What is the use of space exploration
What is the use of space exploration
Space Exploration Pays Off Here on Earth
Every so often someone asks the question, «What good does space exploration do for us here on Earth?» It’s one that astronomers, astronauts, space engineers and teachers answer nearly every day.
It’s simple: space exploration pays off in goods, technology, and paychecks. The work is done by people who are paid to do it here on Earth. The money they receive helps them buy food, get homes, cars, and clothing. They pay taxes in their communities, which helps keep schools going, roads paved, and other services that benefit a town or city. The money may be spent to send things «up there», but it gets spent «down here.» It spreads out into the economy.
Another way to look at the «return on investment» for space exploration is that it helps pay the bills right here on the planet. Not only that but the products of space exploration range from the knowledge that gets taught to science research that benefits a wide variety of industries and technology (such as computers, medical devices, etc.) that are used here on Earth to make life better. It’s really a win-win situation for everybody involved.
What are Space Exploration Spin-offs?
The products of space exploration touch lives in more ways than people think. For example, anyone who has ever had a digital x-ray, or a mammogram, or a CAT scan, or been hooked up to a heart monitor, or had specialized heart surgery to clear blockages in their veins, they’ve benefited from technology first built for use in space. Medicine and medical tests and procedures are HUGE beneficiaries of space exploration technology and techniques. Mammograms to detect breast cancer are another good example.
Farming techniques, food production and the creation of new medicines are also impacted by space exploration technologies. This directly benefits all of us, whether we are food producers or simply food and medicine consumers. Each year NASA (and other space agencies) share their «spinoffs», reinforcing the very real role that they play in everyday lives.
Talk to the World, Thanks to Space Exploration
Cell phones are used all over Earth. They use\ processes and materials developed for space-age communication. They «talk» to GPS satellites circling our planet, giving location data. There are other satellites monitoring the Sun that warn scientists, astronauts, and satellite owners of upcoming space weather «storms» that could affect communications infrastructure.
Users are reading this story on a computer, hooked up to a worldwide network, all made from materials and processes developed for sending science results around the world. Many people watch television using data transferred via satellites stationed in space around the world.
Entertain Yourself
Personal entertainment electronics are also a spinoff from the space age. The music people listen to on personal players is delivered as digital data: ones and zeroes, the same as any other data delivered via computers. It’s also the same method that helps deliver information from weather satellites, orbiting telescopes, and spacecraft at other planets. Space exploration required the ability to transform information into data that our machines can read. Those same machines power industries, homes, education, medicine, and many other things.
Explore Distant Horizons
Travel much? The airplanes we fly in, the cars we drive, the trains we ride in and the boats we sail on all use space-age technology to navigate. Their construction is influenced by lighter materials used to build spacecraft and rockets. Although few of us are able to travel to space, our understanding of it is enlarged by the use of orbiting space telescopes and probes that explore other worlds. For example, every day or so, new images come to Earth from Mars, sent by robotic probes that deliver new views and studies for scientists to analyze. People also explore the sea bottoms of our own planet using craft influenced by the life support systems needed to survive in space.
What Does All This Cost?
There are countless examples of space exploration benefits that we could discuss. But, the next big question people ask is «How much does this cost us?»
As a part of the general budget, NASA’s portion is less than one percent of the total federal spending in the U.S. That’s far, far less than military spending, infrastructure costs, and other expenses the government takes on. It gets us many things in our daily lives that we never connected to space, from cellphone cameras to artificial limbs, cordless tools, memory foam, smoke detectors, and much more.
Future Exploration
In the future, as humans spread out to space, the investment in space exploration technologies such as new rockets and light sails will continue to spur jobs and growth on Earth. As always, the money spent to get «out there» will be spent right here on the planet.
List of Benefits of space exploration
The scientific study of space using especially developed technology is called space exploration. In this post, you’ll learn about the Benefits of Space Exploration.
Let’s Check it out..
Do you know that all-stars, the sun, the Moon, the earth, all planets, and satellites are called heavenly bodies? The heavenly bodies are moving in an unimaginable vast space universe. The sun, the planets, and their moons are the largest objects in the solar system. But asteroids and comets are the smaller parts of the solar system. We have already studied the solar system and planets.
What beyond our solar system?
We know that our solar system is a part of the universe. The universe is immensely vast. Scientists tell that the universe is expanding. They also tell that there are more than 200,000,000,000 billion stars in the universe. Many questions may arise in our mind as: What is the universe? How did it begin?
Let us try to find the answers to these questions about the universe. The universe is all of space and everything in it. Most of the universe is empty space. Our solar system is an extremely small part of the universe. Many theories are given to explain the origin of the universe. These theories are the results of human efforts in understanding the nature and origin of the universe.
The big Bang theory
According to Islam and other Ibrahimic religions, the universe was created by Allah. Scientists have been presenting different theories of the creation of the universe from time to time. One of these theories is “The big bang theory “.According to this theory: About 10 to 20 billion years ago, the universe was packed into one giant fireball. Then a tremendous explosion is known as the Big Bang.
This explosion hurled matter and energy in all directions. After the big bang, the universe assumed the form of huge clouds of extremely hot, expanding, and contracting gases. With the passage of time, the matter cooled: the force of gravity pulled together the particles of matter to form stars and galaxies. The Big Bang theory was first proposed in 1927 by a priest, George Lamaitre of Belgium. This theory was supported by the discoveries of Edwin Hubble and Nobel prize-winning scientists Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson.
Although the Big Bang theory is widely accepted, it probably will never be proved. It cannot answer many questions about the occurrence of the Big Bang. Knowing about space is one of the top priorities of development. Scientists have been using telescopes to look into space to study space objects for a long.
Nowadays many more techniques and facilities are available for further research about space. Telescope, spectroscope, spacecraft, etc are some of the latest technologies in this regard. In this section, we will study the technological tools used in space exploration and their benefits in everyday life. Some of these tools are given:
Spectroscope
A spectroscope is an instrument that is used to examine different wavelengths (colors) of light. It consists of a series of prisms that split white light into different colors. The set of different colors obtained in this way is called a spectrum. The wavelengths of light coming from the stars help the scientists to know about the elements and compounds present in the stars. Spectroscopes are mostly attached to the telescopes.
Spacecraft:
Spacecraft is a vehicle designed to travel in space. It is used for different purposes like communication, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo in space. There are two major classes of spacecraft; robotic spacecraft and manned spacecraft. Robotic spacecraft are sent into space for a collection of data about space, planets, and other heavenly bodies such as asteroids. A robotic spacecraft is controlled from the center of the earth.
Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 were two robotic spacecraft that was used for collecting data about planets Mars and Jupiter. Manned spacecraft carry humans and equipment to space. These spacecraft are larger and have specially built compartments that have the facilities necessary for human survival such as oxygen, pressurized cabins, food, water, and specially built bathrooms. They also have a special structure to protect from dangerous radiations which are very intense in space.
What is a Space station?
For a very long stay in space or for performing experiments in space, large spacecraft called space stations are used. A space station is built in space by carrying its many small parts to space and then assembling them there.
It has more facilities for prolonged living in space. It may have a television for entertainment, bags for sleeping, an exercise machine, and a kitchen for fresh food. One important part of a space station is the scientific laboratory where astronauts perform such experiments that cannot be done on earth because of its gravity.
Nowadays a large space station orbits the earth. Russians, Americans, and other scientists jointly work in this space station. This is called an international space station.
Space shuttle
It is an especially developed manned spacecraft that can be used many times. It is sent into space with the help of a rocket. It carries scientists and equipment. It docks with the space station to transfer its load. After performing its task, it returns and lands back on earth like an airplane.
Benefits of space exploration (video)
Special technologies developed for space are now being used on earth to improve the quality of life.A few examples are as follows:
Benefits of space exploration list
Health and Medicine:
Global navigation:
Weather forecast and prediction of natural calamities:
The accurate and reliable weather reports on an hourly basis are possible because of weather satellites in the space. These satellites have also made it easy to predict natural calamities such as floods, storms, tornadoes, and hurricanes.
Advanced electronics and computers:
Electronic and computer systems were developed mainly to facilitate space exploration. Satellites are fitted with electronic and computer systems that can perform functions automatically. Nowadays many items are made in factories automatically or by controlled robots.
Locating minerals, fossil fuels, and water reserves:
Deeply buried precious ores of minerals, fossil fuels ( coal, petroleum, and natural gas ), and underground water reserves can be located with the help of satellites. This study is known as remote sensing.
How do astronauts survive and research in space?
For living in space, astronauts need basic necessities (air, food, water, shelter, and warmth) for survival and a suitable compartment for personal comfort on the spacecraft. For this purpose, large space stations have been built in the space. Each space station consists of two main sections.
The unprotected human body cannot survive more than a few minutes in space. As the liquid boils at a lower temperature at lower pressure, the water in the human body can begin to boil at low pressure result in immediate death.
The astronauts wear a specially designed suit called a spacesuit to protect them from such hazards when they go out into space. For breathing in space, they carry air tanks with them that contain pressurized oxygen and nitrogen. their suits circulate the air to their helmets and throughout the suit so that they can breathe. special foods are prepared and packaged for easier transportation and a variety of tastes for the astronauts.
Problems Created by space exploration and their solutions:
Space sickness, effects of weightlessness, conditions resulting from exposure to radiation, and many unwanted side effects are the problems created during the stay in space. Pollution caused by the burning of rocket fuel and disposal of rocket parts etc is one of the major problems created by space exploration.
Technological Tools Used in Space
A few of the tools which are used in space exploration programs are mentioned as follows:
Space rocket: 
Space rocket is the means of transporting spacecraft, space shuttles, and space stations into space.
Rocket Launching Pads:
The sites from which rockets are launched into space are called Rocket Launching Pads. These are specially built platforms for firing rockets into space. They can withstand extremely high temperatures and large forces produced by rocket exhausts.
Telecommunication system:
Rockets and spacecraft are provided with a telecommunication system so that the space crew in the rocket capsule can communicate with each other and with the Earth stations.
Ground Mission Control Stations:
Ground stations receive and process the information from satellites to monitor and guide their motion in space. The main tasks in ground mission control are as follows:
Continuously reporting the position of the satellite or space probe.
Receiving signals from a spacecraft and decoding them into useful information from the scientists is known as monitoring. Progress of a space mission is closely observed and necessary introductions are issued from time to time.
New Technologies Developed on the Earth as a Result of Exploration of space
We have learned in the section above about the technologies and benefits of space exploration. In order to reiterate some of the technologies developed on the Earth as a result of space exploration are listed below.
How we benefit from space exploration
Most of us never think about outer space and its intimate connection to our daily lives. It’s a conversation usually reserved for science fiction. But there is more to it than just rockets and stardust. Space impacts almost every aspect of our lives. The development of the space industry has transformed our society from a ginormous list of products that we take for granted to the medical miracles that shape our quality of life.
Technology from Apollo
During the 1960s, the American people had a dream of putting a man on the moon. New technologies needed to be invented in order to achieve this monumental goal. This effort developed technologies that were incorporated into the fabric of our lives. NASA led the way and collaborated with thousands of partners to make it happen. The result is a multitude of products that stem from NASA’s research and discoveries.
A large part of this has to do with NASA and how they treat the technology. Because NASA is a government agency and our tax dollars are used to pay for it, patents and technologies are available to the American people. There is an entire arm of NASA dedicated to sharing new scientific discoveries, patents, and spinoff technologies to businesses.
This is called the NASA Technology Transfer Program. It operates under a primary charter:
“To provide for research into problems of flight within and outside the earth’s atmosphere, and for other purposes.” — NASA
This program has led to all kinds of technology that has entered our lives that we don’t connect to space.
Obvious space-related products
We understand the connection to space for some products, like our cell phones. Many of us know that our signals come from satellites, duh. But did you know that the camera on your phone was invented to take pictures while in space? Other obvious technologies include solar cell technology for satellites, hyperthermia-preventing space blankets, and freeze-dried food to feed astronauts.
Side note: How many of us think of freeze-dried ice cream when we think of astronaut food? Did you know that the iconic dessert has no record of making it to space? It was developed by Whirlpool Corporation who is one example of the many partnerships with NASA. This chalky treat was strictly a novel marketing product that was sold to thousands, if not millions, of children in gift shops but was never recorded to have been eaten by an astronaut.
Not so obvious products
Each step on our space journey resulted in giant leaps of technology here on earth. The Apollo program gave birth to products such as cordless vacuums that were developed to suck up moon dust and wireless headsets for hands-free communication. Did you know that baby formula is the result of developing a nutritious astronaut food for space travel?
Names that we associate with everyday products have used space technology to improve their products or create new ones.
• Goodyear tires are made from the super strong parachute material that brought our astronauts back to earth.
• Speedo swimwear used space technology to improve the performance of their suits to the point that they were banned from use in competitions.
• Temperpedic memory foam mattress was a spinoff from the packing used in the shuttles to keep equipment and astronauts safe during its bumping ride into the heavens.
• LASIK was developed because of the strain an astronaut’s eyes experience in their non-gravity environment.
• Pillsbury developed systems for food safety that we use today.
• Nestle utilized freeze-dried food techniques.
The list of products is extensive and includes LEDs, laptops, the computer mouse, water and air purifiers, athletic shoes, home insulation, baby food, ear thermometers, fire fighter gear, heart pumps, cordless tools, Invisible braces, GPS, and the list goes on.
More than toys and tires.
Each leap added more life-altering developments that we didn’t even notice. The space shuttle is responsible for grooved pavement on highways to reduce hydroplaning. Workout gym equipment was developed to keep astronauts healthy during long stays on the International Space Station. How many lives have these saved?
The medical miracles that are born in space impact our quality of life in unexpected ways. Medical advances that were designed to keep astronauts healthy are keeping everyday humans healthy.
Here are a few medical marvels that you may not have known were space related:
• The scratch resistant coating on your eyeglasses are a result of a coating developed for space suit helmets.
• Insulin pumps were created to monitor an astronauts’ health and sugar levels.
• CAT scans and MRI scans are the result of the technology develop for scanning the moon.
• Robotic advancements for the International Space Station has led to new prosthetics and artificial limbs that keep people moving and thriving.
• Cochlear implants, developed by a NASA scientist, have help over 320,000 people with hearing loss.
Space technology in our future
Research is in full swing for all kinds of manufacturing in space. We cannot take many of the supplies that we will need to live on the Moon or Mars. Supplies will need to be replaced with what is available…out there. Huge strides have been made as we are learning how to do that.
Many compounds and organism growth react differently without gravity. The results could be new cures and new treatments in the future. One company that assists these efforts is Space Tango in Lexington, KY. They assist researchers and companies set up biomedical experiments in space. They have a long-standing partnership with LambdaVision that is researching and developing the manufacturing process for a protein-based artificial retina that could restore vision for patients who would otherwise be unable to see.
Another exciting technology is in 3D printing. 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, provides the freedom to create the tools and parts we will need for our travels beyond earth. The use of this technology has exploded during the last decade. Additive manufacturing prints three-dimensional objects one superfine layer at a time.
By using this technology, replacement parts won’t require expensive molds, milling, machining, carving, or shaping. It is a precise construction with little waste. Metal, plastic, concrete, ceramic, composites, glass, and even food can printed into new creations. Large 3D printers may build habitats and buildings on Mars using the local materials. This technology is used on earth to print everything from jet engines to affordable housing.
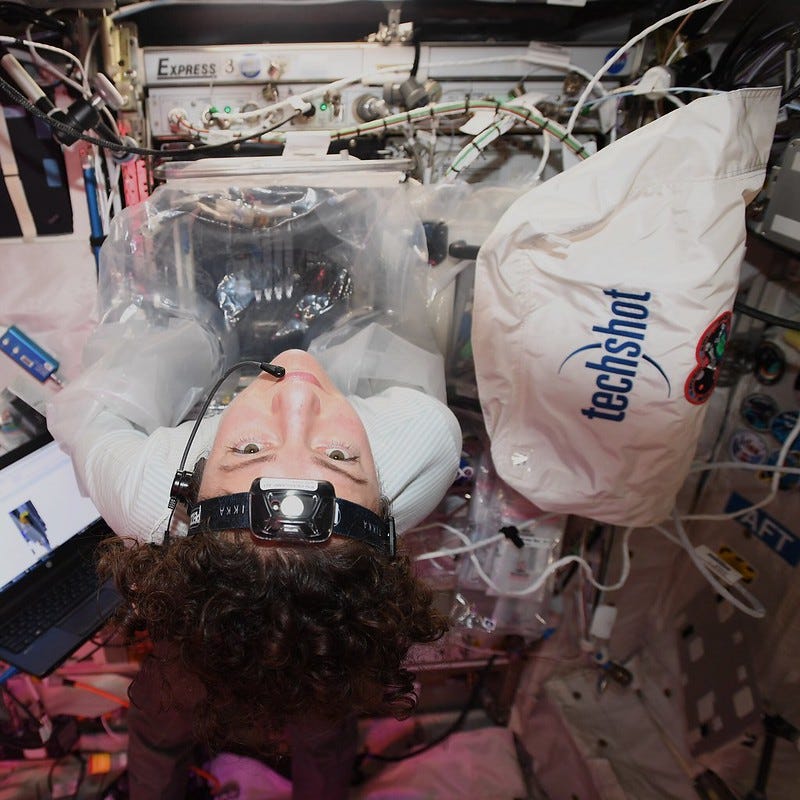
This technology is also being studied to print human organs. This January, Techshot Inc., a company outside of Louisville, was able to successfully print with human heart cells in space using a bioprinter. They say that doing this process with gravity is a lot like 3D printing with water. The network of soft tissues of collapse on themselves in gravity. However, in space, this process works so much better.
Imagine, making a replacement heart from your own cells. In a decade or two, organ rejection could possibly be a thing of the past. At this time, almost 114,000 people in the United States are currently on the waiting list for a lifesaving organ transplant. Twenty people die every day while waiting for a transplant. The ability to print human parts will revolutionize medicine as we know it.
The biggest impact may be in fuel. In order to get to Mars, we will need to be able to produce fuel with the materials found in space. There were no dinosaurs on the moon, so other fuels will be developed. The most likely will be hydrogen-based fuel derived from water. This will ultimately eliminate our dependence on fossil fuels here on earth.
Why should we care about space exploration? Technology innovations that effect everyday life are the result of our aspirations to break free of gravity and explore beyond our planet. This is a small part of what has been achieved without anyone walking on the Moon in the past 48 years. Imagine what would happen if we did.
10 Reasons Why Space Exploration Matters to You
By: Patrick J. Kiger | Updated: Jul 14, 2022
At the time of the moon landing in 1969, many people envisioned that by the beginning of the 21st century, space travel would become routine, and we would be visiting other planets in our solar system and perhaps even daring to venture into interstellar space.
That future didn’t arrive as planned. In fact, humans haven’t made it any deeper into space than when we landed the moon in the late 1960s and early 1970s, though we have operated a manned orbital outpost, the International Space Station, which has been continuously occupied for more than two decades [source: Howell]. NASA currently is planning to resume human missions to the moon in the mid-to-late 2020s, as a prelude to astronauts eventually traveling to Mars [source: Dvorsky].
We’ve also seen the rise of private space entrepreneurs such as Elon Musk, who has described his dream of building a rocket capable of reaching Mars and supporting a permanent human settlement there [source: Torchinsky]. And other countries are looking to reach Mars as well. China, for example, aims to send its astronauts to the Red Planet by 2033 [source: Kharpal].
But those who’ve long dreamed of humans becoming a truly spacefaring race argue that exploring space provides down-to-earth benefits in areas such as health, mining and security. And more inspirational benefits, too. Here are some of the most compelling arguments for continuing the exploration of space.
10: Protection From a Catastrophic Asteroid
If we don’t want to go the way of the dinosaurs someday, we need to protect ourselves against the threat of being hit by a big asteroid. According to NASA, typically about once every 10,000 years, a rocky or iron asteroid the size of a football field could smash into our planet’s surface and possibly cause tidal waves big enough to inundate coastal areas.
But it’s the real monsters — asteroids about 328 feet (100 meters) across or bigger — that we really have to fear. Such a collision would unleash a firestorm of heated debris and fill the atmosphere with sun-blocking dust, which would wipe out forests and farm fields and starve the human and animal life that it didn’t immediately kill [sources: NASA, NSS].
That’s why it’s vital to develop a way to neutralize such a threat to Earth. NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test, set for launch in late September 2022, will be the first mission to demonstrate a technology called asteroid deflection by kinetic impactor. A robotic spacecraft will be crashed into the binary asteroid system Didymos, in an effort to show that it’s possible to slightly alter the path of an asteroid. That would enable NASA to redirect potential threats to miss Earth [sources: DART, Mann].
9: It Will Lead to More Great Inventions
A very long list of gadgets, materials and processes originally were developed for the U.S. space program but found other applications back on Earth — so many that NASA has an office that looks for ways to repurpose space technology as products. We all know about freeze-dried food, but there are plenty of others. In the 1960s, for example, NASA scientists developed a plastic coated with a metallic reflecting agent. When used in a blanket, it reflects about 80 percent of a user’s body heat back to him or her — an ability that helps accident victims and post-marathon runners to stay warm.
Another more obscure but valuable innovation is nitinol, a flexible but resilient alloy that was developed to enable satellites to spring open after being folded into a rocket. Today, orthodontists equip patients with braces made from the material [source: Independent].
According to NASA, other inventions spawned by the space program include CAT scans, LED lights, memory foam, freeze-dried food, shock absorbing materials used in artificial limbs, the computer mouse and portable computers, and a key nutritional ingredient in baby formula [source: JPL].
8: It Will Be Good for Your Health
The International Space Station alone has generated scores of medical innovations with uses on Earth, such as a method for delivering cancer-fighting medication directly to tumors; gadgetry that a nurse can hold to perform ultrasounds and transmit the results to a doctor thousands of miles away; and a robotic arm that can perform delicate surgery inside an MRI machine.
NASA scientists, in an effort to protect astronauts from losing bone and muscle in the microgravity environment of space, also helped a pharmaceutical company to test Prolia, a drug that today helps protect elderly people from osteoporosis. Although mice and humans don’t have identical physiology or biology, it made sense to test this drug on mice in space, since astronauts lose around 1.5 percent of their bone mineral density each month in microgravity, which correlates to the 1.5 percent yearly bone density loss of an elderly woman on Earth to osteoporosis [source: Kiger].
7: Space Exploration Is Inspirational
If we want a world in which our kids aspire to being great scientists and engineers instead of reality show hosts, rappers or Wall Street financial tycoons, having a great enterprise to attract and inspire them is crucial.
6: It’s Important for National Security
The U.S. needs to detect and prevent a hostile nation or terrorist group from deploying space-based weapons or attacking its navigational, communications and surveillance satellites. And while it and other major powers such as Russia and China are signatories of a 1967 treaty that forbids nations from claiming territory in space, it’s not hard to think of examples of past treaties that were tossed aside when someone saw a benefit in doing so.
Even if the U.S. privatizes much of space exploration, it still wants to ensure that companies can mine the moon or asteroids without worrying that interlopers will usurp their claims or steal their production [source Minter]. That’s why it’s crucial to back up diplomacy with a NASA spacefaring capacity that could be converted to military use, if needed. In 2019, a law passed by Congress with bipartisan support created the U.S. Space Force, a new branch of the U.S. armed forces devoted to protecting U.S. interests in space [source: Space Force].
5: We Need Raw Materials From Space
There’s gold out there in the cosmos, and silver, platinum and other valuable substances, too [source: Letzter]. A lot of attention has been given to a private-sector venture that envisions mining operations on asteroids, but space miners wouldn’t have to go that far to find riches.
The moon, for example, is a potentially lucrative source of helium-3, which is used for certain MRIs and a possible fuel for nuclear power plants. The moon also is believed to be a potential source of rare earth elements such as europium and tantalum, which are in high demand for use in electronics, solar panels and other advanced gadgetry [source: Ouellette].
4: Nations Can Work Together Peacefully
Earlier, we mentioned the ominous notion of international conflict in space. But it doesn’t have to be that way, as evidenced by the cooperation of multiple nations on the International Space Station. And a U.S. space program could allow other countries, large and small, to join in their exploration efforts.
A 2018 paper from NASA points out the benefits of international cooperation. For one, the hefty costs could be spread around. For another, it could forge stronger diplomatic ties between nations such as the U.S. and India, and help create new jobs in both countries, for example.
In 2020, NASA awarded the first contracts to four companies to collect small amounts of lunar regolith, the loose rock and dust that sits atop the surface, when missions to the moon eventually resume in the 2020s. It could be the first step toward mining of raw materials from the moon. «Space resources are the fuel that will propel America and all of humanity to the stars,» Mike Gold, NASA’s then-acting administrator for international and interagency relations, explained at the time [source: NASA].
3: It Could Help Answer a Really Big Question
Nearly two-thirds of Americans (close to 65 percent) believe that intelligent life exists on other planets, according to a 2021 Pew Research Center survey. In general, the public does not view UFOs as a major threat to the country. When asked to think about U.S. national security, 51 percent of Americans say that UFOs are not a threat at all, and 36 percent believe they are a minor threat.
But so far, sweeps of the sky with Earth-based telescopes for signals that might be beacons from distant civilizations have proven fruitless, possibly because the Earth’s atmosphere interferes with such messages reaching us. That’s why searchers for extraterrestrial civilizations are eager for the deployment of more orbital observatories such as the James Webb Space Telescope. That satellite, which was launched on Christmas Day 2021, has the ability to search for the chemical signs of life in the atmospheres of distant planets outside our solar system [sources: Kramer, Howell]. That’s a start, but an even more aggressive space-based effort to look for clues of extraterrestrials might finally help us to answer the question of whether we have company out there.
2: Humans Need to Fulfill Their Urge to Explore
Our primitive ancestors spread from east Africa to all over the planet, and since then, we’ve never stopped moving. We’re running out of fresh territory on Earth, so the only way to meet this ancient urge is to find somewhere new to go — whether it’s making brief jaunts to the moon as a tourist, or signing up for an interstellar voyage that will take multiple generations.
In a speech, to the Bay Area Houston Economic Partnership, former NASA administrator Michael Griffin differentiated between «acceptable reasons» and «real reasons» for space exploration. Acceptable reasons would be issues like economic benefit and national security. But real reasons include concepts like curiosity, competitiveness and monument-building.
«Who among us does not know the wonder and mystery and awe and magic of seeing something, even on television, never seen before, an experience brought back to us by a robotic space mission?» Griffin added that «when we do things for real reasons as opposed to acceptable reasons, we produce our highest achievements.»
1: We May Need to Colonize Space to Survive
19 Advantages and Disadvantages of Space Exploration
One of the reasons why fictional universes like those in Star Wars or Star Trek are popular is because they show us a reality where hope is possible anywhere. In the former, space exploration leads to an independent spirit where the fate of one’s culture and identity are at risk of being overrun by a zealous government. In the latter, humanity overcomes its core problems of conflict, hunger, and poverty to become great explorers of space.
Numerous science-fiction novels and stories over the years show us that exploring space could be exciting and profitable. What we don’t always discuss are the potential dangers and expenses that such an action would bring to us as well. When European settlers came to the Caribbean as explorers, some tribes lost up to 90% of their population because of the introduction of new diseases.
If we were to begin exploring alien worlds or encountering new life, our entire planet could experience the same problems as those island tribes.
That is why it is critical to examine the advantages and disadvantages of space exploration before launching these missions to ensure that we can all achieve the best possible result.
List of the Advantages of Space Exploration
1. Space exploration allows us to prepare for potential hazards.
The universe is a vast place where hidden dangers could be lurking almost anywhere. Even if you consider only our solar system, there are asteroid and comet threats which could devastate our planet if an impact were to occur. Exploring space gives us an opportunity to locate these hazards in advance to prepare an encounter that could help to preserve our race.
Then there are the interstellar items to consider. Oumuamua, or 11/2018 U1, was discovered by the Pan-STARRS1 telescope in 2017 by the University of Hawaii through funding from the Near-Earth Object Observations Program. It was originally thought to be an asteroid, then a comet since it was accelerating, and up to 10 times as long as it was wide. These items could create interstellar impacts as well.
2. It gives us more information about our solar system, galaxy, and universe.
When we take on the effort to start exploring space, then we can discover new truths about our planet and culture simultaneously. The information we obtain from these studies can then be applied to our STEM resources here at home. NASA technologies that were originally developed for space programs include infrared ear thermometers, LED lighting, ventricular-assist devices, anti-icing systems, and even temper foam.
Because it requires us to innovate to reach to the stars, our efforts to solve critical problems create opportunities to make life better here on our planet at the same time.
3. Exploring space is one of the few human endeavors that crosses borders.
There are currently 72 countries who claim to have a space program, but there are only three which have an operating government space agency: China, Russia, and the United States. Despite the political conflicts that occur between these nations, their capability of producing human spaceflight provides the gold standard for future exploration efforts. Only 14 of the 72 nations who operate in this space even have a basic launch capacity and six (adding Europe, India, and Japan) have the capability to launch or recover multiple satellites.
Because of the expenses and resources necessary to achieve space flight, the remaining nations work together with those who have the capability of a full launch to manage this aspect of human existence. This endeavor is one of the few ways that humans from all nations cooperate without conflict.
4. We can see humanity in a different way with space exploration.
Carl Sagan suggested that Voyager 1 take a picture of Earth while it was 4 billion miles away at more than 30 degrees above the ecliptic plane. In that image, our planet appears as a 0.12 pixel crescent. All of our conflicts, political battles, successes, failures, love, loss, and life occur on this one-tenth of a pixel. In the scope of a universal lens, we are but one small point of light amount countless others.
“Look again at that dot,” wrote Sagan. “That’s here. That’s home. That’s us. On it everyone you love, everyone you know, everyone you ever heard of, every human being who ever was, lived out their lives. The aggregate of our joy and suffering, thousands of confident religions, ideologies, and economic doctrines, every hunter and forager, every hero and coward, every creator and destroyer, every king and peasant… every saint and sinner in the history of our species lived there – on a mote of dust suspended in a sunbeam.”
5. Space exploration provides us access to new raw materials.
When we began to launch satellites into space, it allowed us to find new raw material deposits on our planet that we could access to make life easier here. If we apply this technology as an extension to the rest of our solar system, then it gives us the same benefit to find minerals, precious metals, and even new materials that we can use. Although the expense of exploring space is admittedly high, this advantage gives us a way to offset those costs somewhat. There is even the potential that it could become profitable one day if we can provide these efforts with enough capital.
6. Investments into space exploration create real economic benefits at home.
The governments which provide the majority of our space exploration infrastructure employ over 20,000 people per agency who make direct positive economic impacts on their community. There are private companies who look at the potential benefits of this industry and contribute to this advantage as well, such as SpaceX and their thousands of staff.
People from all walks of life contribute to space exploration every day, ranging from astronomers to actual rocket scientists. Even though many of these programs receive taxpayer funding, the wages, manufacturing, and indirect investments contribute over 70% more in overall value at the local level compared to each dollar spent in the United States. These opportunities allows us to explore many different fields of study in addition to what is waiting in the universe as well.
7. Anyone can become a space explorer.
Space exploration doesn’t need to involve starships, space stations, or intergalactic travel. If you own a telescope and can look up at the sky, then you can embrace this element of human existence. Our scientists have taken this advantage to the next level with the Hubble Space Telescope, which has made over 1 million observations in almost 30 years of service. We have made some incredible discoveries with this technology already.
8. Space exploration encourages us to share instead of being selfish.
Being human-first from a space exploration standpoint isn’t about dominating other cultures that we might find waiting for us in the universe. It is a way for us to find common ground outside of our physical appearance, cultural differences, or religious preferences. For far too long, we have allowed ourselves to be consumed by our petty problems instead of looking at the big picture.
If someone is hungry, then we should feed them. If they are cold, then we should clothe them. If they need a job, then we should help to train them. Space exploration unites us in ways that other global efforts do not because we see ourselves as humans first. This advantage won’t solve our problems, but it can shift our attitude toward something that is healthier than our current state.
9. We know more about our planet thanks to our efforts to explore space.
Because space exploration gives us a different perspective, it allows us to look at our planet in a different way. The view from outside of our atmosphere allows us to see the big picture instead of trying to extrapolate information from micro-scale research. This advantage allowed us to discover the problem of ozone depletion in the upper atmosphere, begin the conversations on global warming, and examine the current and future impact of weather pattern changes that may happen because of a changing climate.
Space exploration helps us to look inward as well as outward, helping us all to find the changes that are necessary to keep our planet healthy for our children, grandchildren, and beyond.
List of the Disadvantages of Space Exploration
1. Our current technology makes it dangerous to get into space in the first place.
Several agencies are developing “space tourism” packages that can take people in a comfortable aircraft to the very outer layers of our atmosphere, but that is not an exploration effort. We currently strap astronauts into a vehicle that gets attached to a very large rocket so that there is enough speed available to break the grasp of gravity.
Starting with Theodore Freeman, who was killed in the crash of a T-38 in October 1964, there have been over 20 individuals who lost their lives in the line of duty while advancing U.S. space program interests. There have been two individuals (Gus Grissom and Peter Siebold) who were able to survive a problem that resulted in the loss of a space vehicle.
Manned missions in our solar system could cost 10 times that amount, and that might get us to Mars or one of Jupiter’s moons. Technology advancements in recent years could make this issue cheaper for the next generation, but we should ask ourselves if spending billions on space exploration is the right thing to do if we have people dying of hunger on our planet.
3. Astronauts receive exposure to natural dangers while in space.
If the launching process doesn’t kill you during a manned space exploration effort, then the natural dangers that are present outside of our planet’s atmosphere could become problematic in a variety of ways. The radiation that comes from the sun is a constant danger to astronauts when they are in space, and the weightless environment can change their physical conditioning. Experiments with identical twins, with one staying on our planet and the other spending a lengthy assignment in space, show that there are changes at the cellular and genetic level that occur with space travel as well.
4. Current space exploration efforts could be a one-way trip.
When we sent astronauts to the moon, our technology provided them with a chance to land on the surface and return to their spacecraft. It is possible that we could perform a similar action for asteroids, moons around other planets, and other celestial bodies that do not have an atmosphere. If we are going to start exploring Mars, then that journey could be a one-way trip for the astronauts.
Even if this journey does not become a one-way trip, the amount of time necessary to reach a destination beyond the moon makes it virtually impossible to mount a rescue mission if something goes wrong. Our current vision of space exploration requires perfection to create a successful result.
5. There may not be a reason to start exploring at this time.
Human cultures have always had a fascination with exploring space because it satisfies our need to learn more about the universe. Taking long-distance pictures with the Hubble telescope is not the same as visiting the location in-person. What we must ask ourselves right now is if there is a valid reason to begin this effort, and the truth is that there are few pragmatic applications to consider.
We could start mining asteroids for their raw materials and mineral content in the future. Planetary colonization could be necessary in future generations. Since we are still dealing with issues like crime and poverty here at home, addressing our immediate concerns might be better than looking at future needs which might never be necessary.
6. Unmanned probes are even a waste of resources.
One of the ways that we attempt to limit expenses with our space travel needs is to send unmanned probes into the dark vastness that lies beyond. There have been some successes with these efforts, most notably the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 missions that allow us to peer outside of our solar system. This option allows us to almost eliminate the risk to human life entirely as well.
7. Our current information is well out-of-date.
On February 22, 2017, NASA announced that it had found seven planets the size of Earth in a single solar system. Three of the planets were in the so-called Goldilocks Zone, which means they are at a distance from their star that is not too hot and not too cold. It is called the Trappist-1 group, and this set of planets lies in the Aquarius system. That’s about 235 trillion miles away, which is at least a measurable distance.
The problem is that this planetary system is 40 light-years away from us. That means the information that we can observe right now took forty years to get to our scientists. Think about all of the changes that have happened in your life in just the past 5 years, and then apply that concept to a planetary scale. When we start exploring space, we must take into account that this delay is present so that we don’t fly into an unexpectedly dangerous situation.
8. It may lead us into future conflict with beings who have superior technology.
Space exploration makes us think in noble terms about what lies in wait for us in the universe. When we sent the Voyager spacecraft into our solar system and beyond, there were two records placed on the devices to communicate with whoever might find them to let that intelligent life know that we exist.
Most theorists who seriously consider the pros and cons of meeting alien life say that there are only two possible outcomes that can occur with first contact. That alien species will either be so advanced that their technological presence as led to a peaceful society where an exchange of information may one day be possible, or it will be aggressive and want to access our planetary resources.
9. Space exploration creates a lot of trash around our planet.
There are over half-a-million items of trash from over 50 years of space travel and satellite placement which orbit our planet right now. Unless these items fall into the atmosphere and burn up, they will stay in place forever. The ring of debris that we have created makes space exploration more dangerous because an impact with a ship’s hull could have deadly results. We will need to clean up this mess in the future to provide better safety to our future explorers, and we have no idea what the expense might be.
Verdict on the Advantages and Disadvantages of Space Exploration
Space exploration is beneficial even if we only look at it through the lens of hope. It is an idea that unites us as one race instead of over 190 different countries. We can proceed into the universe as one people, taking the first steps toward new experiences just like we did when we placed astronauts on the moon for the first time.
Explorers always face danger, and space is no exception to that rule. The vacuum of the universe was not meant for humans, which means we must constantly adapt and protect ourselves when we are outside of our atmosphere. Then there is the risk of an encounter with alien life to consider too.
The advantages and disadvantages of space exploration must come from a common sense perspective. Other races could harm us, but there is also the possibility that we could be dangerous to other life as well. We should continue with these efforts, but with the understanding that this work is not a race. It is a cooperative effort that will eventually define our humanity.
Author Biography
Keith Miller has over 25 years of experience as a CEO and serial entrepreneur. As an entrepreneur, he has founded several multi-million dollar companies. As a writer, Keith’s work has been mentioned in CIO Magazine, Workable, BizTech, and The Charlotte Observer. If you have any questions about the content of this blog post, then please send our content editing team a message here.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/spinoff_embrace1-5b045ea93de423003998d9f1.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ccp_head2-58b8438e3df78c060e67b2ce.jpg)