Part of speech of that
Part of speech of that
What Part of Speech is “That”
The word “THAT” can be used as a Definite Article, a Conjunction, an Adverb, Pronoun, and Adjective. Take a look at the definitions and examples below to learn how “THAT” works as different parts of speech.
“That” is classified as a definite article when it is used to indicate something/someone specific that the listeners or readers already know. For instance, read the sample sentence below:
“Pick up that book on the floor.”
The person being talked to knows exactly what “book” the speaker is referring to.
Definition:
a. refers to a specific person or thing, assuming that the person being addressed understands or is familiar with it
2. Conjunction
Sometimes, “that” can also serve as a conjunction by combining two clauses. For instance, in the sentence:
“I bought the materials that are required for the project.”
“That“ is used to introduce the clause “…are required for the project.” It combines the dependent clause with the independent clause, “I bought the materials…”
Definition:
a. used to introduce a clause that is the subject or object of a verb
b. used to introduce a clause that completes or explains the meaning of a previous noun or adjective or of the pronoun it
c. used to introduce a clause that states a reason or purpose
3. Adverb
The word can also be used as an adverb, especially in verbal communication. It is normally used to show the intensity of a particular adjective. Take for example the sentence below:
“He is that old.”
In this sample sentence, the word “that” somehow intensifies and shows the degree of the adjective “old.”
Definition:
a. to the degree that is stated or suggested
b. to the degree or extent indicated by a gesture
c. to a great degree
4. Pronoun
In some cases, the word “that” also functions as a freestanding pronoun. Look at the sample sentence below:
“That’s exactly what I thought.”
It can be presumed that the word “that” is representing or replacing a specific thought.
Definition:
a. used to identify a specific person or thing observed by the speaker
b. referring to a specific thing previously mentioned, known, or understood
5. Adjective
The word “that” functions as an adjective when it is used to modify a noun. It is also useful in clarifying which noun the speaker is referring to in the sentence. Take for example, the sentence below:
“That cat is so adorable.”
The word “that” modifies “cat” by emphasizing that it is the particular noun being referred to.
Definition:
a. used to indicate which person, thing, or idea is being shown, pointed to, or mentioned
b. used to indicate the one that is farther away or less familiar
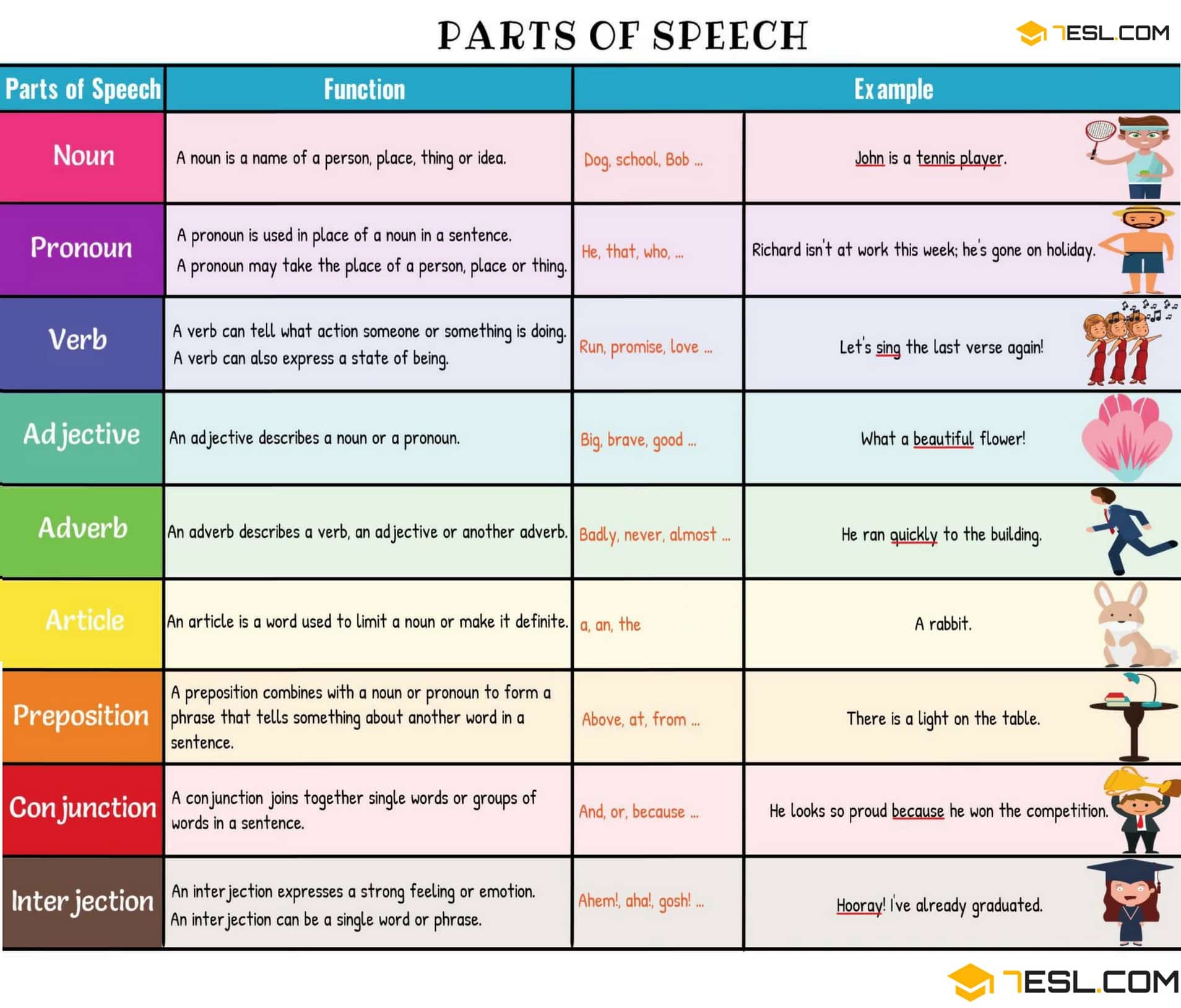
The 9 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
A part of speech is a term used in traditional grammar for one of the nine main categories into which words are classified according to their functions in sentences, such as nouns or verbs. Also known as word classes, these are the building blocks of grammar.
Parts of Speech
Every sentence you write or speak in English includes words that fall into some of the nine parts of speech. These include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections. (Some sources include only eight parts of speech and leave interjections in their own category.)
Learning the names of the parts of speech probably won’t make you witty, healthy, wealthy, or wise. In fact, learning just the names of the parts of speech won’t even make you a better writer. However, you will gain a basic understanding of sentence structure and the English language by familiarizing yourself with these labels.
Open and Closed Word Classes
The parts of speech are commonly divided into open classes (nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs) and closed classes (pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections). The idea is that open classes can be altered and added to as language develops and closed classes are pretty much set in stone. For example, new nouns are created every day, but conjunctions never change.
In contemporary linguistics, the label part of speech has generally been discarded in favor of the term word class or syntactic category. These terms make words easier to qualify objectively based on word construction rather than context. Within word classes, there is the lexical or open class and the function or closed class.
The 9 Parts of Speech
Read about each part of speech below and get started practicing identifying each.
Nouns are a person, place, thing, or idea. They can take on a myriad of roles in a sentence, from the subject of it all to the object of an action. They are capitalized when they’re the official name of something or someone, called proper nouns in these cases. Examples: pirate, Caribbean, ship, freedom, Captain Jack Sparrow.
Pronoun
Pronouns stand in for nouns in a sentence. They are more generic versions of nouns that refer only to people. Examples: I, you, he, she, it, ours, them, who, which, anybody, ourselves.
Verbs are action words that tell what happens in a sentence. They can also show a sentence subject’s state of being (is, was). Verbs change form based on tense (present, past) and count distinction (singular or plural). Examples: sing, dance, believes, seemed, finish, eat, drink, be, became
Adjective
Adjectives describe nouns and pronouns. They specify which one, how much, what kind, and more. Adjectives allow readers and listeners to use their senses to imagine something more clearly. Examples: hot, lazy, funny, unique, bright, beautiful, poor, smooth.
Adverb
Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, and even other adverbs. They specify when, where, how, and why something happened and to what extent or how often. Examples: softly, lazily, often, only, hopefully, softly, sometimes.
Preposition
Prepositions show spacial, temporal, and role relations between a noun or pronoun and the other words in a sentence. They come at the start of a prepositional phrase, which contains a preposition and its object. Examples: up, over, against, by, for, into, close to, out of, apart from.
Conjunction
Conjunctions join words, phrases, and clauses in a sentence. There are coordinating, subordinating, and correlative conjunctions. Examples: and, but, or, so, yet, with.
Articles and Determiners
Articles and determiners function like adjectives by modifying nouns, but they are different than adjectives in that they are necessary for a sentence to have proper syntax. Articles and determiners specify and identify nouns, and there are indefinite and definite articles. Examples: articles: a, an, the; determiners: these, that, those, enough, much, few, which, what.
Some traditional grammars have treated articles as a distinct part of speech. Modern grammars, however, more often include articles in the category of determiners, which identify or quantify a noun. Even though they modify nouns like adjectives, articles are different in that they are essential to the proper syntax of a sentence, just as determiners are necessary to convey the meaning of a sentence, while adjectives are optional.
Interjection
Interjections are expressions that can stand on their own or be contained within sentences. These words and phrases often carry strong emotions and convey reactions. Examples: ah, whoops, ouch, yabba dabba do!
How to Determine the Part of Speech
Only interjections (Hooray!) have a habit of standing alone; every other part of speech must be contained within a sentence and some are even required in sentences (nouns and verbs). Other parts of speech come in many varieties and may appear just about anywhere in a sentence.
To know for sure what part of speech a word falls into, look not only at the word itself but also at its meaning, position, and use in a sentence.
For example, in the first sentence below, work functions as a noun; in the second sentence, a verb; and in the third sentence, an adjective:
Learning the names and uses of the basic parts of speech is just one way to understand how sentences are constructed.
Dissecting Basic Sentences
To form a basic complete sentence, you only need two elements: a noun (or pronoun standing in for a noun) and a verb. The noun acts as a subject and the verb, by telling what action the subject is taking, acts as the predicate.
In the short sentence above, birds is the noun and fly is the verb. The sentence makes sense and gets the point across.
You can have a sentence with just one word without breaking any sentence formation rules. The short sentence below is complete because it’s a command to an understood «you».
Here, the pronoun, standing in for a noun, is implied and acts as the subject. The sentence is really saying, «(You) go!»
Constructing More Complex Sentences
Use more parts of speech to add additional information about what’s happening in a sentence to make it more complex. Take the first sentence from above, for example, and incorporate more information about how and why birds fly.
Birds and fly remain the noun and the verb, but now there is more description.
When is an adverb that modifies the verb fly. The word before is a little tricky because it can be either a conjunction, preposition, or adverb depending on the context. In this case, it’s a preposition because it’s followed by a noun. This preposition begins an adverbial phrase of time (before winter) that answers the question of when the birds migrate. Before is not a conjunction because it does not connect two clauses.
Parts of Speech: A Super Simple Grammar Guide with Examples
Parts of speech are categories of words that perform similar grammatical roles in phrase and sentence structures. But what exactly are the different parts of speech and how do you know which words correspond to different grammatical categories? This article will explain parts of speech and how to identify, modify, and use them in simple and complex sentences.
Table of Contents
Parts of Speech
In the English language there are various parts of speech which are put together in order to form a sentence. Without these, the language would never be able to function.
What Are Parts Of Speech?
Parts of speech are word categories that are defined by the grammatical roles they play in sentence structures. The categories of words are organized by the grammatical functions and meanings they produce and convey.
In the English language, there are around ten common parts of speech. These include nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, determiners, and articles.
Though the meanings of these categories are explained in the following sections, just know that these parts of speech play a grammatical role, or serve a grammatical function in language, including sentence structure and meaning.
Open and Closed Word Classes
Closed word classes are parts of speech that are consistent and do not have newer words introduced to them over time. These include pronouns, conjunctions, determiners, and prepositions.
Open word classes are parts of speech that have newer words introduced to them over time. These include nouns, verbs, adjectives, interjections, and adverbs.
Different Parts of Speech (with Examples)
In this section, we are going to looking a little more closely at the various parts of speech such as the verb, the noun and the adjective, amongst others. This will allow us to gain a better understanding of how a sentence is formed and how the various parts of speech work.
The Noun (n.)
A noun is a word which gives a name to something, in some cases you might hear them referred to as a ‘naming word.’ There are various different subcategories of nouns such as the proper noun, the collective noun, the possessive noun and the common noun. Each one of these serves a different purpose, let’s look at this a little more closely.
Jeffrey, Korea, pen, New Year, dog, cat, elephant, garden, school, work, music, town, Manila, teacher, farmer, Bob, Sean, Michael, police officer, France, coffee, football, danger, happiness…
Noun example sentences:
The Proper Noun
The proper noun is used to name a specific item, for example the names of places or people or perhaps a movie or song title.
The Collective Noun
A collective noun is used to refer to a group of nouns, for example people or animal groups.
The Possessive Noun
A possessive noun is used to show ownership of something, this is done by adding an apostrophe and an s, like in the following examples.
The Common Noun
A common noun is the most simple form of a noun and gives a name to an item.
Determiners and Articles
Determiners and articles are parts of speech that are used with nouns or noun phrases to clarify them. They are usually placed in front of nouns (or noun phrases) and can help specify their identity, quantity, distance (from the speaker), or specific number (among other things).
Determiners
Determiners are a part of speech that are placed in front of nouns to clarify their reference. They include categories such as:
Articles
Articles are a sub-category of determiners that serve as a type of adjective to identify nouns. They may be:
The Verb (vb.)
A verb is one of the most important parts of speech and is a word which is used to describe an action. There are three main types of verbs which are detailed below.
Walk, is, seem, realize, run, see, swim, stand, go, have, get, promise, invite, listen, sing, sit, laughed, walk…
The Action Verb
An action verb does exactly what you might expect, it describes an action.
The Linking Verb
A linking verb is used to show a state of being rather than a physical action.
The Modal Verb
A modal verb is used to ‘help’ the main verb and can show the speakers thoughts or attitude about what they are saying. For example, words such as might, must, could and can are all modal verbs.
The Pronoun (pron.)
A pronoun is one which replaces a noun, and once again there are various different types of pronouns within the English language. Each one is used in a different way, let’s take a look at some examples of this.
Pronoun example sentences:
The Reflexive Pronoun
A reflexive pronoun is used to refer to self, for example myself or yourself.
The Indefinite Pronoun
This type of pronoun is used to refer to a non specific person or item, you might see words such as anything, few, everyone or all.
The Possessive Pronoun
A possessive pronoun is used to show possession or ownership of something, for example my, his, their or yours.
The Relative Pronoun
A relative pronoun is used to introduce an adjective clause. You might recognise these as words such as who, which, that or whose.
The Adjective (adj.)
An adjective is a word which describes a noun or pronoun, there are thousands of adjectives within the English language.
Beautiful, seven, cute, second, tall, blue, angry, brave, careful, healthy, little, old, generous, red, smart, two, small, tall, some, good, big, useful, interesting…
Brown dog, red car, tall boy, fat cat, big garden.
The Adverb (adv.)
Neatly, in the market, every day, tomorrow, very, badly, fully, carefully, hardly, nearly, hungrily, never, quickly, silently, well, really, almost…
Adverb example sentences:
The Conjunction (conj.)
A conjunction is used as a way of joining two or more ideas or words together. Most commonly you will see the words for, and, not, but, or, yet and so used as a conjunction.
And, however, still, but, or, so, after, since, before, either, neither, because, unless…
Conjunction example sentences:
The Preposition (prep.)
A preposition is used in English to show a relationship between two words or phrases. You might recognise a preposition as being words such as in, before, on, at, to, between etc.
In, on, at, about, apropos, according to, after, along, above, except, from, near, of, before, since, between, upon, with, to, after, toward…
The Interjection (interj.)
An interjection could also be thought of as a exclamation. They are used to emotion, reaction or excitement and have no grammatical link to anything else within the sentence they appear.
Ahem!, aha!, gosh!, aw!, great!, hey!, hi!, hooray!, oh!, yeah!, oops!, phew!, eh!, oh!, ouch!, hi!, well!…
Interjection example sentences:
How To Determine The Part Of Speech In A Sentence
In order to determine a part of speech in a sentence, look at the word being used, its context, and what meanings it brings to the sentence structure. Here are some questions you can ask about a particular word in a sentence, in order to figure out what part of speech it is.
Parts of Speech and Sentence Construction
In sentence construction, parts of speech are present in what are known as the clauses of sentences. Clauses are groups of words that have a subject and a verb. The verb is also part of an entire verb phrase known as a predicate.
Simple/Basic Sentences
In its simplest form, a sentence can have one independent clause.
For example, the sentence “I walk to the store” contains one clause.
This entire sentence “I walk to the store” is an independent clause, expresses one subject doing one action — and is known as a simple sentence.
Knowing this, apply the fact that nouns and pronouns will often be the subjects or objects of simple sentences, while verbs will convey actions. So once again:
Complex Sentences
Complex sentences also contain a subject and a verb, but can not stand alone as independent clauses. For example:
“since the weather is sunny.”
Here, “weather” would be the subject, and “is” would be the verb. So, “I walk to the store since the weather is sunny” would be a complex sentence. The parts of speech in the second part here would be:
Parts of Speech in English | Pictures
In the English language, there are eight different parts of speech and each one serves its own purpose. Without them, we would not be able to form a coherent sentence and so it is important that we are familiar with what each of them is. In these images, we are going to look at each of the different parts of speech, what they are used for, and some examples of how they work within a sentence.
Parts of Speech in English Image 1
English Parts of Speech Table Image 2
Parts of Speech Video
Learn all parts of speech in English with a useful video lesson.
These eight parts of speech can all be merged together to help you in creating grammatically correct and cohesive sentences in English. Whilst some are further split into subcategories, others function on their own, but each one is just as important as the next.
Parts Of Speech Quiz
A. In the sentence “I ran to the tallest tree”, what part of speech is the word “tallest”?
B. In the 2000s, the word staycation described the act of staying home for a vacation. Since “staycation” is a noun and a new word, what class of words does it belong to?
C. In the sentence “I’ll have a few tacos”, what part of speech are the words “a few”?
What Part of Speech is “THIS”
The word “this” can be used for a variety of purposes and contexts. Basically, it can be classified as an adjective, a definite article, a pronoun, or an adverb depending on how it is used.
“THIS” can be categorized under adjectives if it is used to describe a noun. It is commonly placed before a noun to emphasize the person, place, or thing that is being referred to in the sentence. Look for example, at the sentence below:
This phone is mine.
The word “this” is used to modify the noun “phone.” It is used to make it clear to the audience that it is the noun being talked about.
Definition:
a. being the person, thing, or idea that has been recently mentioned or is present or near in place, time, or thought
b. used to indicate the thing that is closest to you or that is being shown to you
In some cases, the word “this” is regarded as a definite article when it is used to indicate a specific person or thing that the audience knows already. Take for example, the sentence:
Bring this gun with you.
In this sample sentence, the person being addressed knows exactly which object the speaker is referring to.
Definition:
a. referring to a specific thing or situation just mentioned
Sometimes, the word “this” can be classified as a pronoun if it is used to substitute a particular thing. For example, in the sentence:
This is the pilot speaking.
The word is used to replace a specific noun, which the listeners or readers (more likely) know already.
Definition:
a. the person, thing, or idea that is present or near in place, time, or thought or that has just been mentioned
b. the one nearer or more immediately under observation or discussion
In other cases, the word “this” is classified under the part of speech adverb, when it is used to describe an adjective, a verb, or another adverb. For instance, in the sample sentence:
He needs a container this big.
The word “this” is considered as an adverb that modifies the adjective “big.”
Definition:
a. to the degree or extent that is suggested in the present situation
b. to the degree or extent indicated by a gesture
Part of Speech
Part of Speech Overview
In the English language, words can be considered as the smallest elements that have distinctive meanings. Based on their use and functions, words are categorized into several types or parts of speech. This article will offer definitions and examples for the 8 major parts of speech in English grammar: noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, adjective, conjunction, preposition, and interjection.
1. Noun
This part of a speech refers to words that are used to name persons, things, animals, places, ideas, or events. Nouns are the simplest among the 8 parts of speech, which is why they are the first ones taught to students in primary school.
There are different types of nouns namely:
This great list of nouns can help you explore more nouns.
2. Pronoun
A pronoun is a part of a speech which functions as a replacement for a noun. Some examples of pronouns are: I, it, he, she, mine, his, hers, we, they, theirs, and ours.
The italicized words in the sentences above are the pronouns in the sentence.
3. Adjective
This part of a speech is used to describe a noun or a pronoun. Adjectives can specify the quality, the size, and the number of nouns or pronouns.
4. Verb
This is the most important part of a speech, for without a verb, a sentence would not exist. Simply put, this is a word that shows an action (physical or mental) or state of being of the subject in a sentence.
Examples of “State of Being Verbs” : am, is, was, are, and were
5. Adverb
Just like adjectives, adverbs are also used to describe words, but the difference is that adverbs describe adjectives, verbs, or another adverb.
The different types of adverbs are:
6. Preposition
This part of a speech basically refers to words that specify location or a location in time.
Examples of Prepositions: above, below, throughout, outside, before, near, and since
7. Conjunction
The conjunction is a part of a speech which joins words, phrases, or clauses together.
Examples of Conjunctions: and, yet, but, for, nor, or, and so
The italicized words in the sentences above are some examples of conjunctions.
8. Interjection
This part of a speech refers to words which express emotions. Since interjections are commonly used to convey strong emotions, they are usually followed by an exclamation point.
Examples of Interjections:
The bold words attached to the main sentences above are some examples of interjections.
You must familiarize yourself with the different parts of speech discussed in this article because they are among the most fundamental concepts that you will encounter throughout your study of grammar. An in-depth knowledge of this topic will not only make you a better writer, but an effective communicator as well.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ThoughtCoChalkboard6-5b2aa124eb97de0037de8ba9.png)