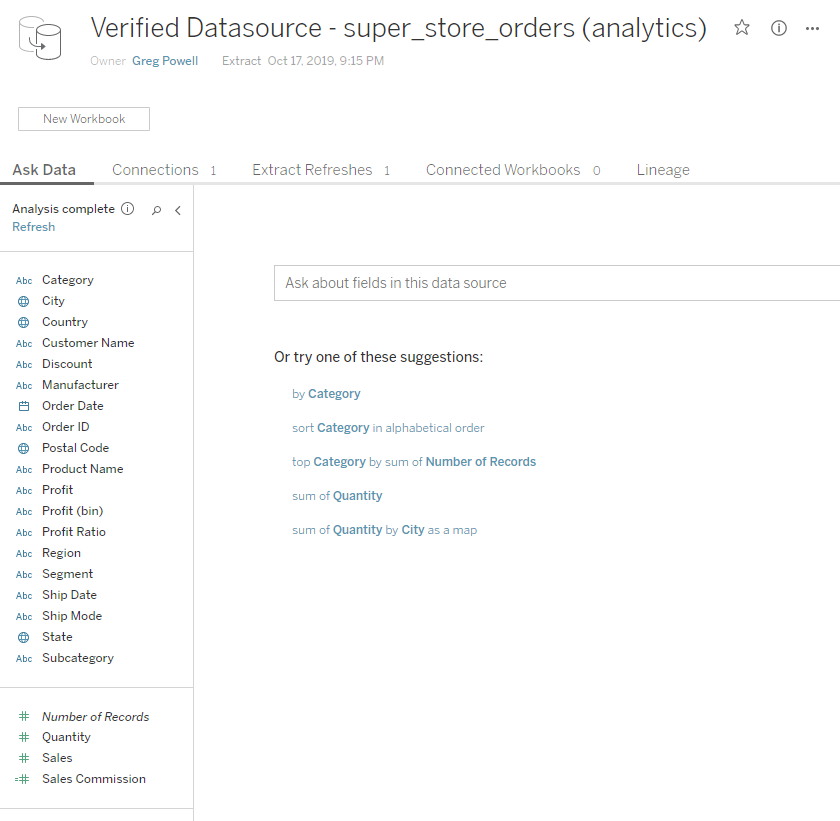
Tableau Data Extracts & Tableau Data Sources
Are you wondering how to use Tableau data extracts and data sources? This is an informative guide.
Greg Powell
Overview
Tableau Data Extracts are quick and easy to manage, but if your organization has a large data set that needs to be shared, a Tableau Published Data Source is an excellent solution.
Tableau Desktop allows the user to connect to and analyze many types of data sources.
When a user establishes a connection to a data source, a couple of choices face the user. This article covers two options for managing this data, Tableau Extracts* and Tableau Published Data Sources.
Need help managing these data sources and extracts? We are Tableau masters!
What are Tableau Data Extracts?
Tableau data extracts are a “snapshot” of data that is compressed, stored, and loaded into the memory.
Understanding a Tableau Data Extract
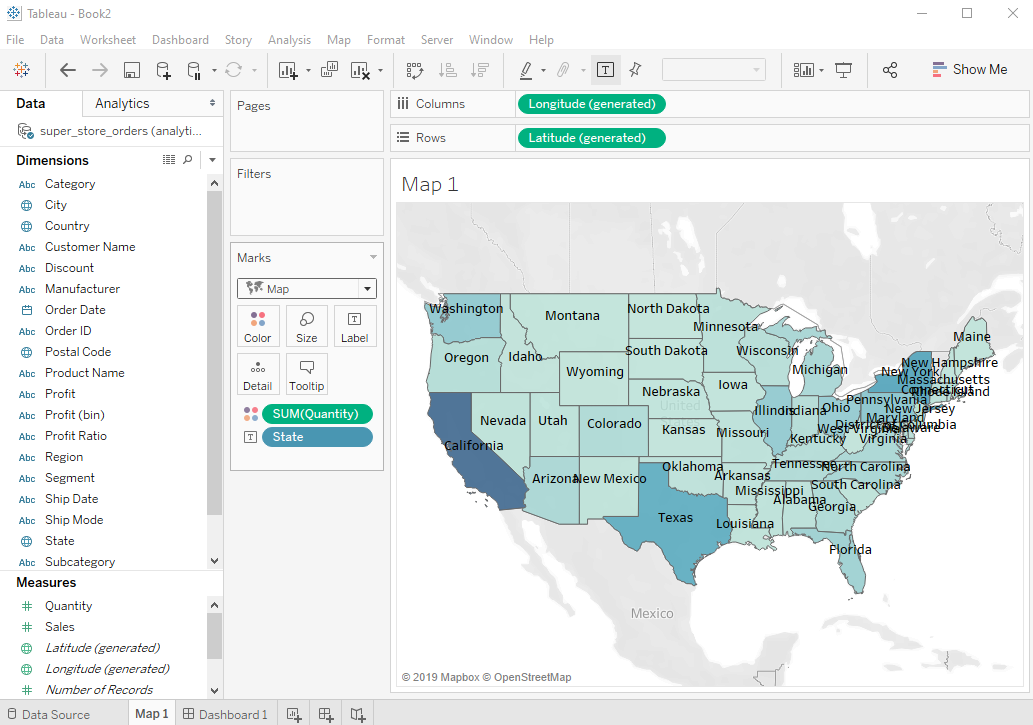
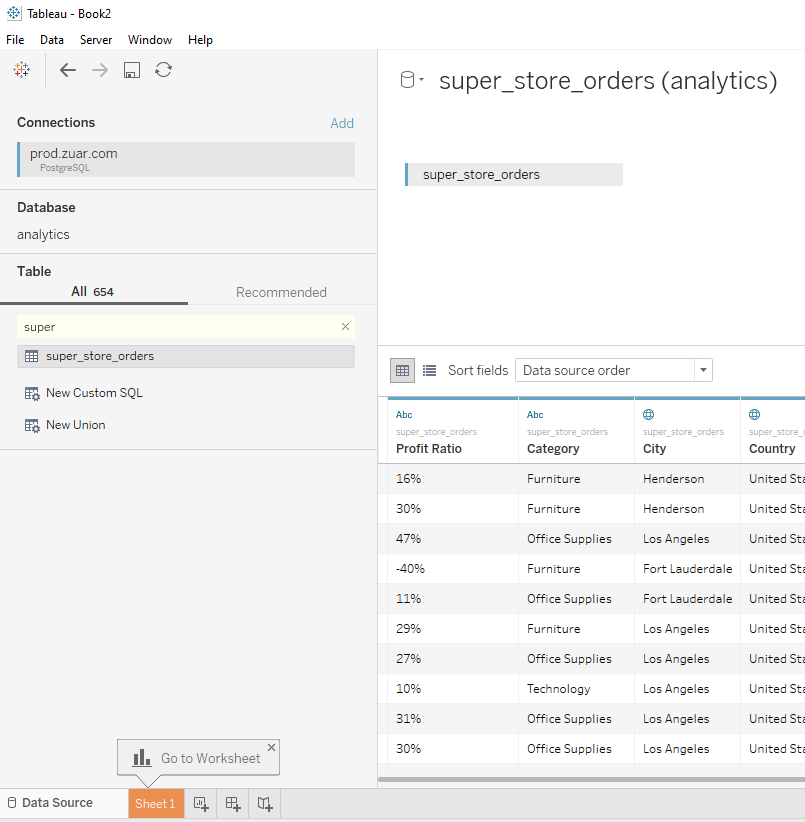
The best way to understand a Tableau data extract is to look at an example scenario: 1. User 1 will connect to the Superstore PostgreSQL Table. Since this is an extensive database, a data extract will be created. Multiple members of the organization can use this table.
2. Some sheets/dashboards are then created using this data extract:
3. User 1 then publishes the Dashboard to Tableau Server and sets up a refresh extract to refresh this dashboard from the database every hour:
4. The next day User 2 comes along and makes the same connection with same data extract schedule to the same database table but creates a slightly different Dashboard:
5. So now there are two dashboards with two data extracts from the same database table. The data extract is also querying the database twice when it really only needs to be querying it once.
Disadvantages of a Tableau Data Extract
Based on this example, we can address a couple of disadvantages of Tableau data extracts.
Redundant Multiple Data Source Queries
If dashboards continued to be published in this manner the following situation arises.
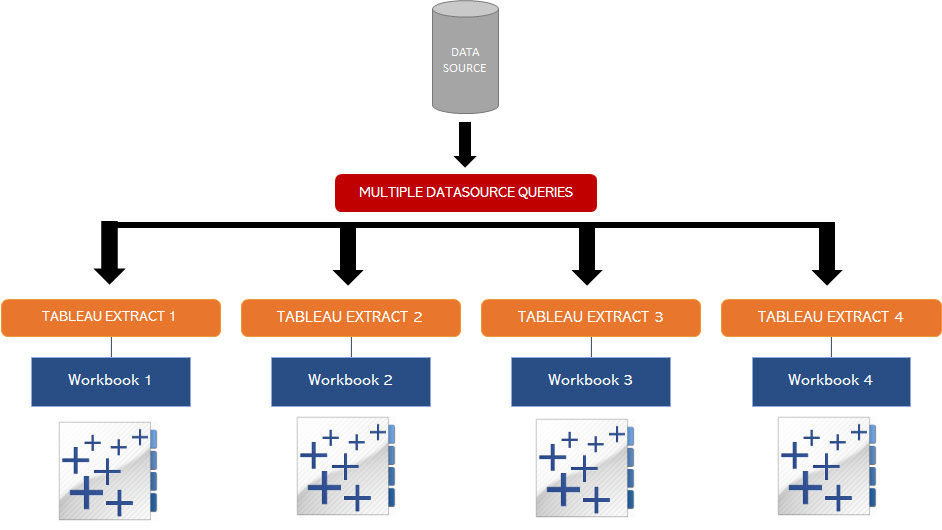
Querying Inefficiencies and Inconsistencies
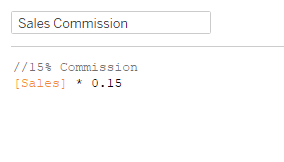
In addition to this, on day 3, User 1 goes into her dashboard and creates the following calculation for Sales Commission, and uses this figure on a dashboard:
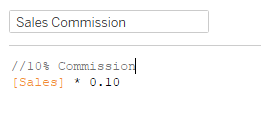
Unknown to each other and not to be outdone User 2, goes in and creates the same calculation, but uses a rate of 15%, and uses this figure on a dashboard:
User 1 and User 2 have the same boss, who looks at both User’s dashboards. The boss is confused. Not only do we have inefficiencies with the querying of the same data, but now we have inconsistencies in the actual data.
This is where a Tableau Published Data Source can help.
What is a Tableau Published Data Source?
A Tableau published data source is a centralized source that allows users to share data connections that they have defined. The Tableau source establishes a single source of truth and allows users to have confidence in the extracted data they are analyzing.
Understanding a Tableau Published Data Source
The best way to understand a Tableau Published Data Source is to look at an example scenario:
Two Options for Data Extracts Management
In this situation, there are two options to manage and maintain consistent data extracts:
How a Tableau Published Data Source Works
A Tableau Published Data Source does start with a data extract, but once all the checks have been made, it needs to be published to Tableau Server or Tableau Cloud:
2. The data source now becomes available on Tableau Server. If the user has permission they can even create a Workbook using web edit with that data source.
However, if you’re using Tableau Desktop to build your Dashboards, then you can connect to the data source.
3. So now, User 1 and User 2 can connect to this new Verified Data Source and use it as an established single source of truth of the data.
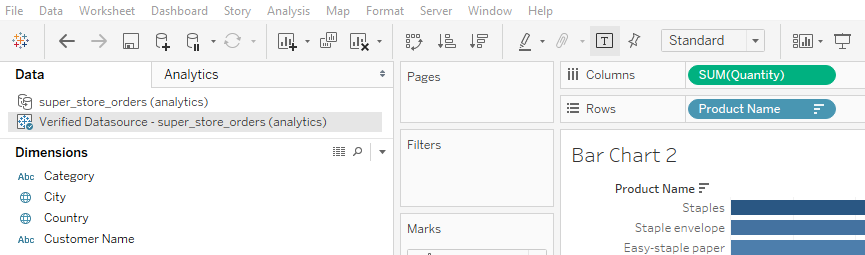
The data pipeline has also been made more efficient as the data source is refreshed once from PostGreSQL, not by every workbook that is connected to it. The pipeline from PostGreSQL to Dashboard now looks like this:
Certify the Published Data Source
As an additional step, you need to verify that the data source is indeed the source of truth. User 1 or User 2, or even their Boss, if permissions allow, can certify this Published Data Source by:
2. Certifying the data source puts a little green tick on the icon:

Other users can then be confident about using this Data source.
Data Quality Warnings
Users with appropriate permissions can also place warnings on Published Data Sources. This can be useful during periods when the data source might be going through changes:
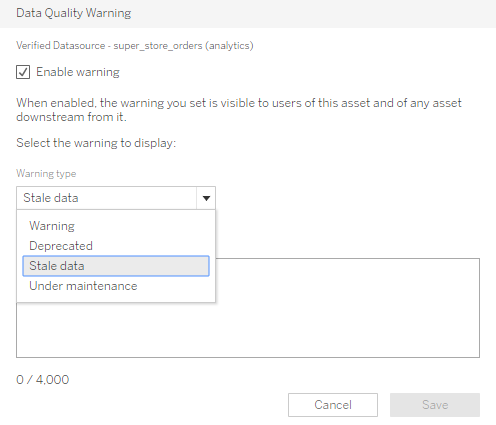
If a Published Data Source has a warning on it, any attempt to connect to it, displays a warning:
Best Practices for Maintaining Tableau Published Data Sources
It does take some extra management to maintain a Tableau Published Data Source. At Zuar, the recommended practice is to separate the Published Data Source workbook from the workbook that is intended to be worked upon.
Common Pitfalls of using Tableau Published Data Sources
There are several common pitfalls of using Tableau Published Data Sources that you should be aware of before adopting them into your system:
Tableau Workbooks and Sheets
Tableau workbooks are where you are going to store your collections of data. Worksheets contain data sets within the workbook. The dashboard is where you can view a collection of data from multiple worksheets.
A “story” includes an organized series of worksheets or dashboards that contain data sources that relate to each other. Tableau workbooks are a great way to keep all of your data sources and extracts organized for maximum efficiency.
Tableau Data Extracts vs. Tableau Data Sources
There is a place for both Tableau extracts and Tableau Published Data Sources. It just depends on the use case.
Data Extracts
Data extracts are essentially a snapshot that is saved to your system memory and can be recalled quickly for visualization. This offers a much faster access to your workbooks.
Tableau Published Data Sources
Tableau Published Data Sources are a great way to centralize data, establish a single source of truth, and allow users to have confidence in the data they are analyzing.
These Tableau Data Sources offer real time-updates for your data, but the information is pulled straight from the database instead of your local memory; the performance usually isn’t as fast as Tableau extracts.
| Criteria | Tableau Extracts | Tableau Data Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Snippets of data | Centralized Data |
| Performance | Faster because data is saved in memory | Slower because pulling data from database |
| Speed | Faster access to workbooks | Real-time updates for data |
| Trusted Sources | Snapshot of some data | Single source of truth for all data |
Still confused about Tableau extracts and data sources? Get in touch with Zuar today!
Learn about our Portal products for Tableau:
*Generally a Tableau Extract is used for large data sources. Live connections can be used with small (or optimized) data sources.
References:
Sign up for more like this. Our Guarantee: we email infrequently and a single click will unsubscribe you.
Reverse ETL vs. ETL vs. ELT
Learn about the key differences between ETL, ELT, and Reverse ETL and how they can be leveraged in your data integration strategy.
Customer Success Manager (CSM)
Zuar is hiring our first Customer Success Manager!
What is Google Cloud Composer?
Get an overview of Google Cloud Composer, including the pros and cons, an overview of Apache Airflow, workflow orchestration, and more.
Sources of Information
Introduction- Literature of a Subject is its Foundation. It represents a record of achievements of human race. Literature is diverse, Complex and multilingual in nature. It is becoming more and more inter-disciplinary. It is growing at a fast pace. In sciences, it is almost doubling itself in every very few years according to some studies. In social Sciences, it is doubling at the rate of every eight to twelve years. Literature serves the informational needs of various kinds of Users. It forms source of Information. Traditionally Specking, information Sources would include primarily books, periodicals and newspapers. However, the number and forms of source are continuously increasing. In addition, unpublished sources are becoming increasingly important to scholars. Occasions will arise, especially in a special library of University library, when information would be required by a user without precondition about the form of document. In such a situation, what matters is the finding of information not the sources of information.
What is source- Source means the origin of something?
What is Information Source:
An Information Source is a source of information for somebody, i.e. anything that might informs a person about something on provide knowledge to somebody. Information sources may be observations, people speeches, documents, pictures, organizations etc.
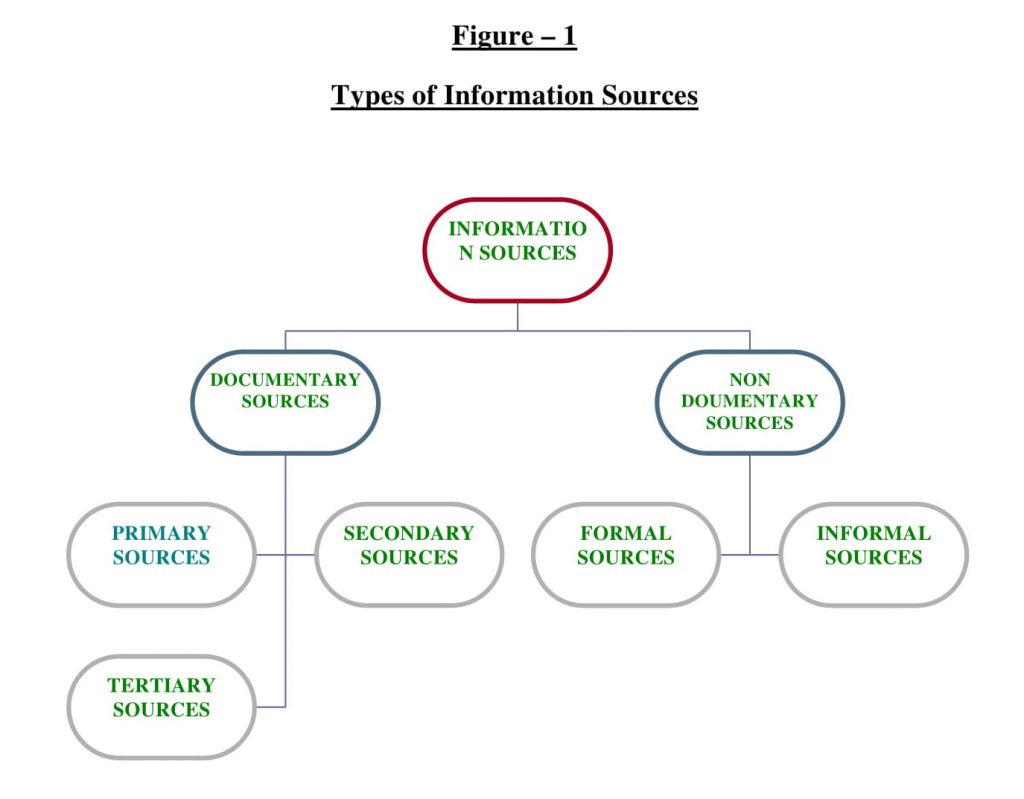
Types of information sources:
Different epistemologies have different views regarding the importance of different kind of information sources. Empiricism regards sense data as the ultimate information sources, while other epistemologies have different views (Kragh 1989)(4. The various types of information sources can be divided into two broad categories.
A) Documentary Sources
B) Non-Documentary Sources
1. Documentary sources:- These are generally published or recorded documents of knowledge. Documentary sources may be as under:-
1.1 Primary Sources of Information:- Primary sources of information are the first published records of original research and development or description of new application or new interpretation of an old theme or idea. There are original documents representing unfiltered original ideas.
These constitute the latest available information. A researcher producing new information can make it available to the particular community through the primary sources. Often, it may be the only source of information in existence. Primary sources are unorganized sources, which are rather difficult to use by them, the secondary sources helps us to use these. These are important sources of information. A subject becomes a discipline in its own right when independent primary sources begin to be produced in that area. The rate of growth of a discipline to a large extent depends upon the amount of literature being produced in the form of primary sources reporting development in the concerned field.
Primary source is a term used in a number of disciplines to describe source material that is closest to the person, information, period or idea being studied.
In historiography, a primary source (also called original source) is an artifact, a document, a recording, or other source of information that was created at the time under study. If created by a human source then a source with direct personal knowledge of the events being described.
It serves as an original source of information about the topic. Similar definitions are used in library Science, and other areas of scholarship.
In journalism, a primary source can be a person with direct knowledge of a situation or a document created by such a person. Primary sources are distinguished from secondary sources, which cite, comment on, or build upon primary sources. Though the distinction is not a sharp one. “Primary and secondary are relative terms, with sources judged primary or secondary according to specific historical contexts and what is being studied.” (Kragh 1989)
➢ Industrial and trade literature
> memorandum
> Laboratory notebooks
> Diaries
> Company
> Files
> Portraits
> State Papers
➢ Web sites
➢ Video Recordings
> Speeches
> Works of Arts, architecture,
> literature and music.
1.2 Secondary Sources of Information:- Secondary sources of information are those which are either compiled from or refer to primary sources of information. The original information having been casually modified selected or reorganized so as to serve a definite purpose for group of users. Such sources contain information arranged and organized on the basis of some definite plan. These contain organized repackaged knowledge rather than new knowledge. Information given in primary sources is made available in a more convenient form. Due to their very nature, secondary sources are more easily and widely available than primary sources. These not only provide digested information but also serve as bibliographical key to primary sources of information. The primary sources are the first to appear, these are followed by secondary sources. It is difficult to find information from primary sources directly. Therefore, one should consult the secondary sources in the first instance, which will lead one to specific primary sources.
Types of Secondary Sources of Information:
“Bonn” has divided the secondary sources into three types which are as below
(c) Indexing periodicals
(d) Abstracting Periodicals
3. Reference Type:
(c)Hand book, Manual
(d) Critical Tables
Important ones are Discussed below:-
1. Periodicals:- All periodicals do not report original work. There are a number of periodicals which specialize in interpreting and providing opinions on developments reported in primary sources of information. Such periodicals may be considered secondary sources.
e.g. New Society (1962). London: New Science Application. Weekly.
2. Indexes:- An Index to a work contains an alphabetical list of names, topics, places, formulae, titles of any significant item referring to material presented in the main part of the work. Sometimes, these items may be arranged chronologically, geographically or in some other way. A well compiled index adds to usefulness of a work.
e.g. Index of Economic Journals(1961-62).Homewood III. Irwin : American Economic Association. 5 Vols.
3. Bibliographies:- A bibliography is an organized list of primary or other sources relating to a given subject or person. It is usually arranged alphabetically by author or chronologically or topic wise. It may be comprehensive or selective. Sometimes it may be provided with annotations. It may be published as a part of a larger work or as a separate work. The basic aim of a bibliography is to assist the users in locating the existence of or identifying a book or any other material which may be interest to him. A well prepared bibliography provides a definite coverage of documents over a period of time within specified limits. Thus, it also serves the purpose of retrospective searching of literature.
e.g. Griffith, Dudley David (1955), Bibliography of Chaucer, 1908-53. Seattle: University of Washington Press.
4. Indexing Periodicals:- An Indexing Periodical is a regularly issued compilation of titles of articles that appear in current primary source journals. Generally, titles of new books pamphlets etc. are also included. An index to a publication contains an alphabetical list of names, topics, places, formulate, titles of any significant items referring to material presented in the main part of the work. These items are arranged chronologically, geographically or in some other way. An indexing periodical is a regularly issued compilation of titles of articles that appear in current primary source journals, generally titles of new books, pamphlets are also included.
5. Abstracting Periodicals:- Abstracts appear in different formats. The best known format for abstracting services is periodical. An abstracting periodical ” is a regularly issued compilation of concise summaries of (i) significant articles (often in a very limited subject field) that appear in current primary sources journals and (ii) important new research monographs, reports, patents and other primary source publication in that field.”(Bonne, George S.1971) An Abstracting Periodical serves as an index, a tool for retrieval of information on a specific subject. However indexing periodicals are earlier to appear than abstracting periodicals.
6. Reviews (Survey Type):- A review is a survey of the primary literature. It aims to digest and correlate the literature over a given period. It also indicates the development and trends in the field concerned. It may appear as a collection of papers on regular basis (annual or quarterly or monthly) or in the form of an article in a periodical. A review provides background information to a new problem in a suitable form and serves as a key to literature. List of references given in a review can serve as an excellent bibliography of the concerned subject for a period covered by it,
e.g., Annual review of biochemistry (1932) Palo Alto: Annual Reviews. Annual.
7. Reference Books (also considered tertiary):- Reference works, which contain the desired information itself, are considered secondary sources of information. These include encyclopedias, dictionaries, handbooks, tables, formularies, etc. these form an essential part of secondary sources of information. The sources of ready reference books are as follows:-
(a) Dictionaries: A dictionary is a book, which deals with words of a language or of some special subjects, authors, etc. Thus a dictionary is a wordbook. Although a dictionary is supposed to deal with words but often it may go beyond this.
e.g. Websters third new International dictionary of English language unabridged with seven language dictionary (1966). Spring field: mass, Marriam.
(b) Encyclopedias (also considered tertiary): An encyclopedia is a book giving information on all branches of knowledge or a specific subject. It is an ideal book, which deals with concepts. An encyclopedia is a storehouse of knowledge giving all information of significance. However, it is best used for finding answers to background questions related to general information and self-education. One often turns to encyclopedias for one’s everyday information requirements. This is also true of scientists and technologists.
e.g. Encyclopedia Americana (1976). New York: Grolier. 30 vols.
(c) Handbook: A handbook is a compilation of miscellaneous information in a compact and handy form. It contains data, procedures, principles, including tables, graphs, diagrams and illustrations. Scientists and technologists use handbooks in their fields rather frequently.
e.g. Britain, (1948/49) an official handbook. London: stationary office, annual.
(d) Tables: Many of the handbooks contain data in the form of tables. Some of the handbooks devote substantial portion of the work to tables as compared with text. Tables are convent form to present data. There are extremely useful in Science.
e.g. Tables of contents and numerical data (1947). Oxford: Pergamon Press.Vol.1
(e) Manuals: In common practice, a manual is an instruction book, which instructs how to do something by means of specific and clear directions.
e.g. Greenly, R.S.(1974). Professional Investor’s Manual. London: Greenly.
(f) Magazine and newspaper articles (this distinction varies by discipline): A news article is an article Published in a print of Internet news medium such as a newspaper, newsletter news magazine, news oriented website, or article directory that discusses current or recent news of either general interest (i.e. daily newspapers) or on a specific topic (i.e. political or trade news magazines, club newsletters, or technology news websites).
(8) Text Books (other than fiction and autobiography): A textbook is a book of instruction. Its Primary aim is not to impart information about a specific subject but to enable one to develop proper understanding of the subject. Presentation is extremely important and it is prepared to serve a particular level of readership. It cannot be comprehensive. Often presentation is colorful and attractive, giving plenty of illustrations and diagrams. A good textbook takes into consideration the method of teaching and level of readership. It is revised keeping in view new developments and changing methodology of teaching. There is a difference of opinion about the place of text books as tertiary sources.
e.g. Text Book of Crop Production, by P.C. Rahaja, etc Bombay.
(9) Translations: Translations are an important part of secondary sources. Their characteristics are the same as those of primary or secondary or tertiary sources from which these are translated. Many of the authors of research papers prefer to cite original sources rather than translations.
(10) Treatises: A Treatise is a comprehensive compilation or summary of information on a subject. A treatise on a subject provides enough information to a person to acquire basic knowledge, so essential for carrying out advanced research. It also provides facts, along with discussion. The fact may include physical constants methods of preparation and purification of compounds etc. Usually, it is limited to a broad field. Due to the very nature, these become out of date within a short period of time.
e.g. Treatise on the calculus of finite differences(1960). 4th ed. New York: Chelsa.
(11) Monographs: A Monograph is a short treatise on a specific subject. A monograph and treaties serve the same purposes with the difference that a monograph is an attempt on a limited scale. Very often a monograph may be brought out as a part of a series.
e.g., Baldwin, E. (1971). Study In The History Of Ideas (Monographer in arts and archeology series, 25). Princeton, N.J: Princeton university press.
(12) Biographical words: A biography is a description or account of someone’s life and the times, which is usually published_in the form of a book or an essay, or in some other form, such as a film. An autobiography (auto meaning “self’, giving “self-biography”) is a biography of a person’s life written or told by that same person. A biography is more than a list of impersonal facts (education, work, relationship, and death), it also portrays the subject’s experience of those events. Unlike a profile or curriculum vitae (resume), a biography presents the subject’s story, highlighting various aspects of his or her life, including intimate details of experiences, and may include an analysis of the subject’s personality.
(13) Literary criticism: It is the study, evaluation, and interpretation of literature. Modern Literary criticism is often informed by literary theory, which is the philosophical discussion of its methods and goals. Though the two activities are closely related, literary critics are not always, and have not always been, theorists.
1.3. Tertiary Sources of Information:- This is the most problematic category of all. However, people rarely expected to differentiate between secondary and tertiary sources. Materials in which the information from secondary sources has been digested- reformatted and condensed, to put it into a convenient, easy to read form. Sources which are once removed in time from secondary sources and works which index, organize and compile citations to, and show you how to use secondary sources.
Tertiary sources of information contain information distilled and collected from primary and secondary sources. The primary function of tertiary sources of information is to aid the searcher of information in the use of primary and secondary sources of information. Most of these sources do not contain subject knowledge. Due to the increase in literature, tertiary sources are becoming increasingly important. Out of the various kinds of sources, tertiary sources are the last to appear.
1. Bibliography of Bibliographies
2. Directories and yearbooks
3. Guide to literature
4. List of research in progress
2: Non-documentary sources: Non documentary sources of information form a substantial part of communication especially in science and technology. User’s studies have underlined the importance of such sources. These sources provide information which other sources do not.
Types:- There are two kinds of sources:-
(1) Formal Sources:-
(2) Informal Sources:-
– Conversation with colleges
– Attendance at Professional Meetings.
Conclusions:- The above categorization is based on the characteristics of the documents. Primary sources are more current and accurate than secondary and tertiary. In searching for Information, a researcher usually starts with secondary and tertiary sources and ends the search with primary sources. Secondary and tertiary sources contain information in organized form and these serve as guides or indicators to detailed contents of primary literature. With increasing amount of literature being produced, it is becoming almost impossible to use primary sources directly for searching of information. A scholar would also not be able to keep himself up to date and well informed in his field of specialization without the aid of secondary and tertiary sources. This goes to show the importance of there sources of information.
Original Reference Article:
Different kinds of sources
For writers who make use of previous research, it is important to be able to distinguish between different kinds of sources and knowing whether they are useful or not. If you are a student and have been asked to locate sources for an assignment, for instance, you need to know what kinds of sources you have found in order to know if they can be used.
On this page, we explain different kinds of sources and how to find out whether they are reliable or not.
Source and reference
The source is the text or other work that provides the information that is being used, whereas the actual mention of the source that is being used is called a reference. To some extent, these terms are synonymous; in several reference styles, the list of sources used in an academic text are called References, for instance. When discussing the actual function of the reference in the written text, however, it may be useful to distinguish between the two terms.
In order to use sources efficiently and in a correct manner, you must be able to identify the nature of each source and the reason for using it. By clarifying to yourself what kind of use you make of different kinds of sources, you will be able to distinguish between your own contribution and the argument expressed by the sources that you use.
It should be noted that the distinctions that are made below may be more relevant in some fields than in others. If you are a student, discuss the use of sources with your supervisors and with the library staff at your departmental library. Note, though, that all writers need to be aware of the importance of originality, in the sense of first-hand results, in scholarly writing.
Common forms of publication
Research writing is published in various forms. Depending on discipline, some publications forms are more common and relevant than others. Here we list some common types of publications:
Anthology / edited volumes
An anthology (or edited volume) is a collection of texts (or other created works) on a specific subject that are published (or otherwise presented) together. Usually, the different chapters in the book will be written by different authors, and there will be an introductory chapter written by the editor(s), providing a general introduction to the contents of the book.
Conference proceedings
Volumes consisting of papers presented at a conference are often referred to as conference proceedings. Such publications usually consist of articles based on the plenary lectures and on a selected number of conference presentations.
Journal / Periodical
A journal (or periodical) is publication that is issued regularly (periodically = ‘at regular intervals’).
Journal article
An article is a text that has been published in a journal (periodical), magazine or newspaper. There are different kinds of articles; apart from original articles (articles that present new, original, research), there are review articles, letters and editorials, for instance. Original articles can be divided into, for instance, methodological articles, theoretical articles and case studies. For further information about different kinds of articles, see
Monograph
A monograph is a text (often book-length) that treats one specific subject.
Thesis / Dissertation
A thesis (dissertation) is an extensive research paper that is written as partial fulfilment of an academic degree.
Thesis of dissertation? Most reference style manuals have been published in the US and therefore use the American English ‘dissertation’ for ‘doctoral dissertation,’ whereas the word ‘thesis’ or ‘doctoral thesis’ is more common in British English.
How to choose sources
One of the central learning outcomes of university studies is the ability to assess information. When writing, students train their ability to decide whether a source is appropriate and how to use it. Read more here:
Remember that LU Libraries provide valuable resources for LU students in need of help concerning the choice of sources. Faculty and department libraries provide support geared to students’ subject areas.
Primary, secondary and tertiary sources
Sources are sometimes divided into three types, depending on the way in which they relate to the subject of study:
Primary sources
A primary source is usually a document or result that is being reported first hand. In other words, primary sources are original sources, not interpretations made by someone else. The following kinds of texts/sources often function as primary sources:
Secondary sources
Secondary sources are texts that value, discuss or comment on primary source materials. Previous research in the field is often defined as secondary sources. The following are examples of such secondary sources:
Tertiary sources
A tertiary source is a source that summarises or compiles facts and knowledge produced by someone else. Tertiary sources are often some kind of assemblage of primary and secondary sources. They are convenient for quick access to summarised facts, but not all sources that belong to this category are considered suitable for scholarly writing. In most cases, it is not acceptable to use compilations of facts instead of reading the original sources, for instance. Therefore, students writing essays are recommended to consult their teachers and library on the suitability of using tertiary sources in their writing. Sources that would be regarded as tertiary sources include:
A note of caution
The distinction between primary, secondary and tertiary sources is not a fixed one. For instance, in an analysis of an encyclopaedic article, that article would be regarded as a primary source, whereas it in another context would be seen as a tertiary source. Students are advised to check with their teachers what types of sources are expected and accepted.
Academic Sources: Here Is How You Find the Best!
You may not be aware of this yet, but academic sources are very important to students of all ages. When you need to write an essay on a complex topic, you need to support all your statements and ideas with accurate information. And where does this information come from? Well, from various sources, of course! While there are plenty of examples of academic sources, some sources are better than others.
Keep in mind that you have to list the resources you’ve used to conduct the research and to write the academic paper in the Bibliography or Works Cited section. And we can assure you that your professors really do check your academic sources. Your grade depends on them in large measure actually.
Table of Contents
What Are Academic Sources And Why Do You Need Them?
Let’s start with the beginning. What are academic sources? It’s relatively difficult to give you a very specific academic sources definition because there are many different opinions on what an academic source really is.
If you are wondering “what are scholarly sources?”, you now have your answer. “Scholarly sources” is just another name for academic sources.
Various Types Of Academic Sources
There are various ways to source data for your academic research paper. When working on an essay, you can use information from peer reviewed sources, academic journals from sites like Science Direct, DOAJ (directory of open access journals) and even from non scholarly sources. Very few professors demand that you use only information from scholarly works. Something you need to keep in mind is that there are several types of academic sources. Here are the main resources of information you can use as a student researcher:
What is a primary source? A primary source is also referred to as “raw data.” These are the resources that are original and that are the basis for all the other sources. In other words, these are all original written works that have been published in academic journals and publications. Furthermore, primary sources are direct information, they are also freshly collected data for the purpose of research. For research purposes, primary data provides a researcher with the exact information they are sourcing for. But, aside from this, gathering primary data requires a lot of input before you can access needed information. This is to say that primary sources require effort before they can be accessed.
There are so many primary source examples a researcher can explore. Some of them include:
What is a secondary source? Apart from primary sources, another way to source data is through a secondary source. Secondary sources are data previously or originally obtained from a primary source. Secondary data relies more on analyzing original sources for the purpose of information. Many researchers prefer using a secondary source for collecting data mostly due to the ease in accessing this information. When using a secondary source for research, it is important that these sources are accurately referenced; else, it will be regarded that the research is plagiarized. There are so many secondary source examples for the purpose of research. They include:
What is a tertiary source? These resources normally contain both the primary and the secondary resources. In other words, tertiary sources can be abstracts that summarize sources, indexes that organize sources, and even databases (these are basically online indexes, but they may include an abstract for each work). Other tertiary source examples include:
But why are scholarly sources more appropriate for academic research? Do you always have to use information from primary, secondary or tertiary resources? Truth be told, it is a good idea to use these as your research source. However, it is perfectly OK to use information from other sources as well, as long as they are credible and accurate. In most cases, you can use sources that come from experts in the field without any problems.
Websites like Wikipedia, on the other hand, are not suitable for academic research. Why? Because they are user-maintained and users are not always experts. The information you find on such sites is generally unacceptable and cannot be used as academic sources in an academic paper.
But why are scholarly sources more appropriate for academic research? Do you always have to use information from primary, secondary or tertiary resources? Truth be told, it is a good idea to use these as your primary source. However, it is perfectly OK to use information from other sources as well, as long as they are credible and accurate. In most cases, you can use sources that come from experts in the field without any problems.
Websites like Wikipedia, on the other hand, are not suitable for academic research. Why? Because they are user-maintained and users are not always experts. The information you find on such sites is generally unacceptable in an academic paper.
Here Is How You Find the Best Academic Sources
There is a lot of misinformation on the Internet regarding where to find academic sources. Many companies will have you believe that the only way to get access to quality sources is to buy their subscription. Some people will tell you that you need to go to the local library if you need quality material. But it’s not that difficult. Here is how to find academic sources quick and easy:
There are also databases from where you can download a long list of academic sources. However, in most cases an academic sources database like ProQuest, Scopus, Web of Science, The McQuade Library, EBSCOhost, or INFOTRAC will ask you to get a paid membership. And the membership can be quite expensive, unfortunately.
What Are Popular And Scholarly Academic Sources
When conducting research, especially, when you are searching for secondary sources, you’ll often come across popular sources.
Difference Between Scholarly and Popular Sources
The major difference between scholarly and popular sources is the validity of the available information. For the purpose of research, it’s academically advised to rely more on scholarly sources.
Between scholarly and popular sources, which is the best? It depends on what type of paper you need to write and what you need to write about. In most cases, popular sources are perfectly acceptable and your professor will not have any objections. However, remember to avoid user-maintained websites like Wikipedia because the information is not accurate in many cases. If you can find high quality scholarly sources, it is best to use them. It is important to find something trustworthy and reliable, especially if you’re writing a thesis and writing dissertation literature review for it.Your professor will surely appreciate it and you will most likely be rewarded with some bonus points.
Below is a table outlining the characteristics of popular and scholarly sources.
| Scholarly Sources | Popular Sources | |
| Author | Scholars and researchers usually within the academia. | Content writers, staff writers, anyone who researches information to publish online. |
| Documentation Source | Valid references, bibliographies and all cited sources. | Often without a known or acknowledged source. |
| Editorial Process | Peer reviewed by research experts within the academia. | Mostly reviewed on a surface-level by an in-house editor. |
| Purpose | To contribute to research study and provide solid knowledge and findings in an academic area. | MTo provide quick-access information on a particular subject. |
| Article Structure | Starts with an approved proposal. Abstract, literature review, methodology, objectives, results and findings, references. | Mixture of short or long-form articles. |
| Publication Frequency | Quarterly, Bi-monthly, Annually | Daily, weekly, monthly |
| Titles | Academic-based | Less wordy, usually straightforward |
| Language | Follows an academic writing style of formal and complex writing style. | Simple, easier to read and less formal. |
| Target Audience | Academics, scholars, researchers, lecturers | General audience |
| Research Value and Relevance | Contributing to existing studies and research. | Provision of information on current topics. |
Now that you know what scholarly sources are and where you can get academic peer reviewed sources from, it’s time to discuss another way to get access to the resources you need. Instead of paying for memberships and searching for hours on various search engines, why not let an expert handle it for you? An academic writing company usually has paid memberships with most databases and online libraries. Their academic writers are using these resources to write the essays for their clients, of course.
Need Help With Writing Your Thesis?
Still wondering “what are peer reviewed sources”? Or “I still need to do my thesis…” Need help finding the best resources on the Internet quickly? If the deadline for your academic paper is tight, you need to take action right away. You don’t need to spend a lot of money on various premium subscriptions and you definitely don’t have enough time to search everywhere for the academic sources you need. This is why your best option is to get in touch with a reliable academic writing company and ask their writers to prepare a list of scholarly sources ASAP. And the good news is that you can also get some writing assistance at the same time. If you need it, of course.