What is bill of landing
What is bill of landing
Bill of Lading
What Is a Bill of Lading?
A bill of lading (BL or BoL) is a legal document issued by a carrier (transportation company) to a shipper that details the type, quantity, and destination of the goods being carried. A bill of lading also serves as a shipment receipt when the carrier delivers the goods at a predetermined destination. This document must accompany the shipped products, no matter the form of transportation, and must be signed by an authorized representative from the carrier, shipper, and receiver.
Key Takeaways
Bill of Lading
Understanding Bills of Lading
The bill of lading is a legally binding document that provides the carrier and the shipper with all of the necessary details to accurately process a shipment. It has three main functions:
As an example, a logistics company intends to transport, via heavy truck, gasoline from a plant in Texas (shipper) to a gas station in Arizona (recipient). A plant representative and the driver sign the bill of lading after loading the gas on the truck. Once the carrier delivers the fuel to the gas station in Arizona, the truck driver requests that the station clerk also sign the document.
Every business needs to have internal controls in place to prevent theft. One key component of internal control is the segregation of duties, which prevents one employee from having too much control within a business. No two internal controls systems are the same. However, most follow a standard set of core philosophies that have become standard management practices. Implementing internal controls can help streamline operations and prevent fraud. A bill of lading is one of several key documents that must be properly managed and reviewed to prevent asset theft.
Types of Bills of Lading
There are several types of bills of lading. Some of the most common include:
Choosing the appropriate bill of lading is essential. For example, doing so can either prevent delivery delays or help locate goods that get lost during transport.
Bill of Lading Example
Assume, for example, that XYZ Fine Dining receives shipments of fresh meat and fish five times a week. The restaurant manager determines the type and amount of meat and fish that the restaurant needs to order. They then fill out a purchase order (PO), and XYZ’s owner reviews and initials each PO before it is emailed to the food vendor. The vendor gathers the meat and fish and signs a bill of lading along with a representative from the overnight carrier.
Next, the carrier delivers the food to the restaurant, and the manager compares the information on the bill of lading to what was requested on the PO. If the information matches, the PO and the bill of lading are sent to the owner, who reviews the documents and writes a check payable to the food vendor.
In this example, the owner does not issue a check to the vendor without reviewing the purchase order and the bill of lading. This step ensures that XYZ pays only for what it ordered and received. If the two documents do not match when the restaurant manager compares them, the manager will ask the vendor about the exception. A third employee reconciles the bank statement and makes company deposits. All of these steps must be in place to prevent theft.
Why is a bill of lading important?
The importance of a bill of lading lies in the fact that it’s a legally binding document that provides the carrier and the shipper with all of the necessary details to accurately process a shipment. This implies that it can be used in litigation if the need should arise and that all parties involved will take great pains to ensure the accuracy of the document.
Essentially, a bill of lading works as undisputed proof of shipment. Furthermore, a bill of lading allows for the segregation of duties that is a vital part of a firm’s internal control structure to prevent theft.
What is the purpose of a bill of lading?
A bill of lading has three main purposes. First, it is a document of title to the goods described in the bill of lading. Second, it is a receipt for the shipped products. Finally, it represents the agreed terms and conditions for the transportation of the goods.
What is in a bill of lading?
Typically, a bill of lading will include the names and addresses of the shipper (consignor) and the receiver (consignee), shipment date, quantity, exact weight, value, and freight classification. Also included are a complete description of the items, including whether they’re classified as hazardous; type of packaging used; any specific instructions for the carrier; and any special order tracking numbers.
What is a bill of lading vs. an invoice?
A bill of lading is a legal document between a shipper and a transport company (carrier) that spells out the type, quantity, and destination of the goods being transported. An invoice tracks the sale of goods between a buyer and a seller.
The Bottom Line
A bill of lading is a contract issued by a transport company to a shipper that spells out the quantity, type, and destination of the goods being shipped. It serves as a receipt of the shipment and can help prevent the theft of goods being transported. It’s crucial to understand the different types of bills of lading to ensure that the right ones are chosen. If not, your shipment will likely be delayed.
What is a Bill of Lading, and How is it Used in Freight Shipping?
Bonus: Downloadable Bill of Lading Template
Table of Contents
What is a Bill of Lading?
The definition of a bill of lading is a document that is signed by the shipowner or a representative to prove that the vessel or the carrier received the goods. It serves as a contract of carriage, which outlines the shipping details. Lastly, The cargo can be claimed in exchange for the bill of lading as it is considered the title of the goods.
The bill of lading was commonly used as early as the sixteen hundreds by the Spaniards to describe their cargo and the number of bags received by the carrier. By the eighteenth century, merchants had established a refined way of the bill of lading. The bill’s legal ramification has continued in the nineteenth century and has given birth to the modern Bill of Lading that we use today.
The word bill is the statement of charges for either products or services that were rendered by the supplier or service provider to the buyer. Lading means the act of loading cargo into a vessel. Therefore, combined, the Bill of Lading outlines the agreement between the shipper and the shipping line (or carrier). It includes all of the information regarding the goods that are going into the vessel. These details include the classification of the goods, number of cartons, total volume, weight, the ports of loading and destination, the carrier’s name, and the voyage number. The term Bill of Lading is usually abbreviated with either B/L or BOL.
The functions of a Bill of Lading are as follows:
Why Would I Use a Bill of Lading?
The Bill of Lading serves as the document of title of goods. Therefore, for the named consignee to take the delivery of products from the shipping line (or carrier), at least one original copy must be presented. The original copy is used to avoid theft, which could lead to international trade litigation.
The use of the Bill of Lading is not limited to knowing the details of the shipment; it serves as a legal document that can be used for claims if anything undesirable happened during the logistics process.
If the buyer decides to take over the arrangement for the transportation of their goods, instead of using a shipping agent or a freight forwarder to handle both ends, having the original Bill of Lading is necessary. The process will involve the buyer forwarding the copy of the Bill of Lading to the destination port’s selected shipping agent. The shipping agent will then issue a Delivery Order to the port for the release of the goods.
It is still best for the buyer to have a copy of the Bill of Lading for shipments arranged by a freight forwarder on both the origin and destination. Having this will give the buyer the option to cross-reference the shipment information and to confirm if they are correct. In addition, the buyer will also have the ability to trace the vessel’s location using the vessel’s information on the document.
Who Issues a Bill of Lading?
The Bill of Lading document is issued by the carrier or their authorized agent, such as Non-Vessel-Operating Common Carrier (NVOCC), to the shipper to acknowledge that they have received the goods.
There are two kinds of Bill of Lading: The HBL, which is also known as the House Bill and the MBL, which stands for Master Bill of Lading. An NVOCC can only issue an HBL; on the other hand, the MBL is issued by the shipping line upon the receipt of the goods from the freight forwarder. Although NVOCC does not own any vessels, it is considered an actual cargo carrier, as they are regulated both by local and international laws. The original copies of either HBL and MBL are considered legal documents. A freight forwarding company is not always an NVOCC and vice versa. However, there are freight forwarders that are also NVOCC licensed.
The buyer usually gets a copy of the HBL if using a freight forwarding company. The buyer would need the original copy of either the HBL or MBL from the shipper if shipping on certain Incoterms such as CFR (Cost and Freight) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, & Freight). The original copy is necessary because the buyer needs to take over the shipment’s responsibility from the shipper at a certain point. The original copy of the Bill of lading can be presented to the carrier from the port or destination on the contract to get the cargo released. Presenting of the original copy can be skipped if the shipper has organized a Telex Release.
For shipments with the HBL, the shipper can file a telex release application to the NVOCC or freight forwarder to request the release of the cargo to the consignee without needing the original Bill of Lading. The consignee can then arrange the Delivery Order after the release of the goods.
The term Telex Release is being used by the industry wherein the carrier is giving the green light to the destination port to release the cargo without the presence of the original Bill of Lading. The original Bill of Lading needs to be surrendered by the shipper at the origin port, upon the request for a Telex Release.
What Types of Bill of Lading Are There?
Based on history, the Bill of Lading was initially used for sea shipments as it is the common mode of transport during the pre-modern times. However, the Bill of Lading is now being used by other methods of shipments such as rail and inland freight. There are several types of Bill of Ladings, and their individual use depends on whether it is negotiable or non-negotiable or based on the carrier’s responsibility.
Types of Bill of Ladings based on whether it is negotiable or non-negotiable
The main difference between the negotiable and non-negotiable Bill of Lading is the ability to change the consignee or cargo ownership. A negotiable Bill of Lading notifies the carrier to deliver the goods, depending on the endorsement of the shipper. A non-negotiable B/L defines the specific consignee and is non-transferrable.
Straight Bill of Lading
This is a standard B/L, used if the shipment is going to a customer who has already paid a shipment. The shipment can only be received by the consignee and the bill and cannot be transferred.
Order Bill of Lading
This is the type of shipment that is usually used for consignments. The consignee on the record is considered the owner of the cargo unless the consignee has transferred the title of the cargo ownership to another entity by endorsing the Bill of Lading.
Charter Party Bill of Lading
This type of Bill of Lading is used when a shipper, or group of shippers, charter or rent a whole vessel to carry the cargo.
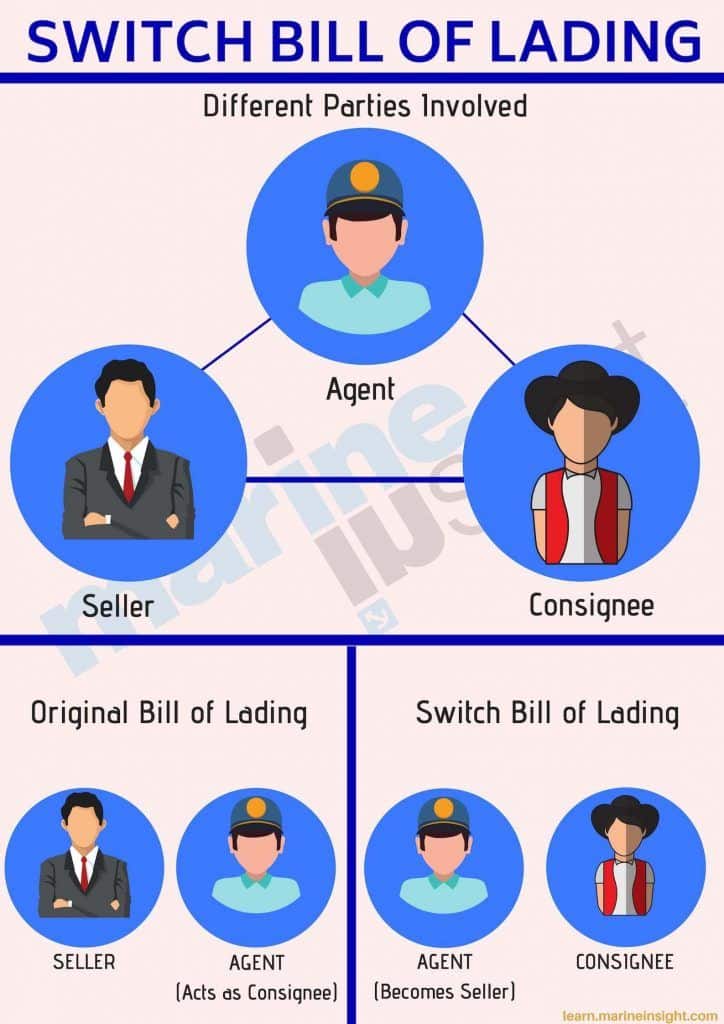
Switch Party Bill of Lading
This Bill of Lading is considered a duplicate. The consignee can request the carrier to switch the Bill of Lading when the consignee does not want to divulge the carrier information to the new consignee or buyer.
This is a non-negotiable document that is only used for cargo that is transferred via air freight. Unlike an ocean’s Bill of Lading, an Air Waybill does not act as a title of goods.
Types of Bill of Ladings based on the carrier’s responsibility
Ocean Bill of Lading
This type allows the carrier to ship the goods domestically or internationally. The carrier’s responsibility starts from the port of origin and typically ends at the port of discharge, stated in the document. This is also known as a port-to-port Bill of Lading.
Inland Bill of Lading
This document shows the information of the carrier transporting the cargo domestically either by road or rail.
Direct Bill of Lading
This is used if the carrier will be the same carrier who will handle the shipment to the final destination. The responsibility of the carrier in this case is from the receipt of the goods until it gets delivered to the final destination.
Multimodal or Combined Transport Bill of Lading
This B/L covers at least two modes of transport. An example is a combination of sea, rail, and road. The carrier can subcontract the other mode of shipment to other carriers.
Through Bill of Lading
This type of bill is very similar to combined transport or multimodal, where there are different legs of shipments. The only difference is that there is no change in the shipping mode (an ocean shipment will remain on the waters) on this Bill of Lading.
Transshipment Bill of Lading
If a carrier doesn’t have a direct service between two ports, a carrier can transship the cargo to another port at the carrier’s expense.
The types of Bill of Ladings could be overwhelming; however, as a buyer, looking to ship cargo, it is not necessary to know all of the types of Bill of Ladings. However, it is best for the buyer to know the Bill of Lading that is applicable to their business.
What’s in a Freight Bill of Lading?
The Bill of Lading contains essential information about the shipment. The buyer is encouraged to know and understand what is on this document. Below are the details that can be found on any Bill of Lading, regardless if it is a House Bill or a Master Bill.
Here’s an example of how an Ocean Bill of Lading on a regular EXW shipment from China to the US.
The steps above are a simple representation of how the Bill of Lading works and how it is being transferred. Freight forwarders can help buyers to streamline those steps and arrange everything that the buyer needs.
Sample Bill of Ladings: Sea Freight and Air Freight
An original Ocean Bill of Lading is a legal document that represents the title of goods and can be exchanged for the possession of the cargo. Although an original Air Waybill has similar details and is considered as a type of Bill of Lading, it doesn’t act as the title of goods.
Below is an example of the common Bill of Ladings: Ocean House Bill of Lading, Master Bill of Lading, and Air Waybill.
Bill of Lading meaning and types used in Global Trade
What is a Bill of Lading in Import, Export and Shipping?
First, a Bill of Lading is a the most important shipping document involved in the import export process. However, some shippers may not understand the bill of lading meaning or the types of bill of lading that are issued along the supply chain. So, in this article we give insight into the bill of lading and the different types of bill of lading used in International trade.
A Bill of Lading (B/L or BoL) document is an extremely important document involved in the shipping and logistics industry. A Bill of Lading is a document that the Carrier of goods issues to the “Shipper” of the goods.
It’s a document to provide evidence or proof of shipment. This is extremely important in International Trade as it provides ‘title’ as to who legally owns the cargo. Moreover, the Bill of Lading acts as evidence of Contract of Carriage, receipt of goods and document of Title to the goods.
Also, the owner of the cargo (the holder of the B/L) has the legal rights to claim the goods or arrange transfer ownership of the cargo to another party in the supply chain.
How to use a Bill of Lading between the Parties involved in Global Trade
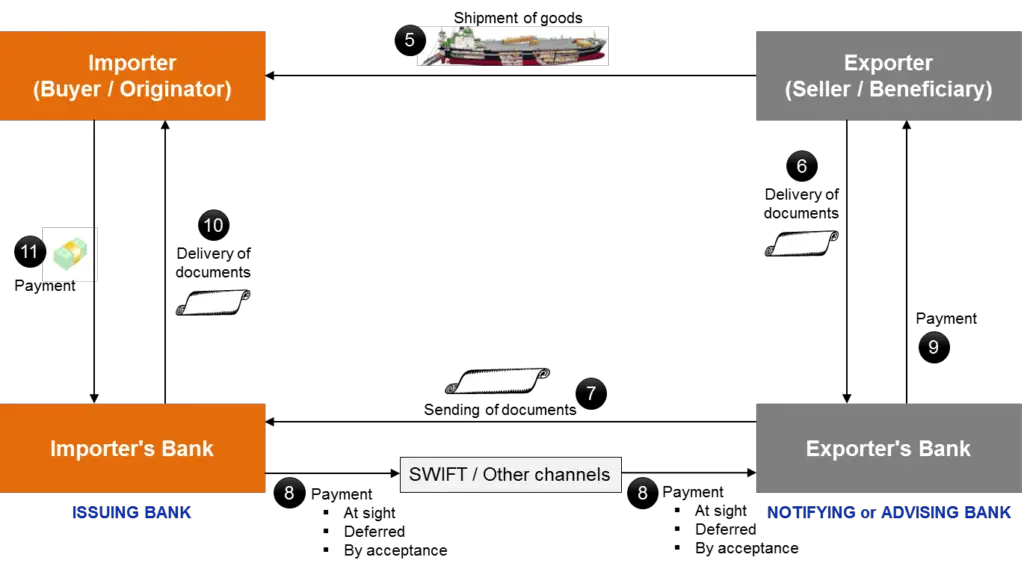
The Bill of Lading is important in International Trade when it comes to the Incoterms® that the goods are sold on and the payment terms agreed between buyer and seller. In alot of cases, buyers and sellers will agree to pay a deposit to the supplier then arrange the balance payment ‘upon receipt of Bill of Lading’.
This means that when the goods have been shipped and the shipper receives the B/L from the carrier (shipping line). The shipper will use this document as security and will only email a ‘copy’ of the Bill of Lading and other shipping documents to the buyer to prove that the goods have been shipped and to request the balance payment. The shipper will hold title to the original Bill of Lading (originals) and therefore legally retain ownership of the cargo. The shipper will use this as security to ensure that they receive the balance payment for the goods.
A B/L is also used when shippers and consignees arrange Letter’s of Credit (L/Cs) with both party’s banks. Letters of Credit are contracts written between the shipper’s bank and the consignee’s bank that will guarantee payment of goods ‘upon Bill of Lading’.
Once the buyer has made the balance payment the shipper will ‘surrender’ the B/L and tell the shipping company to issue an ‘Express Release’ or ‘Telex Release’ Bill of Lading.
This Express Release B/L will allow the title of goods to be transferred to the buyer without the buyer having to actually receive the original B/L documents in the mail. The buyer will use this Express Release B/L to arrange customs clearance and release of their cargo at the port of destination.
Types of Bill of Lading
There are many types of Bill of Lading documents and formats that carriers can issue along the supply chain. Below are a few examples of B/L types:
House Bill of Lading
Surrender Bill of Lading
Straight Bill of Lading
Master Bill of Lading
Blank Bill of Lading
What is the difference between Freight Collect and Freight Pre-Paid?
The B/L will state that the shipment has been sent on ‘Freight Collect’ or ‘Freight Pre-Paid’ terms. These terms relate to which party will be paying for the International Freight costs.
If the shipment is sent Freight Collect – the freight charges will be ‘collected’ by the Consignee. If the shipment has been sent on Freight Pre-Paid terms, the shipper will be billed for the freight charges.
It’s important to note that the carrier must receive payment of the shipping charges (by either party) BEFORE they will release the cargo to the Consignee.
Freight Collect Incoterms® include – EXW, FCA, FAS, FOB
What information is on a Bill of Lading format?
See below Bill of Lading example format.
What is a Bill of Lading (B/L or BoL) in Shipping?
What Is A Bill of Lading?
Bill of Lading Definition
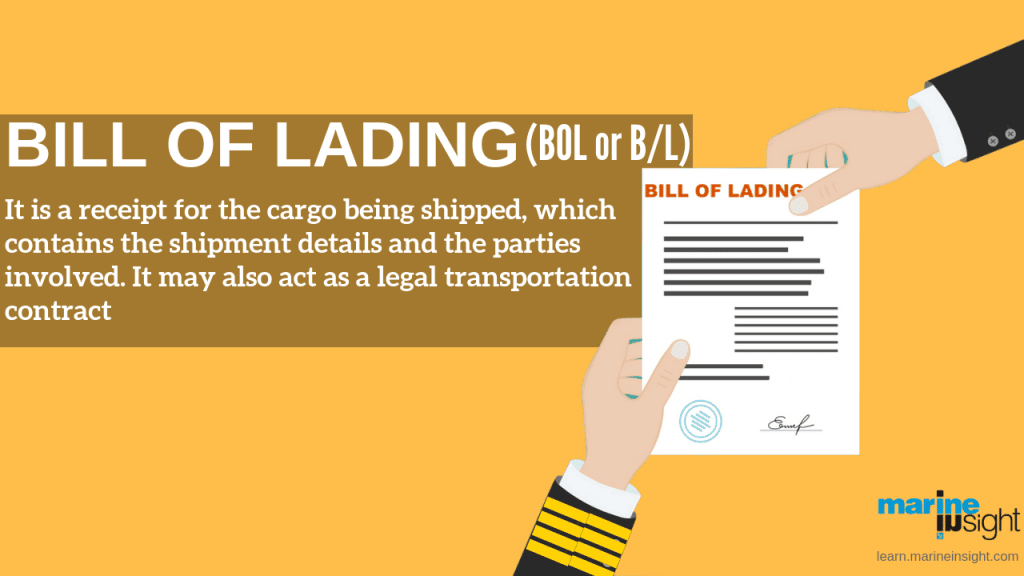
Bill of lading is a document issued by a carrier to a shipper, confirming the particular good that has been received on board as cargo transporting it to a destination and delivering it to the consignee.
The word ‘lading’ means ‘loading’. It refers to the loading of cargo aboard a ship. Simply put, the Bill of Lading or BoL or B/L is a receipt.
The document acknowledges that the carrier (or the agent) has received the goods (cargo or shipment). Though the British term refers strictly to shipping, the American definition is not as strict and can be applied to the transportation of any type of good.
To ship any cargo, a BoL is required and acts as a receipt and a contract. A completed BOL legally shows that the carrier (agent) has received the shipment as described and is now contractually bound to deliver the goods in good condition to the consignee. In a sense, it is a service level agreement between the freight company and the client. In case of a dispute, Bill of Lading becomes a very vital piece of documentary evidence. For this reason, all parties have to ensure that all details are filled accurately with no scope of error.
It is a standard-form document that is transferable by endorsement or by legal transfer of possession.
Functions Of Bill Of Lading
The information in a Bill of Lading (B/L) documents the actions of the carrier throughout the shipment. Information like where the shipment is going, the piece count, how it has been billed, and also how the freight has to be handled on the dock and trailers. It could be on a prepaid or collect basis.
A BoL serves these purposes:
Different Types of Bill of Lading
There are many types of Bill of Lading which can be divided into many 4 main categories.
A) Based on Carrier
1. Master BoL
2. House BoL
It is issued and signed by the freight forwarder.
3. Switch BoL
It is also issued by the carrier or its agent in exchange for the first set of BoL. It cannot be issued until the first BoL is inactive.
B) Based on Payment
1. Straight BoL
This is used when the money for the goods has been paid in advance and so a carrier needs to deliver the correct merchandise to the right party.
2. Bearer BoL
It is a bill stating that delivery shall be made to the party holding the bill. The creation of such a bill may be explicit or if an order bill fails to nominate the consignee then it can be considered as one whether in its original form or through an endorsement in blank. A bearer bill can be negotiated by physical delivery.
3. Order BoL
When shipping merchandise prior to payment, a carrier is required to deliver the merchandise to the importer. Under such a situation order bill lading is used and at the endorsement of the exporter, the carrier may transfer title to the importer. These order bills of lading can be traded as a security or they may be used as collateral against pledged loans.
4. Surrender BoL
Here the importer does not pay the bank until the maturity of the draft under the relative credit which works under the term ‘Import Documentary Credit’. The bank undertakes to remit the payment to the seller on behalf of the buyer. To receive the payment, the seller must present the documents specified in the terms of the documentary credit to its bank during the validity of the documentary credit. This direct liability is called the Surrender Bill of Lading. (SBL).
C) Based on Shipment Condition
1. A Clean BoL
This is one which states that the cargo has been loaded on board the ship in apparent good order and condition.
2. Claused Bill of Lading
It is also known as a soiled bill of lading. Such a bill of lading bears a clause or notation suggesting that the goods were received by the carrier in poor or damaged condition.
D) Based on Mode of Transportation
1. Inland BoL
This allows the carrier to transport the consignment by road, air, or rail across the land.
2. Ocean BoL
It is used when cargo has to be sent overseas across seas.
3. Through BoL
This B/L enables the carrier to carry the cargo across different distribution centers. It can need an inland or ocean BoL
4. Multimodal BoL
It is used in the case where more than one mode of transportation will be used.
Legal Frameworks And Conventions Governing Bill Of Lading
Important Terms in Bill of Lading
Disadvantages of Paper Bill of Lading
Though paper BoL serves a very important role in the shipping industry, it comes with some inherent risks associated with paper system costs, authenticity, and delay. Let’s explore each aspect closely.
2) Authenticity: A BoL can be easily forged due to the sheer number of parties involved and the complex shipping process. This can lead to theft or other illegal things.
3) Delay: BoL is sent using a mail system which is slow compared to the modern transportation system used for cargo delivery. The carrier can only deliver to the cargo when the consignee produces the original BoL. In case of the dealy ion receiving the BoL by the consignee, the carrier has to deliver the goods in return for a letter of indemnity. This adds extra administrative load on the carrier and the liability still hangs on it.
Electronic Bill of Lading
Electronic BoL presents an ideal solution to the disadvantages of a paper BoL but has met some resistance due to various reasons. But slowly, more and more companies and organizations are adopting electronic BoL. In 2015, BIMCO, the world’s largest international shipping association, added an electronic bill of lading clause to its NYPE 2015 time charter form. The International Group of P&I Clubs also gave approval for three electronic trading systems: Bolero, e-title, and essDOCS.
Advantages of Electronic Bill of Lading
The electronic bill of lading or e-bill has the potential to addresses many of the drawbacks of the paper BoL system.
1) Electronic BoL is fast. In fact, electronic BoL can be sent instantly via the internet to any destination which lowers the administrative costs and delays that plague the paper B/L. In the case of multiple transfers of ownership during the transport, an electronic bill of lading can be even more effective
2) In an electronic bill of lading the modifications or corrections can be made very efficiently and cost-effectively as compared to the traditional BoL.
3) Electronic BoL provides a higher level of security which minimizes any chances of forgery. The introduction of blockchain has made this system even more secure and unpenetrable by hackers.
4) As mentioned earlier, paper BoL is very expensive. Electronic BoL saves paper and costs involved in mailing BoL physically to different locations.
Disadvantages of Electronic Bill of Lading
1) A paper Bill of Lading is a physical document of title which can be negotiated and transferred as the possession of the boL is proof of title to the cargo. This is not the case so for Electronic bill legally speaking.
2) Electronic BoL needs to be accepted and adopted by all the parties involved. Therefore, it has taken time to take off.
3) Electronic and internet-based systems are susceptible to hacks, malware attacks, viruses, e-theft, and internet/computer outages.
Why Is Bill of Lading Important?
Particularly related to the case of a buyer, the bill of lading is used as a document of title. Suppose a buyer is supposed to receive goods from a carrier. The bill of lading then acts as the document of title for the goods. Two types of Bill of Lading can be used as a document of title. They are straight bill of lading and order bill of lading.
Legally, a seller cannot sell anything that is not solely entitled to him. So if the goods he is trying to sell turn out to be encumbered, maybe due to mortgage or charge or is stolen property, the bill of lading will prevent him from being granted the full title of the holder.
The Bill of lading can also be used as evidence of a contract of carriage between a carrier and a shipper. Basically, when a bill of lading is used as a cargo receipt, it is issued by the carrier when the goods have been loaded onto the vessel.
Bill Of Lading in Shipping: Importance, Purpose, And Types
If we search the meaning of the term “bill”, it is defined as a printed or written statement of the cost for the goods or services delivered or to be delivered. The term “ lade” means to put the cargo onto a ship or other form of goods carrier.
Thus, a bill of lading in shipping is a record of the traded goods which have been received on board. It is a document that establishes an agreement between a shipper and a transportation company for the transportation of goods. Transportation Company (carrier) issues these records to the shipper.
A bill of lading indicates a particular carrier through which the goods have been placed to their final destination and the conditions for transporting the shipment to its final destination. Land, ocean and air are the means used for bills of lading.
Table of Contents
The Importance of Bills of Lading
The carrier need not require all originals to be submitted before delivery. It is therefore essential that the exporter retains control over the full set of the originals until payment is effected or a bill of exchange is accepted or some other assurance for payment has been made to him.
A bill of lading, therefore, is a very important issue when making shipments to move the cargo or freight from one point to the other. On one hand, it is a contract between a carrier and shipper for the transportation of goods and on the other hand, it serves as a receipt issued by a carrier to the shipper.
Hence, the bill of lading is considered a legal document which provides all the vital details to the shipper and the carrier to conveniently process the freight shipment through different maritime countries and invoice it correctly.
The original copy of the bill of lading is provided to the carrier, and a copy of the same should also be ascribed to the packaged freight.
A blank bill of lading template can be downloaded from this link here.
Negotiable and Non-negotiable bill of lading?
Negotiable bill of lading: In this type of bill, clear instruction is provided to make the delivery of the goods to anyone having the possession of the original copy of the bill, which itself signifies the title and control of the freight. In this type of bill, the buyer/ receiver or his/her agent has to acquire and present an original copy of the bill of lading at the discharge port. In the absence of original bill copy, the freight will not be released.
Non-negotiable bill: This type of bill of lading fixes a specific consignee/name of the receiver to whom the freights will be shipped and delivered. It, however, does not itself serve the ownership of the goods. Under this type of bill, the assigned receiver/ buyers can claim the cargo by confirming their identity.
Purpose of Bill of Lading:
The bill of lading document is meant to act as a transport document enacting as the evidence of the contract of carriage of the goods. A negotiable bill of lading has the following legal qualities:
Types of Bill of Lading
The bill of lading can be classified on the basis of “how it is executed” and “Method of operation”-
On the basis of execution:
1. Straight bill of lading reveals that the goods are consigned to a specified person and it is not negotiable free from existing equities. It means any endorsee acquires no better rights than those held by the endorser. This type of bill is also known as a non-negotiable bill of lading, and from the banker’s point of view, this type of bill of lading is not safe. This type of bill is prominently used for military cargo.
2. Open bill of lading – This is a negotiable bill of lading where the name of Consignee can be changed with consignees’ signature and thus transferred. This can be transferred multiple times. Switch bill of lading is a type of open bill of lading.
3. Bearer bill of lading is a bill that states that delivery shall be made to whosoever holds the bill. Such bill may be created explicitly or it is an order bill that fails to nominate the consignee whether in its original form or through an endorsement in blank. A bearer bill can be negotiated by physical delivery. They are used for bulk cargo that is turned over in small amounts.
4. Order bill of lading is the bill uses express words to make the bill negotiable. This means that delivery is to be made to the further order of the consignee using words such as “delivery to A Ltd. or to order or assigns. The cargo is only delivered to the bonafide holder of the bill of lading, and it has to be verified by an agent who issues delivery order and the verified bill of lading. The order bill of lading:
– is the most modern type bill which is widely used all over the world
– ensures the safety of delivery of cargo to a bonafide holder of B/L
– Since the ship visits several foreign ports where the language, practice, procedures may be different the master might be inconvenienced during the delivery of the cargo. People might fraudulently collect the cargo.
– To overcome this difficulty and avoid future cargo claims and litigations, the consignee or the holder is required to surrender the bill of lading to the ship’s agent at the discharge port who will verify the genuineness of the bill of lading. When satisfied the agent will issue a delivery order and the verified bill of lading. Now any person can collect the cargo from the ship by surrendering the bill of lading and the delivery note to the ship.
As the bill of lading is made to “to order” of the consignee, it is a negotiable instrument of title. This means that the ownership of the bill of lading can be transferred from one person to another by authorising signature and delivery of the bill of lading.
All goods which have not been paid in advance and are shipped under “To order” of the bill of lading can be categorised into two types:
ON the basis of Method of Operation:
Sets of Bill of Lading:
This is an old practice where the bills are signed in the sets of three originals to facilitate the goods are timely delivered even when the original is lost. They are stated as the first original, second original, third original on top of the bill. A duplicate copy with a stamp – “Non-negotiable” may also be distributed.
The master will sign the original bill of lading, and when the master of agent signs the three-bill of lading, all other copies are considered void. This clause is clearly written on the bill of lading which is supplied in sets.
This is a reason why the bank, negotiating a letter of credit that covers the cargo, will always ask for the full set of B/Ls. This is to prevent other B/L holders from legally claiming the cargo before the bank does.
Bill of lading as Contract Of Carriage:
The contract between the carrier and the shipper is already created before issuing the bill of lading when the cargo is loaded on the ship. This is done to safeguard the shipper in case the cargo is damaged before loading it on board the vessel and to help the shipper in the claim process. For the carrier and the consignee, the bill of lading will act as the actual contract of carriage.
The popularly used conventions and rules which covers the contract of carriage for carrying goods by sea :
The convention which governs the contract of the carriage is usually stated in the first page of the bill of lading. Upon booking space for shipment by the consignee the carrier sends a booking confirmation which states Clauses sent by the carrier, it will indicate the terms and conditions that will govern the booking and contract of carriage.
Contents of Freight Bill of Lading:
The bill of lading comprises of the following details:
Bill of Lading Tracking:
Different companies use different forms of bill of lading which makes it difficult to track them unless a specific tracking service is provided by the carrier. There are few companies which tie-up with the shipping carriers to track the bill of lading for easy trade.
Electronic Bill of Lading:
With the modernisation of the shipping industry as a whole, the bill of lading is also modernised to the electronic bill of lading to solve the issues occurring while using a paper bill of lading under the latest iteration of International Group of P&I Clubs. The problem faced when using a paper bill of ladings are:
The paper bill uses printed bills of lading which are both costly. The bill has to be couriered which is an additional cost
– The slow movement of the paper-based bill of lading.
– Carriers are obligated to release the goods only on the production of an original bill of lading, which if not received in time will slow the process.
– The paper bill can be forged, and delivery of goods against a forged bill of lading will lead to a huge loss
Advantages of Electronic Bill of Lading:
Problems with the Electronic Bill of Lading
It is possible to negotiate and transfer the possession of the paper bill as it is the evidence of title of the goods. However, this is not automatically the case with e-bill.
(Source – A paper bill of lading is a document of title, enabling it to be negotiated and transferred as possession of the bill is evidence of title to the goods. This is not automatically the case at law with an e-bill)
If the electronic bill system is not secured, it can be hacked, and the details can be manipulated as per the convenience of the hacker, leading to fraud and loss of cargo
Implementation of electronic bill system across the industry needs consent from all the stakeholder, which will take time.
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendation on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/picture-53886-1440626964-5bfc2a89c9e77c005876da24.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/HeadshotThomasBrock03.08.20-ThomasBrock-924a228f9b25436183c3d61b0fc6f263.jpeg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SuzannesHeadshot-3dcd99dc3f2e405e8bd37271894491ac.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bill-of-lading-01-9ea02358e8a04863b781b4fe33ff809d.jpg)