What is quality control
What is quality control
Quality control: что это такое и что значит Quality? Терминология
Quality Control (QA) — это «контроль качества», а точнее, это процесс, который отвечает за соблюдение ожидаемого качества продукции путем тестирования, выявления и устранения его неисправностей.
Quality Control — что это?
Quality Control идет очень плотно с другим процессом в тестировании — Quality Assuran c e (QA). Очень часто эти процессы принимают за один и тот же, хотя по факту они отличаются и обозначают разные мероприятия. QC и QA направлены на общее действие — улучшить качество программного продукта, но применяются на разных этапах продукта и ориентированы на разные цели. Поэтому, чтобы точно понять, что это такое — Quality Control, нужно разобраться с обоими понятиями.
Quality Control и Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance — это процесс, который описывает все требования к программному продукту, чтобы его состояние было максимально близким к идеальному. Помимо самих требовании, это т процесс также описывает инструменты для достижения указанных требований:
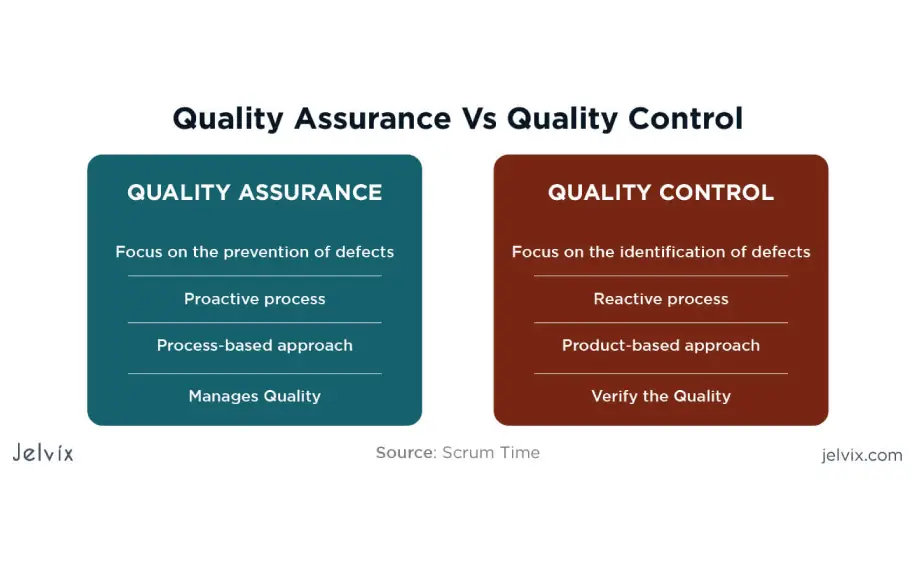
Получается, что процесс QA по иерархии стоит «выше» процесса QC, является более «широким» и «включает» Quality Control в свое описание. QA старается предотвратить дефекты ПО в процессе его разработки и тестирования, а Quality Control предусматривает устранение недоработок и ошибок уже в готовой программе.
Чем отличаются Quality Control и Quality Assurance?
Терминологию этих процессов мы определили. Давайте подробнее остановимся на их различиях.
Различия по цели. Q u ality Assurance преследует цель — улучшить процессы разработки и тестирования, чтобы не было дефектов. Quality Control преследует более простую — выявить и устранить недостаток в рабочей программе.
Разная направленность. QA направлен на процесс разработки продукта. QS направлен на уже разработанный продукт.
Разные методы. Методы работы Quality Assurance являются профилактическими, а методы работы Quality Control — конкретно-техническими.
Разное распределение ответственности. В QA ответственность за должное качество продукта лежит абсолютно на всех участниках разработки программы. В QC ответственность лежит на конкретной команде или разработчике, которые ищут дефекты в программе и устраняют их.
Различная последовательность. QA — это процесс, который обеспечивает качество до наступления контроля качества. QC — это процесс, который начинает применяться после окончания обеспечения качества. То есть сначала идет процесс QA, а после него включается процесс QC.
Quality Control и Quality Assurance на практике
отсутствие кнопки покупки;
нет кнопки «Подняться наверх»;
постоянно выскакивает какое-то назойливое сообщение с какими-то предложениями, а само сообщение невозможно просто закрыть;
сложная форма заказа, которая постоянно сообщает о какой-то ошибке;
не работают фильтры сортировки товара по нужным вам параметрам;
Вроде небольшие недоработки, но они создают негативное отношение к этому интернет-магазину. Каждый такой обнаруженный вами недостаток снижает вероятность, что вы в этом интернет-магазине что-то купите. В итоге настает момент, когда вы просто закрываете вкладку с этим магазином и ищете другой.
Заключение
Мы будем очень благодарны
если под понравившемся материалом Вы нажмёте одну из кнопок социальных сетей и поделитесь с друзьями.
What Is Quality Control? How to Build a QC Strategy
Quality control is important to ensure your product is consistent. Image credit: William Warby
Markets have become ever more competitive due to being saturated with businesses. Not only is it important to market your business to a large audience, but you must also maintain these customers. So what is quality control?
Customers expect the highest of standards and sometimes all it takes is some inconsistency in the products that may cause the business to go under.
This is why it’s essential for businesses to have a clear understanding of what is quality control and its implications on your business. Now, lets define quality control and the preceding benefits your business can get by utilizing it.
What Is the Quality Control?
To define quality control, it is important to understand the significance of having a consistent product. By having consistent products, customers can know what to expect from your brand.
This maintains customer loyalty and boosts word-of-mouth advertising which ultimately boosts sales. Quality control is the process by which a business ensures that its product is up to standards.
By checking the finished product before it is shipped, your business is able to maintain a standard of quality that you set for yourself. This can be done in several ways.
The simplest being inspection of all products released. As the business grows, it becomes much more efficient to draw samples from the production line relying on statistical analysis.
There are key differences between the aims of QA and QC. Image credit: Jelvix.com
What Is Quality Control in Management?
Managers use quality control more than anyone in their day to day lives. In fact, managing a team effectively is essentially impossible without managing the quality of their work in some way or another.
This is because managers are ultimately responsible for their team’s output. This is true if you’re managing a couple of software developers, or a whole factory full of workers. The same principles apply in either case.
Here’s what quality control means for managers.
Efficiency
By constantly checking the products for inconsistencies in quality, any problems happening in your production line may be identified quickly in order to minimize wastes.
By reducing wastes, your production costs are reduced as you are able to save the raw materials that would otherwise be wasted as well as the labor put into a product that will never be sold.
High efficiency is the goal of any growing company.
At a large enough scale, a 1% increase in efficiency might mean thousands of dollars in increased sales. Additionally, higher efficiency allows you to provide competitive prices that give you the edge over less efficient businesses.
Increased Quality Standards and Project Awareness
Your decision to monitor quality will be known throughout your company. Your employees will know that you value quality and thus will work their hardest to provide the highest quality of goods in order to impress you.
By inspecting the quality of products, you create a motivation for workers to be more thorough with their work.
For labor intensive products, it is often found that the better your quality control process is, the less likely there are to be defects in the products since workers will be extra thorough to ensure that their products are not rejected.
Consistency
By enforcing quality control, your products will have less variability. By having consistent products, customers are a lot more likely to keep using your brand over the competition. A consistent product builds customer loyalty, making them less likely to try out a new brand.
Eliminating competition before it is even established. Furthermore, consistency of your product builds your brand’s image.
By getting people accustomed to a certain standard of quality from your brand, they will feel a lot safer recommending your product to people they know.
This is otherwise known as word-of-mouth advertising and is regarded as one of the most effective methods of advertising as people trust the opinion of people they know.
Quality Control Tools
Of course, quality control is much easier nowadays, as there are a raft of dedicated tools available. Some of these are dedicated project management software. Others are simple techniques with pens and paper.
Let’s take a look at some of the best quality control tools you can use.
Fishbone Diagrams
When diagnosing problems in your production line that may be causing the fluctuations in quality, a fishbone diagram may prove useful. This simple diagram will help you identify the several causes for a problem clearly.
This helps with brainstorming and troubleshooting. By plotting down all the possible causes that have led to your problem, it becomes much easier to convey the current problem to several people as well as discuss possible solutions that address these problems.
Quality Control
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
What Is Quality Control?
Quality control (QC) is a process through which a business seeks to ensure that product quality is maintained or improved. Quality control requires the company to create an environment in which both management and employees strive for perfection. This is done by training personnel, creating benchmarks for product quality, and testing products to check for statistically significant variations.
A significant aspect of quality control is the establishment of well-defined controls. These controls help standardize both production and reactions to quality issues. Limiting room for error by specifying which production activities are to be completed by which personnel reduces the chance that employees will be involved in tasks for which they do not have adequate training.
Quality Control
Key Takeaways
Understanding Quality Control
Quality control involves testing units and determining if they are within the specifications for the final product. The purpose of the testing is to determine any needs for corrective actions in the manufacturing process. Good quality control helps companies meet consumer demands for better products.
Quality testing involves each step of the manufacturing process. Employees often begin with the testing of raw materials, pull samples from along the manufacturing line, and test the finished product. Testing at the various stages of manufacturing helps identify where a production problem is occurring and the remedial steps it requires to prevent it in the future.
The quality control used in a business is highly dependent on the product or industry. In food and drug manufacturing, quality control includes ensuring the product does not make a consumer sick, so the company performs chemical and microbiological testing of samples from the production line. Because the appearance of prepared food affects consumer perception, the manufacturers may prepare the product according to its package directions for visual inspection.
In automobile manufacturing, quality control focuses on how parts fit together and interact and ensure engines operate smoothly and efficiently. In electronics, testing might involve using meters that measure the flow of electricity.
Quality Control Methods
There are several methods of measuring the performance of quality control. A quality control chart is a graphic that depicts whether sampled products or processes are meeting their intended specifications—and, if not, the degree by which they vary from those specifications. When each chart analyzes a specific attribute of the product, it is called a univariate chart. When a chart measures variances in several product attributes, it is called a multivariate chart.
X-Bar Chart
Randomly selected products are tested for the given attribute or attributes the chart is tracking. A common form of a quality control chart is the X-Bar Chart, where the y-axis on the chart tracks the degree to which the variance of the tested attribute is acceptable. The x-axis tracks the samples tested. Analyzing the pattern of variance depicted by a quality control chart can help determine if defects are occurring randomly or systematically.
Taguchi Method
The Taguchi Method of quality control is another approach that emphasizes the roles of research and development, product design, and product development in reducing the occurrence of defects and failures in products. The Taguchi Method considers design to be more important than the manufacturing process in quality control and tries to eliminate variances in production before they can occur.
100% Inspection Method
This 100% inspection method is a quality control process that involves looking at and assessing all parts of a product. This type of quality control is done to rule out flaws in products. This method is often used to evaluate valuable metals and produce. When conducting the 100% inspection method calls for data about the manufacturing process and software to analyze inventory.
The challenge for using this method is that looking at every single item that makes up a product is expensive, and it could destabilize or render the product unusable. For example, if you use this method to examine organic strawberries, you would risk the delicate berries being bruised or mushed, rendering them unsellable to customers.
Quality control methods help standardize both production and reactions to quality issues in various industries from food production to automobile manufacturing.
The Role of Quality Control Inspectors
Quality control inspectors protect the consumer from defective products and the company from damage to its reputation due to inferior manufacturing processes. If the testing process reveals issues with the product, the inspector can fix the problem himself, return the product for repairs, or tag the product for rejection. When issues arise, the inspector notifies supervisors and works with them to correct the problem.
The Benefits of Quality Control
Implementing quality control procedures ensures you are selling the best products to your customers. In addition, practicing quality control has a positive impact on employee conduct. Quality control can inspire employees to create high-quality goods leading to greater customer satisfaction.
Quality control protocols may help you lower your inspection costs and use your resources in a more cost-effective manner, too.
Example of Quality Control
In 1986, Motorola, Inc. created a quality control methodology called Six Sigma, which uses data-driven review to keep defects to a minimum. The process focused on cycle-time improvement to reduce defects in its manufacturing of products to no more than 3.4 occurrences per million units.
This methodology was created to minimize mistakes while documenting all the manufacturing procedures.
Motorola introduced this method because, at the time, they faced fierce competition from similar companies overseas, primarily the success of the Japanese manufacturing market, and complaints by Motorola’s customers were high.
After implementing this then-new form of quality control, the company’s performance improved dramatically. By the end of the initial five-year period (1986-1991), Motorola had reached its target for improvement in every sector of business.
The continued use of Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma (another form) occurs in the 21st century and is used by Microsoft and local governments. Six Sigma uses a five-factor approach (DMAIC) to define, measure, analyze, improve, and control to help companies identify and address quality control problems and fix them.
Quality Control FAQs
What Does Quality Control Mean?
Quality control means how a company measures that its product quality is maintained (if it is good) or improved if need be. Quality control can be done in many ways, from testing products, reviewing manufacturing processes, and creating benchmarks. This is all done to monitor significant variations in a product.
What Are the 4 Types of Quality Control?
There are several methods of quality control. These include an x-bar chart, Six Sigma, 100% inspection mode, and the Taguchi Method.
Why Is Quality Control Important?
Quality control ensures that defective goods do not go out to the public. Companies that have quality control methods in place often have employees who pay close attention to their work.
In food and drug manufacturing, quality control prevents products that make customers sick, and in manufacturing, quality control can ensure that accidents don’t happen when people use a product.
What Is an Example of Quality Control?
An aspect of quality control in food production would be overseeing the ingredient specifications, reviewing supplier lists, and ensuring the facility where the food product is made is sanitary.
What Is the Difference Between Quality Assurance and Quality Control?
Quality assurance is about how a process is performed or how a product is made. For example, if milk is labeled non-fat, the factory would have a method to ensure the type of milk in the carton is reflected by the label on the package. Quality control focuses on quality management and how the overall quality of the products overseen by the company.
The Bottom Line
Having quality control in place within a business can only help ensure product quality and the overall success of a business. The environment of quality control influences employees’ attitudes about the workplace and creates a sense of ownership in the products and company as a whole. Quality control can be done in various ways, from training personnel to creating data-driven tools to test products and set standards. Quality control methods help create a safe work environment and product safety that benefits customers and the company alike.
What Is Quality Control : Definition, Benefits, Examples, and Top Techniques Explained
Table of Contents
In today’s world, it’s not uncommon that we take the reliability and quality of products and services for granted. At the start of the 20th century, however, quality control in manufacturing was not exactly a reliable process.
Now, decades after early pioneers created business problem-solving processes and analysis frameworks to determine and control consistency and value, it’s possible more than ever for a business to implement and scale best practices.В
What Is Quality Control?
Quality does not have a singular definition. Despite the relative meaning of “value,” quality control is the process by which products/services are tested and measured to ensure they meet a standard. Through this process, a business can evaluate, maintain, and improve product quality.В
Ultimately, there are two crucial goals of quality control: (1) to ensure that products are as uniform as possible and (2), to minimize errors and inconsistencies within them.В
Types of Quality Control
Just as quality is a relative word with many interpretations, quality control itself doesn’t have a uniform, universal process. Some methods depend on the industry. Take food and drug products, for instance, where errors can put people at risk and create significant liability. These industries may rely more heavily on scientific measures, whereas others (such as education or coaching) may require a more holistic, qualitative method.В
At its core, quality control requires attention to detail and research methodology.В
PGP in Lean Six Sigma With Modules From UMass
So, what is quality control? There are a wide range of quality control methods, including:В
There are other quality control factors to consider when selecting a method in addition to types of processes.В
Some companies establish internal quality control divisions when defining what is quality control. They do this to monitor products and services, while others rely on external bodies to track products and performance. These controls may be largely dependent on the industry of the business. Due to the strict nature of food inspections, for example, it may be in a company’s best interest to sample products internally and verify these results in a third-party lab.
Why Is Quality Control Important? What Are the Benefits?
In the long run, investments in quality control measures can protect the reputation of a company, prevent products from being unreliable, and increase trust on the side of consumers. These processes are determined through rigorous methodology and testing, as well as industry standards and best practices.В
Moreover, quality control is necessary because it ensures that a company will look at evidence-based data and research — not just anecdotal observations — to ensure that products are living up to their standard. One essential aspect of quality control is that the process doesn’t just happen once but is a routine evaluation of the product to ensure that it’s continuously meeting both the manufacturing standards and consumer demand.В
No consumer wants to risk using a product that could endanger them or fail expectations. A company’s reputation, reliability, and efficiency are all at risk if quality control is overlooked. A product’s testing can play a role in marketing and sales as well since consumers may trust it more.
Quality Control Roles and Responsibilities
When answering what is quality control, it is critical to understand that it consists of multifaceted responsibilities and roles. Moreover, it shouldn’t be confused with quality assurance. Whereas quality assurance looks at the processes used to prevent defects, quality control is focused specifically on the measurement and analysis processes involved with determining product quality.В
Quality control uses specific research tools to accomplish fact-finding processes and conduct analyses. A quality control professional is tasked with analyzing these measurements against some sort of standard determined by the quality management department, company policies, and industries or regulatory bodies. Based on this evidence-gathering, quality control will recommend changes.В
Free Course: Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
We can see from this roadmap, too, how quality assurance and quality control differ. Quality assurance looks at the holistic picture to prevent a product from becoming defective. Quality control, on the other hand, later determines if a product is, in fact, defective or not. Both roles fit under the broad umbrella of quality management.В
Thus, an individual in quality control is tasked with communicating results to stakeholders and significant parties. A good quality control specialist will be able to disseminate scientific and research-based thinking to a business community and assist with the problem-solving process. These specialists are a key component of a product’s design process, as they determine whether a company’s creation is truly acceptable for the market.
Interested in learning Lean Six Sigma and it’s importance? Check out the Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification course preview!
Train to Assess Quality With Lean Today
Learn how to define what is quality control with Simplilearn’s Post Graduate Program in Lean Six Sigma, offered in partnership with the University of Massachusetts Amherst. This Lean Six Sigma certification program will help you gain key skills to lead tranformational projects by improving overall quality and delivering the best results.
This course focuses on two important management methodologies — Lean practices and Six Sigma — that will enable you to accelerate business improvement.
Find our Post Graduate Program in Lean Six Sigma Online Bootcamp in top cities:
| Name | Date | Place | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post Graduate Program in Lean Six Sigma | Cohort starts on 21st Sep 2022, Weekend batch | Your City | View Details |
| Post Graduate Program in Lean Six Sigma | Cohort starts on 5th Oct 2022, Weekend batch | Your City | View Details |
| Post Graduate Program in Lean Six Sigma | Cohort starts on 19th Oct 2022, Weekend batch | Your City | View Details |
About the Author
Simplilearn is one of the world’s leading providers of online training for Digital Marketing, Cloud Computing, Project Management, Data Science, IT, Software Development, and many other emerging technologies.
Recommended Programs
Post Graduate Program in Lean Six Sigma
Certified Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
*Lifetime access to high-quality, self-paced e-learning content.
Project Quality Management: Perform Quality Assurance Vs Perform Quality Control
Recommended Resources
Free eBook: Quality Management Professionals Salary Report
Learn more about the Control Plan
The Ultimate Guide to Understand Everything on Control Statements in C
Free eBook: Top 25 Interview Questions and Answers: Quality Management
How to use Control Chart Constants?
What is Version Control and What Are Its Benefits?
What Is Quality Control?
What is quality control? Quality control are the systems in your company that detects defects. Quality control prevents customers (internal and external) from receiving defective products. This includes inspection points for receiving inspection, inprocess inspection and final inspection. When establishing these systems you need to consider these items
Snap Sampling Plans! software combines all the key industry standard attribute sampling plans into one place.
With over 10,000 sampling possibilities, Snap Sampling Plans! guides you in selecting the correct AQL sampling plan.
Receiving Inspection
Receiving inspection are the controls you use to prevent defective materials from entering your production lines. Your company decides which materials are critical to your process. Critical materials directly affect product quality. These materials must be controlled.
Consider these questions when creating your receiving inspection procedure.
Inprocess Inspection
You might have inprocess inspection in various departments in your company as production is flowing through those departments. This could include
When establishing an inprocess inspection stage consider these items
Snap Sampling Plans! software combines all the key industry standard attribute sampling plans into one place.
With over 10,000 sampling possibilities, Snap Sampling Plans! guides you in selecting the correct AQL sampling plan.
Final Inspection
Final inspection should occur on the product prior to shipping to the customer or prior to storing in inventory. When implementing final inspection activities, review the above inprocess inspection information.
Final inspection is more dependent on customer requirements. The customer may have a specification or a drawing. Perhaps you are selling to a catalog or web page. Final inspection assures the customer is receiving the items they order.
Final inspection occurs on the product. If defects are found, then the product may need to be reworked or scrapped. Finding defects at this time can cost your company serious money because the process that caused the defect may still be making the same defect on fresh product. In addition all value added steps have been placed in the product. All money spent on creating that product will be wasted if the product is scrapped.
As a preventive measure, final inspection should review the inprocess inspection documentation to assure that the data is in order.
Documentation for final inspection should be formal as the customer may ask for the data. Design The quality record so it meets your customer requirements and formats. If the customer is asking for the data, be sure to get their acceptance to the format prior to sending the initial data to the customer.
What is Quality Control inspection types?
What is quality control definition? The operational techniques and individual activities that focus on controlling or regulating processes and materials to fulfill requirements for quality. The focus is on preventing defective products or services from being passed on.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Pic1-KhadijaKhartit-cc5b57fba2bd46ed87bdb3ddbcd2ef69.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SuzannesHeadshot-3dcd99dc3f2e405e8bd37271894491ac.jpg)



