What is mode in math
What is mode in math
What is mode math?
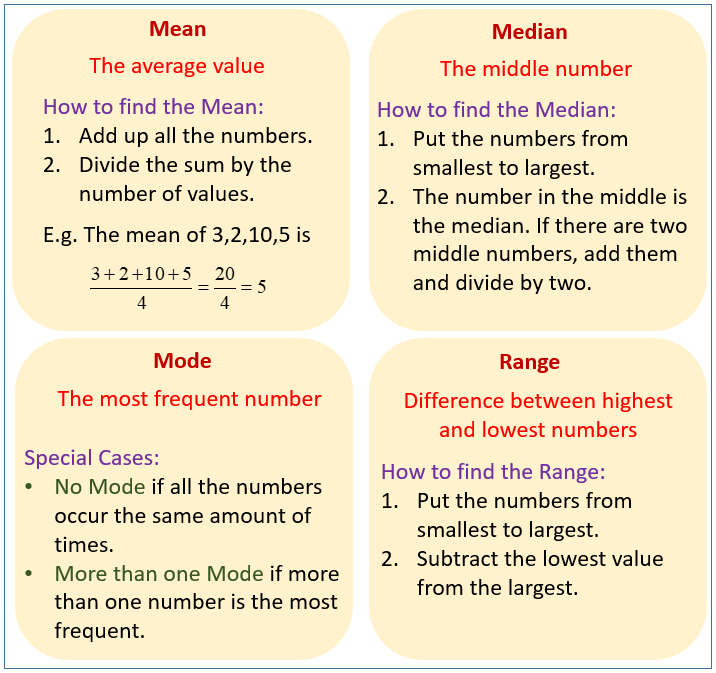
mean, median, and mode, in mathematics, the three principal ways of designating the average value of a list of numbers. The arithmetic mean is found by adding the numbers and dividing the sum by the number of numbers in the list. … The mode is the most frequently occurring value on the list.
Hereof, What is mode formula with example? For example, The mode of Set A = <2,2,2,3,4,4,5,5,5>is 2 and 5, because both 2 and 5 is repeated three times in the given set.
How do you find the mode of a set of data? The mode is the number in a data set that occurs most frequently. Count how many times each number occurs in the data set. The mode is the number with the highest tally. It’s ok if there is more than one mode.
RelatedPosts
What are 3 types of taxes?
How do you find the middle point between two locations?
How do you do staffing projections?
How do you find initial velocity with only time?
Additionally How do you find the mode if there are two modal classes?
How do you solve mean median and mode? The mean (informally, the “average“) is found by adding all of the numbers together and dividing by the number of items in the set: 10 + 10 + 20 + 40 + 70 / 5 = 30. The median is found by ordering the set from lowest to highest and finding the exact middle. The median is just the middle number: 20.
What are the 3 types of mode?
The different types of Mode are Unimodal, Bimodal, Trimodal, and Multimodal. Let us understand each of these Modes.
How do you solve a mode question?
Where is f1 f0 f2 in mode?
Can there be no mode?
There is no mode when all observed values appear the same number of times in a data set. There is more than one mode when the highest frequency was observed for more than one value in a data set.
Also What is the mode of following data? Finding the Mode
To find the mode it is best to put the numbers in order (makes it easier to count them), then count how many of each number. A number that appears most often is the mode.
What is mode in mean?
The mode is the value that appears most frequently in a data set. … Other popular measures of central tendency include the mean, or the average of a set, and the median, the middle value in a set. The mode can be the same value as the mean and/or median, but this is usually not the case.
How do you find the mode in Class 10?
What is the formula of mode Class 10?
| Marks obtained | Number of students |
|---|---|
| 0-10 | 18 |
| 10-20 | 24 |
| 20-30 | 8 |
What is mode vs mean?
The mean (average) of a data set is found by adding all numbers in the data set and then dividing by the number of values in the set. … The mode is the number that occurs most often in a data set.
What are the 5 modes? According to the New London Group, these are the five modes:
How do you find the mode in maths class 7?
What is mode of data?
The mode is the value that appears most frequently in a data set. A set of data may have one mode, more than one mode, or no mode at all. … The mode can be the same value as the mean and/or median, but this is usually not the case.
How do you find the mode of a class? How to find the Mode of Grouped Data?
How many modes are there?
The seven main categories of mode have been part of musical notation since the middle ages. So, the list goes: Ionian, Dorian, Phrygian, Lydian, Mixolydian, Aeolian and Locrian. Some of them are major modes, some are minor, and some are ambiguous.
What is f1 and f2 in mode?
f1 = Frequency of the class preceding the modal class. f2 = Frequency of the class following the modal class.
What does no mode mean? It is possible for a set of data values to have more than one mode. … If there is no data value or data values that occur most frequently, we say that the set of data values has no mode.
What is a modal class?
Modal class or the mode class is the class interval in a frequency distribution table that contains the highest frequency. While calculating the mode in statistics, modal class plays a significant role especially while calculating the mode of grouped data.
How do you find the mode of continuous data?
What is mode math?
mean, median, and mode, in mathematics, the three principal ways of designating the average value of a list of numbers. The arithmetic mean is found by adding the numbers and dividing the sum by the number of numbers in the list. … Tea mode is the most frequently occurring value on the list.
Hereof, What is mode formula with example? For example, The mode of Set A = <2,2,2,3,4,4,5,5,5>is 2 and 5, because both 2 and 5 is repeated three times in the given set.
How do you find the mode of a set of data? The mode is the number in a data set that occurs most frequently. Count how many times each number occurs in the data set. The mode is the number with the highest tally. It’s ok if there is more than one mode.
Related postsPosts
What are 3 types of taxes?
How do you find the middle point between two locations?
How do you do staffing projections?
How do you find initial velocity with only time?
Additionally How do you find the mode if there are two modal classes?
How do you solve mean median and mode? The mean (informally, the “average“) is found by adding all of the numbers together and dividing by the number of items in the set: 10 + 10 + 20 + 40 + 70 / 5 = 30. The median is found by ordering the set from lowest to highest and finding the exact middle. The median is just the middle number: 20.
What are the 3 types of mode?
The different types of Mode are Unimodal, Bimodal, Trimodal, and Multimodal. Let us understand each of these Modes.
How do you solve a mode question?
Where is f1 f0 f2 in mode?
Can there be no mode?
There is no mode when all observed values appear the same number of times in a data set. There is more than one mode when the highest frequency was observed for more than one value in a data set.
Also What is the mode of following data? Finding the Mode
To find the mode it is best to put the numbers in order (makes it easier to count them), then count how many of each number. A number that appears most often is the mode.
What is mode in mean?
The mode is the value that appears most frequently in a data set. … Other popular measures of central tendency include the mean, or the average of a set, and the median, the middle value in a set. The mode can be the same value as the mean and/or median, but this is usually not the case.
How do you find the mode in Class 10?
What is the formula of mode Class 10?
| Marks obtained | Number of students |
|---|---|
| 0 – 10 | 18 |
| 10 – 20 | 24 |
| 20 – 30 | 8 |
What is mode vs mean?
The mean (average) of a data set is found by adding all numbers in the data set and then dividing by the number of values in the set. … Tea mode is the number that occurs most often in a data set.
What are the 5 modes? According to the New London Group, these are the five modes:
How do you find the mode in math class 7?
What is mode of data?
The mode is the value that appears most frequently in a data set. A set of data may have one mode, more than one mode, or no mode at all. … The mode can be the same value as the mean and/or median, but this is usually not the case.
How do you find the mode of a class? How to find the Mode of Grouped Data?
How many modes are there?
The seven main categories of mode have been part of musical notation since the middle ages. So, the list goes: Ionian, Dorian, Phrygian, Lydian, Mixolydian, Aeolian and Locrian. Some of them are major modes, some are minor, and some are ambiguous.
What is f1 and f2 in mode?
f1 = Frequency of the class preceding the modal class. f2 = Frequency of the class following the modal class.
What does no mode mean? It is possible for a set of data values to have more than one mode. … If there is no data value or data values that occur most frequently, we say that the set of data values has no mode.
What is a modal class?
Modal class or the mode class is the class interval in a frequency distribution table that contains the highest frequency. While calculating the mode in statistics, modal class plays a significant role especially while calculating the mode of grouped data.
How do you find the mode of continuous data?
How to Find the Mode or Modal Value
The mode is simply the number which appears most often.
Example:
In <6, 3, 9, 6, 6, 5, 9, 3>the Mode is 6, as it occurs most often.
Finding the Mode
To find the mode it is best to put the numbers in order (makes it easier to count them), then count how many of each number. A number that appears most often is the mode.
Example:
3, 7, 5, 13, 20, 23, 39, 23, 40, 23, 14, 12, 56, 23, 29
In order these numbers are:
3, 5, 7, 12, 13, 14, 20, 23, 23, 23, 23, 29, 39, 40, 56
We can now easily see which numbers appear most often.
In this case the mode is 23.
Another Example:
Arrange them in order:
19 appears twice, all the rest appear only once, so 19 is the mode.
How to remember? Think «mode is most»
More Than One Mode
We can have more than one mode.
Example:
3 appears three times, as does 6.
So there are two modes: at 3 and 6
Having two modes is called «bimodal».
Having more than two modes is called «multimodal».
Try it Yourself
Grouping
In some cases (such as when all values appear the same number of times) the mode is not useful. But we can group the values to see if one group has more than the others.
Example:
Each value occurs once, so let us try to group them.
We can try groups of 10:
In groups of 10, the «20s» appear most often, so we could choose 25 (the middle of the 20s group) as the mode.
You could use different groupings and get a different answer.
Grouping also helps to find what the typical values are when the real world messes things up!
Example: How long to fill a pallet?
Philip recorded how long it takes to fill a pallet in minutes:
It takes longer when there is break time or lunch so an average is not very useful.
But grouping by 5s gives:
«35-39» appear most often, so we can say it normally takes about 37 minutes to fill a pallet.
How to Find the Mean, Median, and Mode
Exploring some measures of central tendency
Kendra Cherry, MS, is an author and educational consultant focused on helping students learn about psychology.
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
Knowing how to find the mean, median, and mode can help you interpret data collected through psychological research. These values provide more insight into what may be considered «normal» or «abnormal» for a specific group of people in terms of cognitive processes or behaviors, for instance.
Because they are all measures of central tendency, psychology students often find it easy to confuse the three. Yet, there are differences in what each one is and how it is found. Here are some useful tips to help you distinguish between these measures, as well as how to calculate mean, median, and mode.
Definition of Mean, Median, and Mode
To understand the differences between the mean, median, and mode, let’s start by defining these three terms.
How to Find the Mean
Take these two steps to calculate the mean:
As an example, imagine that your psychology experiment returned the following number set: 3, 11, 4, 6, 8, 9, 6. To calculate the mean, you first add all the numbers together (3 + 11 + 4 + 6 + 8 + 9 + 6 = 47). Then you divide the total sum by the number of scores used (47 / 7 = 6.7). In this example, the mean or average of the number set is 6.7.
Recap of How to Find the Mean
The mean is calculated by adding all the scores together, then dividing by the number of scores you added.
How to Find the Median
The median is the middle score in the set. To find the median, you take these steps:
As an example, consider this set of numbers: 5, 9, 11, 9, 7. First, you arrange them in numerical order (5, 7, 9, 9, 11). Next, you count how many scores you have (5). Divide the total number of scores by 2 (5 / 2) and you get 2.5.
Since you have an odd number of scores, you round 2.5 up to the number 3. The number in the third position of the data set is the median which, in this case, is 9 (5, 7, 9, 9, 11).
To calculate the median for an even number of scores, imagine that your research revealed this set of data: 2, 5, 1, 4, 2, 7. Your first step is to put them in numerical order (1, 2, 2, 4, 5, 7). Next, add up the total number of scores (6), divide by 2, and you get 3 (6 / 2 = 3).
Go to the score in the third position (1, 2, 2, 4, 5, 7) and add it to the number in the next position (1, 2, 2, 4, 5, 7) to get the sum of the two (2 + 4 = 6). Take 6 and divide it by 2 (the total number of scores you added together), and you get 3. So, the median for this example is 3.
Recap of How to Find the Median
The median is calculated by arranging the scores in numerical order, dividing the total number of scores by two, then rounding that number up if using an odd number of scores to get the position of the median or, if using an even number of scores, by averaging the number in that position and the next position.
How to Find the Mode
Of all the measures, finding the mode requires the least amount of mathematical calculation. Instead, since the mode is simply the most frequently occurring score in a distribution, all you do is look at all your scores and select the most common one.
As an example, consider the following number distribution: 2, 3, 6, 3, 7, 5, 1, 2, 3, 9. The mode of these numbers would be 3 since this is the most frequently occurring number (2, 3, 6, 3, 7, 5, 1, 2, 3, 9).
If no number in a set occurs more than once, there is no mode for that set of data. It’s also possible for a data set to have two modes. This is known as bi-modal distribution.
Bi-modal distribution occurs when there are two numbers that are tied in frequency. For example, consider the following set of numbers: 13, 17, 20, 20, 21, 23, 23, 26, 29, 30. In this set, both 20 and 23 occur twice (13, 17, 20, 20, 21, 23, 23, 26, 29, 30). Therefore, they are both modes.
Recap of How to Find the Mode
To find the mode, you identify the score that occurs most often within the data set. In cases where you have a large number of scores, creating a frequency distribution can be helpful in determining the mode.
Pros and Cons of Mean, Median, and Mode
Each measure of central tendency has its own strengths and weaknesses. Here are a few to consider.
While the mean in math is theoretically neutral, some contend that the use of the mean in psychology can lead to inappropriate conclusions if care is not taken with its application. This is due, in part, to behavior and cognition being both complex and variable in nature.
When to Use Mean, Median, and Mode
How do you determine whether to use the mean, median, or mode when analyzing psychology research? The one you select can depend on the data scores themselves.
If there are no outliers in your data set, the mean may be the best choice in terms of accuracy since it takes into account each individual score and finds the average. Conversely, if outliers exist, the median or mode may be more accurate since the results won’t be skewed.
Also consider what you are trying to measure. Are you looking for the average (the mean), do you want to identify the middle score (the median), or are you looking for the score that appears most often (the mode)? While they are all measures of central tendency, each one looks at this tendency from a slightly different point of view.
An Example of Mean, Median, and Mode in Psychology
Imagine a research study in which psychologists are interested in learning the typical age at which someone might be diagnosed with schizophrenia. To collect this data, they send a questionnaire to mental health providers, asking that they share their patients’ ages upon formal diagnosis.
The responses received indicate that the practitioners’ patients were the following ages:
Using the calculations above, you would find that the mean, median, and mode for this data set are all around 27 years (27.1 years, 27 years, and 27 years respectively). In this case, any of these measures could be used to help you arrive at the typical age of onset.
But what if you had an additional score of 13? In this case, the calculation of the mean would be 25.6, while the median and mode would both be 27. Since the mean includes an outlier, median and mode would be more accurate as they aren’t skewed by this number.
In case you are curious, the National Alliance on Mental Health reports that the average age of schizophrenia onset for men is late teens to early 20s, while women tend to be diagnosed with this condition in their late 20s to early 30s.
A Word From Verywell
Mean, median, and mode all serve a valuable purpose in analyzing psychological data. They all also have their pros and cons. Knowing how to find mean, median, and mode—as well as their strengths and weaknesses—can help you better interpret data collected via psychology research.
Speelman CP, McGann M. How mean is the mean? Front Psychol. 2013;4:451. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00451
National Alliance on Mental Illness. Schizophrenia.
Hogg RV, McKean JW, Craig AT. Introduction to Mathematical Statistics. Boston: Pearson; 2013.
Math Statistics: Mode, Median and Mean
In these lessons, we will learn how to determine the mode of a given set of data. We will also compare between mode, mean, and median.
What Is Mode, Median And Mean?
In statistics, mode, median and mean are typical values to represent a pool of numerical observations. They are calculated from the pool of observations.
Mode is the most common value among the given observations. For example, a person who sells ice creams might want to know which flavor is the most popular.
Median is the middle value, dividing the number of data into 2 halves. In other words, 50% of the observations is below the median and 50% of the observations is above the median.
Mean is the average of all the values. For example, a teacher may want to know the average marks of a test in his class.
The following diagrams show how to find the mean, median, mode and range. Scroll down the page for examples and solutions.
The mode of a set of observations is the value that occurs most frequently in the set. A set of observations may have no mode, one mode or more than one mode.
Example:
Find the mode of the following set of scores.
14 11 15 9 11 15 11 7 13 12
Solution:
The mode is 11 because 11 occurred more times than the other numbers.
If the observations are given in the form of a frequency table, the mode is the value that has the highest frequency.
Example:
Find the mode of the following set of marks.
| Marks | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Frequency | 6 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 3 |
Solution:
The marks 2 and 3 have the highest frequency. So, the modes are 2 and 3.
Note: The above example shows that a set of observations may have more than one mode.
Example:
Find the mode for each of the following frequency tables:
The frequency table below shows the weights of different bags of rice.
| Weight (kg) | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 75 | 80 |
| Bags of rice (Frequency) | 8 | 11 | 7 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 8 |
There are 8 number cards with values 0 – 7. Each time a card is drawn at random and the card value is recorded. The frequency refers to the number of times a value is shown.
| Card values | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Frequency | 8 | 12 | 7 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 12 | 10 |
Solution:
a) Mode: 75 kg (highest frequency of 12)
b) Mode: 5 (highest frequency of 13)
Example:
The following frequency table shows the marks obtained by students in a quiz. Given that 4 is the mode, what is the least value for x?
| Marks | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Number of students (Frequency) | 7 | 9 | 10 | x | 9 | 11 |
Solution:
x is as least 12
(if x is less than 12 then 4 will not be the mode)
Mean, Median, Mode, Range, Interquartile Range
This lesson shows you how to find the mean, median, mode, range and interquartile range for a list of numbers.
Example:
Find the mean, median, mode, range and interquartile range for the following data.
5, 7, 9, 9, 10, 11, 11, 11, 12
This lesson shows you how to find the mean, median, mode, range and interquartile range from a frequency table.
Mean, Mode And Median From Frequency Tables
How to find the mean, mode and median from a frequency table for both discrete and grouped data?
For grouped data:
We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/woman-sitting-at-desk-looking-at-notebook-135384977-574610ff5f9b58723d33b8e3.jpg)