What is the capital of guatemala
What is the capital of guatemala
What Is the Capital of Guatemala?
The National Palace of Culture is one of the most significant buildings in Guatemala City.
What Is the Capital of Guatemala?
Guatemala City is the capital of Guatemala. Additionally, it serves as the capital of the Department of Guatemala and the Municipality of Guatemala. The capital is located in the Valle de la Ermita, which is in the southern region of the country, and where seismic and volcanic activity is relatively common. Guatemala City is surrounded by mountains on either side.
The population of Guatemala City is approximately 2.11 million, making it the most populated city in both the country and the Central American region. It is the seat of government and the most economically important city in Guatemala. The city has an international airport and is connected to nearly all major highways. Given its importance within the country, the city is also an attractive location for the banking and financial services industries. Guatemala’s central bank is based in Guatemala City, as well as a number of other private banks.
Guatemala City is subdivided into 22 zones. Zone 1 holds the most historical importance, and includes buildings such as the Presidential House, the National Congress, Constitution Park, the National Palace of Culture, and the National Library. Given the city’s rapid growth, many nearby towns have been incorporated by Guatemala City as it continues to spread.
History of the Capital City of Guatemala
The site currently occupied by Guatemala City was first inhabited by the Kaminaljuyu, an ancient Mayan civilization that dates back to between 1500 BC and 1200 AD. At its peak, the civilization included approximately 200 pyramids. However, many of these ruins have been destroyed over time by population growth and real estate development.
A Catholic monastery was established on the site in the 17th century, although the population remained small. In the beginning of the Spanish colonial era, Antigua was the capital of the colony. However, after the Santa Marta earthquakes of 1773, Antigua was destroyed and the King of Spain declared Guatemala City as the new capital approximately two years later. During this era, the Central Square played an important role in the economy and culture of the new capital.
After Guatemala gained its independence from Spain in 1821, Guatemala City remained the capital. During the years following independence, the city began to expand and the government established many new public administrative buildings, including the Presidential Palace and the Carrera Theater. This growth continued through the late 19th and early 20th centuries. However, many of these buildings were lost during the earthquakes that occurred between November 1917 and January 1918.
The Guatemalan Civil War occurred between 1960 and 1996. During the 1980s, violence broke out in the city as it experienced political unrest surrounding the military’s treatment of indigenous communities. Attacks occurred at the Spanish Embassy, the National Palace, and the Industrial Bank Financial Center.
Demographics of Guatemala City
The population of Guatemala City has grown exponentially since the late 1970s. The majority of this growth is caused by rural to urban migration, as individuals move to the city in search of economic opportunities. The majority of the population is composed of Spanish and Mestizos, although the indigenous population is also sizable. Approximately 23 different Mayan groups live in the city, each speaking a different language or dialect.
Guatemala
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
Read a brief summary of this topic
Guatemala, country of Central America. The dominance of an Indian culture within its interior uplands distinguishes Guatemala from its Central American neighbours. The origin of the name Guatemala is Indian, but its derivation and meaning are undetermined. Some hold that the original form was Quauhtemallan (indicating an Aztec rather than a Mayan origin), meaning “land of trees,” and others hold that it is derived from Guhatezmalha, meaning “mountain of vomiting water”— referring no doubt to such volcanic eruptions as the one that destroyed Santiago de los Caballeros de Guatemala (modern-day Antigua Guatemala), the first permanent Spanish capital of the region’s captaincy general. The country’s contemporary capital, Guatemala City, is a major metropolitan centre; Quetzaltenango in the western highlands is the nucleus of the Indian population.
After gaining independence from Spain in the 1820s, Guatemala had a long history of government by authoritarian rule and military regimes until it came under democratic rule in 1985. Starting in 1954, Guatemala’s governments faced formidable guerrilla opposition that sparked civil war that lasted for 36 years until peace accords were signed in 1996. The struggles of Guatemala’s Indians during the war years were illuminated when Rigoberta Menchú, a Quiché Maya and an advocate for indigenous people throughout Latin America, was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1992.
A slow political and economic recovery continued into the early 21st century. Elections have been held regularly since 1996, but, because there are many political parties, which tend to be small and short-lived, convergence on political solutions has been rare. Fear of a military return to power has preoccupied voters in the first years of the 21st century.
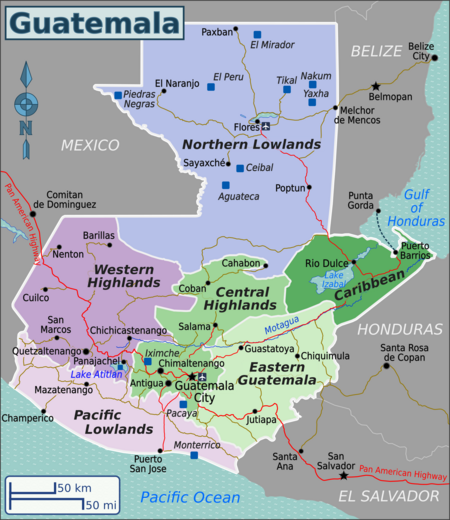
Guatemala is bounded to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize and (along a short coastline) by the Gulf of Honduras, to the east by Honduras, to the southeast by El Salvador, and to the south by the Pacific Ocean.
Relief
The surface of Guatemala is characterized by four major topographical features. Southern Guatemala is dominated by a string of 27 volcanoes extending for about 180 miles (300 km) between Mexico and El Salvador. Between the volcanoes and the Pacific Ocean lies a fertile plain ranging 25–30 miles (40–50 km) in width. The Petén region, a large, low-lying, rectangular area, juts northward to occupy a portion of the Yucatán Peninsula, a limestone platform shared with Mexico and Belize. Sandwiched between the volcanic landscape and the Petén are the high mountain ranges and valleys. These arc gently eastward from Mexico for a distance of 210 miles (340 km), extending into northern Honduras.
The volcanic region of Guatemala consists of three elements: a row of volcanoes of geologically recent origin, flanked by a deeply eroded volcanic tableland of older origin to the north and the narrow coastal plain constructed of volcanic debris on the Pacific slope. The alignment of volcanic cones begins with the Tacaná Volcano (13,428 feet [4,093 metres]), located on the frontier with Mexico, and continues eastward across Guatemala into El Salvador. Among these are three continuously active volcanoes: the growing summit of Santiaguito (8,202 feet [2,500 metres]) located on the southern flanks of Santa María (12,375 feet [3,772 metres]); Fuego (12,582 feet [3,835 metres]); and Pacaya (8,371 feet [2,552 metres]). The highest peak is Tajumulco (13,845 feet [4,220 metres]). The city of Antigua Guatemala is precariously situated beneath three volcanoes: Agua Volcano (12,350 feet [3,760 metres]), Fuego Volcano (12,336 feet [3,763 metres]), and Acatenango Volcano (13,045 feet [3,976 metres]). Lava flow from Pacaya is sometimes visible from Guatemala City.
From the base of the volcanic row, at an elevation of about 1,500 feet (450 metres), the Pacific coastal plain gradually slopes south to sea level at the shoreline of the ocean. The plain extends east-west for a distance of about 150 miles (240 km) and is one of the country’s richest agricultural areas. Three-fourths of the population and most of the major cities are concentrated in the volcanic region and the Pacific slope, and the volcanic eruptions and earthquakes characteristic of this area have repeatedly taken a heavy toll of property and life.
The rugged and deeply dissected volcanic highlands, which lie to the north of the volcanic row, average 9,000 feet (2,750 metres) in elevation near the Mexican border and decline gradually to 3,000 feet (900 metres) at the opposite border with El Salvador. Ash-filled basins and scenic lakes are scattered throughout this region.
The sierras provide a major barrier between the heavily occupied volcanic landscape to the south and the sparsely populated Petén to the north. Sierra los Cuchumatanes to the west rises to elevations in excess of 10,000 feet (3,000 metres). Eastward, the lower sierras of Chamá, Santa Cruz, Chuacús, Las Minas, and the Montañas del Mico are separated by deep valleys that open eastward on a narrow Caribbean shoreline.
The Petén, lying largely below 1,000 feet (300 metres) in elevation, exhibits a knobby or hilly surface characterized by subsurface drainage of water. The region is replete with scattered lakes, Lake Petén Itzá being the largest. Extensive flooding takes place during the rainy season.
Drainage
The east-flowing Motagua River and west-flowing Cuilco pass in opposite directions through a structural trough that serves as the boundary between the volcanic terrain of southern Guatemala and the sierras of its midsection. The sierra region is drained by large rivers that flow primarily north into the Gulf of Mexico by way of the Usumacinta River. The 250-mile- (400-km-) long Motagua River is the longest of a series of rivers draining eastward toward the Caribbean. Several small rivers drain into the Pacific Ocean. Much of the Petén region is drained by the subsurface flow of water.
Guatemala
Contents
 | COVID-19 information: Guatemala’s airports have been re-opened but with restrictions in place. Passengers require a negative COVID-19 test taken within the past 72 hours, a COVID-19 vaccine with proof of vaccination, or proof of recovery from COVID-19 within three months of arrival. You may have to quarantine upon arrival. Travelers coming from the U.K., Brazil, or South Africa are banned from entry into Guatemala. |
Many businesses are open but with social distancing guidelines in place. You must wear a mask while in public areas.
For updates on the COVID-19 situation in Guatemala, see the Ministry of Public Health website.
Guatemala has a rich and distinctive culture from the extended mixing of elements from Spain and the Maya people who are native to Central America. This diverse history and the natural beauty of the land have created a destination rich in interesting and scenic sites. Guatemala is very tough land—you can experience volcanic activity, seismic activity (earthquakes, mudslides), and hurricanes.
Regions [ edit ]
| Central Highlands This region is home to the capital of Guatemala city and at least one active volcano |
| Western Highlands By far the most beautiful part of Guatemala, this region includes many indigenous Mayan villages. Lake Atitlan is also in this region, along with at least 2 active volcanoes. |
| Eastern Guatemala A dry region on the routes to Honduras and El Salvador, with a mostly Hispanic population, and dedicated to cattle ranching. |
| Caribbean Coast This coast is home to many beaches. |
| Northern Lowlands This region has very dense jungled rainforest, and some amazing Mayan ruins, including Tikal. |
| Pacific Lowlands This consists of the rolling foothills of the Sierra Madre, extending across the wide Pacific plain to beautiful beaches. |
Cities [ edit ]
Other destinations [ edit ]
Understand [ edit ]
 | |
| Capital | Guatemala City |
| Currency | quetzal (GTQ) |
| Population | 17.2 million (2018) |
| Electricity | 120 volt / 60 hertz (NEMA 1-15, NEMA 5-15) |
| Country code | +502 |
| Time zone | UTC−06:00, America/Guatemala |
| Emergencies | 123 (fire department), 128 (emergency medical services), 110 (police), 120 (police) |
| Driving side | right |
| edit on Wikidata | |
History [ edit ]
Pre-Columbian [ edit ]
The first evidence of human settlers in Guatemala goes back to at least 12,000 BC. Sites dating back to 6500 BC have been found in Quiché in the Central Highlands and Sipacate, Escuintla on the central Pacific coast. Archaeologists divide the pre-Columbian history of Mesoamerica into the Pre-Classic period (2000 BC to 250 AD).
El Mirador was by far the most populated city in pre-Columbian America. The El Tigre and Monos pyramids each have a volume greater than 250,000 cubic meters. Mirador was the first politically organized state in America.
The Classic period of Mesoamerican civilization corresponds to the height of the Maya civilization, and is represented by countless sites throughout Guatemala, although the largest concentration is in Petén in the Northern Lowlands. This period is characterized by heavy city-building, the development of independent city-states, and contact with other Mesoamerican cultures. This lasted until around 900 AD, when the Classic Maya civilization collapsed. The Maya abandoned many of the cities of the central lowlands or were killed off by a drought-induced famine. The Post-Classic period is represented by regional kingdoms such as the Itza’ and Ko’woj in the lakes area in Petén, and the Mam, K’iche’, Kaqchikel, Tz’utujil, Poqomchi’, Q’eqchi’ and Ch’orti’ in the Highlands. These cities preserved many aspects of Mayan culture, but would never equal the size or power of the Classic cities.
Colonial era [ edit ]
After arriving in what was named the New World, the Spanish mounted several expeditions to Guatemala, beginning in 1519. Before long, Spanish contact resulted in an epidemic that devastated native populations. During the colonial period, Guatemala was an Audiencia and a Captaincy General of Spain, and a part of New Spain (Mexico). It extended from the modern Mexican states of Tabasco and Chiapas to Costa Rica. This region was not as rich in minerals (gold and silver) as Mexico and Peru, and was therefore not considered to be as important. Its main products were sugarcane, cocoa, blue añil dye, red dye from cochineal insects, and precious woods used in artwork for churches and palaces in Spain.
Post-independence [ edit ]
On September 15, 1821, the Captaincy-general of Guatemala (formed by Chiapas, Guatemala, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Honduras) proclaimed its independence from Spain and its incorporation into the Mexican Empire, which was dissolved two years later. After the collapse of the first Mexican Empire Guatemala formed part of the short-lived United Provinces of Central America. Guatemala’s «Liberal Revolution» came in 1871 under the leadership of Justo Rufino Barrios, who worked to modernize the country, improve trade, and introduce new crops and manufacturing. During this era coffee became an important crop for Guatemala. Barrios had ambitions of reuniting Central America and took the country to war in an unsuccessful attempt to attain this, losing his life on the battlefield in 1885 against forces in El Salvador. From 1898 to 1920, Guatemala was ruled by the dictator Manuel Estrada Cabrera, whose access to the presidency was helped by the United Fruit Company.
On July 4, 1944, Dictator Jorge Ubico Castañeda was forced to resign his office in response to a wave of protests and a general strike, and from then until the end of a murderous civil war in 1996, Guatemala was subject to a series of coups with massive attendant civil rights abuses. State-sponsored murders of students, human rights activists and the ethnic Mayan peoples, gained Guatemala a terrible reputation around the world. In 1999, U.S. President Bill Clinton stated that the United States was wrong to have provided support to Guatemalan military forces that took part in the brutal civilian killings.
Since the peace accords in 1996, Guatemala has witnessed successive democratic elections.
Climate [ edit ]
Guatemala’s climate is diverse and varies according to the country’s geography. In the lowlands, the climate is tropical and hot, with afternoon thunderstorms that usually reduce the heat a little. In Puerto Barrios, on the Caribbean coast, average temperatures range from 20.1 °C (68.3 °F) in January to 29.5 °C in March, reaching 3,075 mm (121.1 inches) of rain per year. In the mountains, the climate is generally slightly cooler and tends to be less rainy, reaching just 802.1 mm (31.59 inches) in Quetzaltenango. In Guatemala City, the average maximum temperatures is 27 ºC (80.6 ºF) in the months of April and May and lows of 13.2 ºC (55.8 ºF) in January and 2.3 ºC (36.1 ºC) in Quetzaltenango. In the highlands, the rainy season runs from May to October. Due to Guatemala’s location between the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, the country is vulnerable to hurricanes.
Get in [ edit ]
Entry requirements [ edit ]
Valid passports are required of everyone except citizens of the following Central American countries: Nicaragua, Honduras, El Salvador. There is a treaty of free movement between those countries, similar to the Schengen agreement in Europe.
Proof of onward travel is often required by airlines however rarely checked by officials to gain a visa when flying into Guatemala.
By plane [ edit ]
Guatemala’s main airport, La Aurora International Airport (GUA IATA ), is in Guatemala City. International flights arrive mostly from the other Central American countries, United States, Mexico, Colombia and Spain. The airport is a glass-and-concrete edifice with modern shops and duty-free shops that you might expect in any large city. Food options may be somewhat still limited, however. American Airlines, Avianca, Copa, Delta, and United all offer service to Guatemala, albeit at high prices. Iberia also serves Guatemala City.
Guatemala’s secondary airport is situated in Flores (FRS IATA ), Petén. This small airport receives flights from Guatemala City and neighboring Belize.
By car [ edit ]
From Mexico, Honduras and El Salvador access is via the Pan-American Highway. Road access is also possible with more difficulty from Belize.
By bus [ edit ]
There are several bus companies connecting Guatemala to neighboring countries of El Salvador, Honduras, Mexico and Belize. Some of the companies continue onwards towards through the rest of the Central American isthmus towards Panama via San Jose and Managua from San Salvador and Tegucigalpa or San Pedro Sula. International buses are usually first class pullman services in newer Marcopolo, Mercedes or Volvo type of coaches and operate on limited schedules (usually early morning departures) with limited number of stops. Except Adrenalina Tours and Grupo ADO addresses given are in Guatemala City:
By boat [ edit ]
There are several ferries to and from Puerto Barrios and Livingston, and Punta Gorda, Belize.
Get around [ edit ]
By bus [ edit ]
If traveling by bus, there are two classes of buses. The pullman (first class) buses (pullman, expreso, especiales, primera clase), if available, are usually direct routes and are the best option for most. These buses vary in the quality of vehicles. They range from the older MC coaches (older Greyhound buses from the U.S.) to the newer single or double deck Marcopolo or Volvo coaches and anything similar in between. They are comfortable, have washrooms/toilets and will generally show movies, which may or may not be in English with Spanish subtitles (or vice versa) with reserved seating. Others may even offer a drink and a little snack. They may make limited scheduled stops (semi-directo) at specific places en route otherwise they make no stops en-route. They operate on limited schedules and usually from their own offices or terminals rather than from a central bus station in the cities they serve. The first class pullmans are more common on the route between Guatemala City and Flores and on to neighboring countries but also from Guatemala City to Coban, Huehuetenango, Chiquimula and Quetzaltenango (Xelaju) as well.
The most common option are the second class buses (chicken bus, camionetas, autobuses de parrillas, polleros, mini-bus, microbus); the more ubiquitous are the decommissioned U.S. school buses painted in all sorts of funky colors and patterns. Other second class buses exist in a Toyota Coaster mini-bus, a smaller Toyota «HiAce» van (referred to as «microbus» or «minibus«) or a pick up truck (picop) or some similar type of vehicle that functions the same way as the «chicken bus«. Second class bus routes are more frequent and reach more places for a cheaper fare than first class pullman but they also take considerably longer to travel over longer distances (such as from Todo los Santos to Guatemala City) with multiple stops and maybe multiple transfers. They are the most common way for most to travel in and they get crowded with everything and everyone crammed in. Large cargo and luggage usually get placed on and tied to the roof, including live chickens going to market, hence the term «chicken bus«. To a visitor riding along, the bus may appear to be full but to the driver and his ayudante (helper or conductor) there’s always room for another person even if the space is just a sliver between two people. If it’s physically impossible to squeeze on more people there’s always room up on the roof or cling on from the outside as the bus barrels down the road. The chicken buses operate from a central bus terminal (Terminal de Autobuses) which usually is nothing more than open lot next to an informal market with no ticket offices. You just walk into the lot, hop on and grab a seat. Once the bus is underway and start picking up others along the streets an ayudante will eventually come around to collect the fares (usually Q10 per hour) and he’s usually very good at knowing who paid and giving change, which may not come right away. Check with fellow passengers on what the fare is to a particular destination as it may be more or less than Q10.
A third option many travelers opt for is the tourist shuttle which costs 5 to 15x more than buses but they are more comfortable to ride in and quicker in getting there. They can be in a Toyota HiAce van, a larger Toyota Coaster minibus or some similar type of vehicle. They can make scheduled stops for bathroom and eating breaks at a restaurant en route but otherwise they run non-stop. They typically connect between different popular tourist destinations such as Antigua, Guatemala City, La Aurora Airport, Panajachel, Chichicastenango (on market days), Lanquin, San Cristobal de las Casas, Ruinas de Copan, etc. Tickets on these are available at the travel agencies in the tourist towns they serve. Pick-up and drop off may be at a their office where everybody meet at or is pre-arranged for pick-up and drop off at hotels and hostels.
See the By bus under Get in in the above and in the Guatemala City article for a list of available bus companies.
By plane [ edit ]
Regular domestic flights only operate between Guatemala City GUA IATA and Flores FRS IATA on Transportes Aéreos Guatemaltecos (TAG) and Avianca Guatemala (formerly Taca Regional and Aviateca). TAG also offer flights from Guatemala City to Puerto Barrios.
Talk [ edit ]
Spanish is the official language of Guatemala and is spoken by almost everyone.
The local vernacular is Guatemalan Spanish, which has extensive loanwords from Mayan languages and has different grammatical rules. The most familiar form of Spanish spoken among good friends is the «tú» and «vos» form, but varies between regions. It is considered rude and very informal if used with someone that you do not know. As a tourist, it is safer to stick with the «usted» form. However, don’t be surprised if some homestay families and some language teachers jump right into using the «tú» or «vos» form. If they do, you may respond in kind.
Over twenty-one indigenous languages are spoken, especially in the rural corners of the country. The most commonly spoken indigenous languages are K’iche’ (the second most widely spoken language in the country), Q’eqchi’, and Kaqchikel.
See [ edit ]
Maya ruins are the key attractions in the country and the most notable are El Mirador, perhaps the cradle of Maya civilisation, and Tikal.
Volcanoes [ edit ]
Guatemala has a lot of volcanoes, many of them over 3,000 m high.
Do [ edit ]
Guatemala is rich in natural beauty and travel opportunities, it’s a country that offers so much to those willing to step off the beaten track for a little while.
Antigua Guatemala is often regarded as the travellers’ hub, a crumbling, picture-perfect Central American town ringed by volcanoes. From here you can take a hike up Volcano Pacaya, take a bus to the bustling market of Chichicastenango, or sip some coffee in a street-side cafe and watch the world go by.
Lake Atitlan (or Lago de Atitlán) is another frequent stop on any visitors itinerary. A volcano-rimmed lake with plenty of backpacker hostels and Mayan villages that dot the shores.
Flores in Guatemala’s wild north is a tourist friendly island in the middle of Lake Petén Itzá. From here you can take a bus ride to one of the best preserved Mayan ruins in the world, Tikal. Howler monkeys and dense jungle make walking around the ruins an adventure.
Rio Dulce The Rio Dulce is a majestic emerald river, sandwiched between Belize & Honduras, which sweeps out to the Caribbean. The Rio Dulce area consists of two towns on either side of one of the largest bridges in Central America, Fronteras & El Relleno. Rio Dulce is a haven for sailors and backpackers, with plenty to do and to see. Finca Paraiso is a hot springs waterfall which is like having a spa day in the jungle; Castillo San Felipe de Lara is a historical fort site and an inexpensive way to spend the afternoon touring the castle and swimming in Lake Izabal. The many species of Birds & Animals (including manatees) makes Rio Dulce a great spot for birdwatchers, animal lovers & fishing fans.
Buy [ edit ]
Money [ edit ]
Exchange rates for Guatemalan quetzales
As of January 2022:
Exchange rates fluctuate. Current rates for these and other currencies are available from XE.com
The local currency is the quetzal (Q, ISO code: GTQ) which is named after the national bird, which has ancient and mythic connotations even today. U.S. dollars are widely accepted and can be exchanged in most small towns. ATMs can be found in the major towns but do not expect to find them in every tourist spot. It is fairly easy to find your self in a town without an ATM or a place to change money.
Do not expect to be able to easily exchange travelers checks to Guatemala. You might find a few places willing to accept checks issued by American Express but all other types are universally turned down. Even major banks in Guatemala City do not accept Visa travelers checks.
It is common to use dollars in tourist areas. You will most likely have difficulties in changing other currencies than U.S. dollars, but euros are becoming increasingly common.
Shopping [ edit ]
It is common to bargain for most purchases in the open air market. Though you may be able to bargain in other places, be aware that chain-owned shops have fixed prices (you are no more likely to bargain in a Guatemalan Radio Shack than an American one). These are some characteristically Guatemalan things you might consider buying here:
Eat [ edit ]
A typical breakfast is frijoles and rice with coffee of course.
The type of food really depends on how much you want to spend and what type of place you want to spend it at. You can get almost any type of food at the main tourist locations. In the aldeas (small towns) your choices are mostly limited to those items listed above. Guatemalan food differs from Mexican food in that it is a lot less spicy, and chillies are generally served in a separate dish from the main course to be added as desired, rather than included in the food.
Drink [ edit ]
Popular Guatemalan beers are Gallo (lager, by far the most popular with Guatemalans), Victoria, Brahva (a light pilsner style), Moza (dark bock), Cabro, Monte Carlo (premium), and Dorada. Don’t be surprised if you get salt and lemon with your beer. It’s a custom to put some salt on the toes of the bottle, and screw out the lemon in the beer. Sometimes it is mixed with V8 vegetable juice, and the concoction is called michelada.
Guatemala produces a number of rums, including the superb Ron Zacapa Centenario which is aged up to 30 years.
Tequila is a very popular drink in Guatemala.
If you order a bottled drink, you will normally get a tissue to clean the bottle. Coca-Cola and Pepsi-type products are available, plus many from local soft drink manufacturers.
Sleep [ edit ]
You will likely find cheap hotels (
US$10-15 a night) in every town or village in Guatemala. In the main tourist areas, there are also many high quality hotels (US$200 a night).
Hostels with shared rooms are available in more than 15 towns and villages throughout the country. Very good rated hostels cost about US$6-15 (March 2022).
Learn [ edit ]
Guatemala is a great place to learn Spanish. The prices are low, and Guatemalan Spanish is considered pleasing. Antigua has the most Spanish schools and is also the most popular place for tourists. But if studying Spanish is your main concern, you might be better off elsewhere, because you can actually go around in Antigua for a whole day without hearing anything but English.
Because of this, many language students head towards Quetzaltenango in the Western Highlands, where a wide range of language schools also offer Spanish language courses (some quite inexpensive). Another alternative is San Pedro la Laguna, seated by Lake Atitlan.
Work [ edit ]
There are various volunteering opportunities around the country. If you want to be useful to the local community, it is always a better idea to spend some time understanding what are the real needs of said community, instead of paying to help. If an organization only wants your help if you pay them, then what they really want is your money, not your help. Find a grassroots organization, school or community hall that would like your time and help there instead, or leave a small donation in kind or money.
Cope [ edit ]
If traveling from Mexico, be aware that Guatemala does not observe Daylight Savings Time. Because Guatemala is generally to the east of Mexico, this creates the quite unusual situation of turning the clock back instead of forward while traveling eastward. Both southern Mexico and Guatemala are on the same time when Daylight Savings is not in effect.
Newspapers and Magazines for tourists:
Stay safe [ edit ]
Guatemala has a reputation for being a dangerous country — a reputation that’s not entirely unwarranted, but the average traveller should not be too overly concerned or cautious of their surroundings.
A lot of the crime is drug and gang related, which, to a significant extent, doesn’t affect tourists that much. As long as you apply a modicum of common sense and blend in with the locals, your visit will be trouble-free.
Understand that Guatemala is still recovering from a brutal thirty-year civil war and the war has badly impacted Guatemalan society in many ways; many Guatemalans have been pushed into poverty, economic conditions are far from ideal, and the rule of law is still weak. It’ll take some time for things to get back to normal.
Crime [ edit ]
Guatemala is one of the most criminalised countries in the world; therefore the crime rate is high. Guatemala has one of the highest rates of violent crime in Latin America and reports of theft, carjackings, armed robberies, and sexual assault, are depressingly common.
As a visitor, you may instantly attract the attention of Guatemalan criminals because they normally assume that all foreign visitors are «wealthy». To deter the attention of Guatemalan criminals, don’t display signs of affluence, don’t flash electronic gadgets (cameras, mobile phones, laptops, and the like), and refrain from using electronic gadgets in public. Cell phone theft is the most common crime in Guatemala. Also, it is dangerous to travel at nightime. Doing so significantly increases your risk of being a crime victim.
In the unlikely event you have been threatened by a robber, do not feel tempted to resist or fight back. Cooperate with the robber and give them whatever they want from you. Tourists have been shot and killed for resisting criminals. You should know that many robbers are off-duty police officers.
While it may be tempting to experience a ride on a local bus, refrain from riding on public buses. Buses are routinely targeted by gangs and incidents of armed robbery are not uncommon on public buses. Some countries, such as the United States, forbid their diplomatic staff from using Guatemalan buses.
Express kidnappings are common in Guatemala. As obvious as it may sound, do not hail taxis on the street. Criminal taxi drivers may pick up their associates along the way and force you into doing something you’re not comfortable with (e.g. forcing you to withdraw large sums of money from the ATM).
If you must get around a city, only use trusted, pre-arranged modes of transportation. Your hotel can help you out with this. You may also use radio-dispatched taxis (Taxi Amarillo) and Uber.
Do not travel to areas close to Guatemala’s borders with Mexico, El Salvador, and Belize. Border areas see high levels of criminal and drug-trafficking activity and passing vehicles are routinely targeted by gangs who take people hostage, rob people at gunpoint, and demand ransom payments. You will immediately stick out like a sore thumb if you’re driving a vehicle registered to a foreign country. There’s very little law enforcement can do to help out; gangs operating in border areas far too powerful and influential to be dealt with.
Do not go to the most dangerous areas of Guatemala City (zones 3, 6, 12, 18, 19, and 21).
Corruption [ edit ]
Guatemala is one of the most corrupt countries in the world and the problem seems to be getting worse year by year. According to Transparency International, Guatemala is the third most corrupt country in Latin America. The country’s rule of law is highly weak and corrupt.
The police are woefully ineffective and its safe to say that they are not to be trusted under any circumstances. Guatemalans themselves distrust the police force and often write off them off as inefficient, corrupt, and abusive.
Their response to crimes is severely limited by bureaucracy, inadequate training, corruption, and a lackluster justice system. Don’t expect to be taken seriously if you’re a crime victim and expect no help if you’re not competent in Spanish.
Miscellaneous [ edit ]
One of the best things about Guatemala is the abundance of natural beauty and numerous treks. Some of these are notorious for robberies (Volcan de Agua, trails around Lago de Atitlán, Volcán de Pacaya). Always ask around about the situation before embarking blindly. Inguat, locals, and fellow travelers are safe bets for information. Traveling in groups during daylight sometimes decreases the risk, but not always.
Traffic can be dangerous. You will encounter many one-lane roads (one lane each way) and drivers are apt to swerve back and forth, avoiding potholes and bumps along the way. There are also various multiple lane highways. Traffic in Guatemala City and surrounding metropolitan areas during rush hour is very slow, but general driving everywhere is usually very fast (average speeds of up to 100 km/h (60 mph) in some city roads).
Demonstrations and other forms of political protest frequently turn violent.
Stay healthy [ edit ]
Drink only purified water (Agua Pura Salvavidas is recommended by most of hospitals and hotels).
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control states that malaria risk exists in rural areas at altitudes lower than 1,500 m, with no risk in Antigua or Lake Atitlán. Preventative anti-malarial medication can and should be purchased ahead of visiting malaria-endemic areas.
Dengue fever is endemic throughout Guatemala.
Hepatitis A&B vaccinations are recommended.
Respect [ edit ]
Much of what is considered good manners in Latin and South America is applicable to Guatemala. The various tips found in the respect section of the Latin America article will come in handy when you visit the country.
Address people you don’t know in a formal manner (Señor, Señora, Usted), and greet people in the following way:
You’ll encounter this in more suburban, rural areas. Native Guatemalans are raised to greet strangers formally.
Photography [ edit ]
Do not take photographs of children and/or women without explicit permission, especially if you’re visiting indigenous communities. Doing so would get many Guatemalans to (incorrectly) think that you are either a kidnapper or a rapist. People have been attacked for doing this. In Guatemala, many children have been kidnapped and exploited on the black market, and sexual assault continues to be a heartbreaking social problem in the country.
In major cities, people are somewhat more open towards being photographed, but still, be cautious. If in doubt, always ask and respect the wishes of the person you wish to photograph.
Connect [ edit ]
Internet [ edit ]
Internet access is widely available. Even most of the more remote areas have some type of internet access available. Many larger areas also have WiFi. All of the Camperos chicken/pizza restaurants (which are numerous) offer free WiFi, as well as many other restaurants and cafes. Some hotels may also offer computer banks with internet access. Just ask and you eventually will find some sort of free access.
Mobile internet access [ edit ]
Use the local SIM cards (roughly Q25) and the prepaid access plans, which generally come in lots of data and include a number of minutes for domestic (and US) calls. There are only two mobile carriers in Guatemala: Tigo and Claro.
Tigo offers as of March 2022:
• 1 week including 3.3GB for Q30
• 15 days including 5GB for Q50
Tigo Website with more options.
Claro has as of March 2022:
• 1 week including 4GB for Q30
• 15 days including 6GB for Q50
• 30 days including 4GB for Q50 (without included domestic calls)
Claro website for other rates.
Here is a table for the settings and activation options for the providers.
| Provider | Configuration details | Activation instructions |
|---|---|---|
| TIGO Guatemala | APN: internet.tigo.gt user: any (or blank) pass: any (or blank) | SMS «WAP» to 805 |
| Claro | APN: internet.ideasclaro | SMS «7 dias» to 313 for 7 days. SMS «internet basico» to 313, should give you the settings. Overall, incredibly easy to set up and use. |
Phone [ edit ]
Guatemala’s international calling code is 502. There are no area codes. Phone numbers all have eight digits.
The phone system isn’t great, but it works. Tourists can call abroad from call centers, where you pay by the minute. It is also easy to purchase a calling card to use at public pay phones. The phones there do not accept money, so to use a public phone on the street you must purchase a telephone card. Typically, the cost is around Q8 for a 10 min call to North America. Cell phones are quite cheap and calling to the U.S. through one can get as low as US$0.08 a min. If you are planning to stay for a while and plan to use the phone, you should consider buying a cheap prepaid phone. Wireless nation-wide internet access for laptops is also available as a service from some companies. Telefónica has good coverage with their PCMCIA EV-DO cards.
Post [ edit ]
The postal system is traditionally not reliable and suspended accepting and delivering of almost all mail starting in 2017. This suspension of mail reportedly ended in April 2019.
As of November 2019, the post office still does not accept international bound mail. The post office does have an arrangement with DHL in which normal sized letters and post cards can be mailed from DHL offices for 20Q (a note from the post office may be required for DHL to honour this price). This mail is handled as regular mail once it leaves the country and is handed off to other countries’ post offices.
Go Next [ edit ]
You can cross the land border to Belize, Mexico, El Salvador and Honduras.
Guatemala City has direct low-cost flights to El Salvador, Costa Rica, Mexico and to the United States. (updated March 2022)
Where is Guatemala Located?
Where is Guatemala located on the map? Guatemala is an independent nation located in North America. Check out the following images to see location of Guatemala on maps.
Guatemala Location in World Map
Borders and regions
The country protrudes into the country with a partly square area to the north. Belize is to the east of it. To the north and west lies Mexico. The borders in the south lead to El Salvador and Honduras. Guatemala can be divided geographically into three zones: the Pacific coast, the mountainous highlands and the lowlands of Petén.
The pacific coast
The Pacific coast is also called Costa Sur, meaning south coast. Forest grows here, which sheds its leaves in the dry season (i.e. not an evergreen rainforest ). The coast is joined by the slightly higher Boca Costa, the coastal mouth. There is cloud forest here: it is very humid here, the forest is almost constantly shrouded in fog.
The name of Guatemala
Country of the volcanoes
There are repeated earthquakes and volcanic eruptions in Guatemala. The reason for this is the meeting of two tectonic plates. There are 37 volcanoes in Guatemala, four of which are still active.
Mountains
The central highlands take up a quarter of the country’s area. In the northwest runs the Sierra de los Cuchumatanes mountain range, south of it the Sierra Madre, which comes from Mexico. Several volcanoes belong to it, including the Tajumulco, which is also the highest mountain in Guatemala. In the highlands there are grass areas and rainforest. The highlands are the most densely populated area in the country. The capital, Guatemala City, is also here.
A drier area begins east of Guatemala City. Some of the grass areas even merge into a thorn bush savanna. On the other hand, around Lake Izabal and on the Caribbean coast it is damp again. Tropical rainforest grows here. Lake Izabal is the largest lake in Guatemala.
In the north, in Petén, there is a lowland with tropical rainforest. This rainforest, Selva Maya, extends further into Belize and Mexico and is the second largest rainforest area in America (after the Amazon rainforest). This part of Guatemala is rather sparsely populated. Here is also the Petén-Itzá lake, the third largest lake in the country.
Climate
Guatemala is in the tropics. The Pacific coast, the mountainous highlands and the lowlands of Petén differ not only in terms of landscape, but also in terms of climate. It is warmer on the coasts than in the highlands.
The rainy season in the highlands lasts from May to October and brings a lot of rainfall here. The trade wind blows from the northeast and brings the rain with it. Because the clouds are already raining in the north, there is much less precipitation in the higher highlands. Between November and April almost no rain falls in the highlands.
Most of the rain in the country falls on the coasts and in Petén in the north. In the lowlands of Petén the rainy season lasts until December, on the coasts you can hardly distinguish between rainy and dry seasons, it is humid all year round. The tropical rainforest can also thrive here. Guatemala is repeatedly hit by hurricanes, mostly between June and November.
The maximum daily temperatures in Guatemala City range from 22 degrees in December to 29 degrees in May, so they don’t fluctuate much all year round. On the Caribbean coast it is 27 to 31 degrees during the day, so it is a lot hotter. In Flores in the northern lowlands it is even 27 to 33 degrees. For comparison: In Germany, the monthly average temperatures during the day vary at around 3 to 22 degrees.