What do whales feel ielts reading answers
What do whales feel ielts reading answers
What do whales feel ielts reading answers
An examination of the functioning of the senses in cetaceans, the group of mammals comprising whales, dolphins and porpoises
Some of the senses that we and other terrestrial mammals take for granted are either reduced or absent in cetaceans or fail to function well in water. For example, it appears from their brain structure that toothed species are unable to smell. Baleen species, on the other hand, appear to have some related brain structures but it is not known whether these are functional. It has been speculated that, as the blowholes evolved and migrated to the top of the head, the neural pathways serving sense of smell may have been nearly all sacrificed. Similarly, although at least some cetaceans have taste buds, the nerves serving these have degenerated or are rudimentary.
The sense of touch has sometimes been described as weak too, but this view is probably mistaken. Trainers of captive dolphins and small whales often remark on their animals’ responsiveness to being touched or rubbed, and both captive and free- ranging cetacean individuals of all species (particularly adults and calves, or members of the same subgroup) appear to make frequent contact. This contact may help to maintain order within a group, and stroking or touching are part of the courtship ritual in most species. The area around the blowhole is also particularly sensitive and captive animals often object strongly to being touched there.
On the other hand, the position of the eyes in most dolphins and porpoises suggests that they have stereoscopic vision forward and downward. Eye position in freshwater dolphins, which often swim on their side or upside down while feeding, suggests that what vision they have is stereoscopic forward and upward. By comparison, the bottlenose dolphin has extremely keen vision in water. Judging from the way it watches and tracks airborne flying fish, it can apparently see fairly well through the air-water interface as well. And although preliminary experimental evidence suggests that their in-air vision is poor, the accuracy with which dolphins leap high to take small fish out of a trainer’s hand provides anecdotal evidence to the contrary.
Such variation can no doubt be explained with reference to the habitats in which individual species have developed. For example, vision is obviously more useful to species inhabiting clear open waters than to those living in turbid rivers and flooded plains. The South American boutu and Chinese beiji, for instance, appear to have very limited vision, and the Indian susus are blind, their eyes reduced to slits that probably allow them to sense only the direction and intensity of light.
1 echolocation: the perception of objects by means of sound wave echoes.
What do whales feel ielts reading answers
IELTS Reading-What Do Whales Feel?
Some of the senses that we and other terrestrial mammals take for granted are either reduced or absent in cetaceans or fail to function well in water. For example, it appears from their brain structure that toothed species are unable to smell. Baleen species, on the other hand, appear to have some related brain structures but it is not known whether these are functional. It has been speculated that, as the blowholes evolved and migrated to the top of the head, the neural pathways serving sense of smell may have been nearly all sacrificed. Similarly, although at least some cetaceans have taste buds, the nerves serving these have degenerated or are rudimentary.
The sense of touch has sometimes been described as weak too, but this view is probably mistaken. Trainers of captive dolphins and small whales often remark on their animals’ responsiveness to being touched or rubbed, and both captive and freeranging cetacean individuals of all species (particularly adults and calves, or members of the same subgroup) appear to make frequent contact. This contact may help to maintain order within a group, and stroking or touching are part of the courtship ritual in most species. The area around the blowhole is also particularly sensitive and captive animals often object strongly to being touched there.
The sense of vision is developed to different degrees in different species. Baleen species studied at close quarters underwater – specifically a grey whale calf in captivity for a year, and free-ranging right whales and humpback whales studied and filmed off Argentina and Hawaii – have obviously tracked objects with vision underwater, and they can apparently see moderately well both in water and in air. However, the position of the eyes so restricts the field of vision in baleen whales that they probably do not have stereoscopic vision.
On the other hand, the position of the eyes in most dolphins and porpoises suggests that they have stereoscopic vision forward and downward. Eye position in freshwater dolphins, which often swim on their side or upside down while feeding, suggests that what vision they have is stereoscopic forward and upward. By comparison, the bottlenose dolphin has extremely keen vision in water. Judging from the way it watches and tracks airborne flying fish, it can apparently see fairly well through the air–water interface as well. And although preliminary experimental evidence suggests that their in-air vision is poor, the accuracy with which dolphins leap high to take small fish out of a trainer’s hand provides anecdotal evidence to the contrary.
Such variation can no doubt be explained with reference to the habitats in which individual species have developed. For example, vision is obviously more useful to species inhabiting clear open waters than to those living in turbid rivers and flooded plains. The South American boutu and Chinese beiji, for instance, appear to have very limited vision, and the Indian susus are blind, their eyes reduced to slits that probably allow them to sense only the direction and intensity of light.
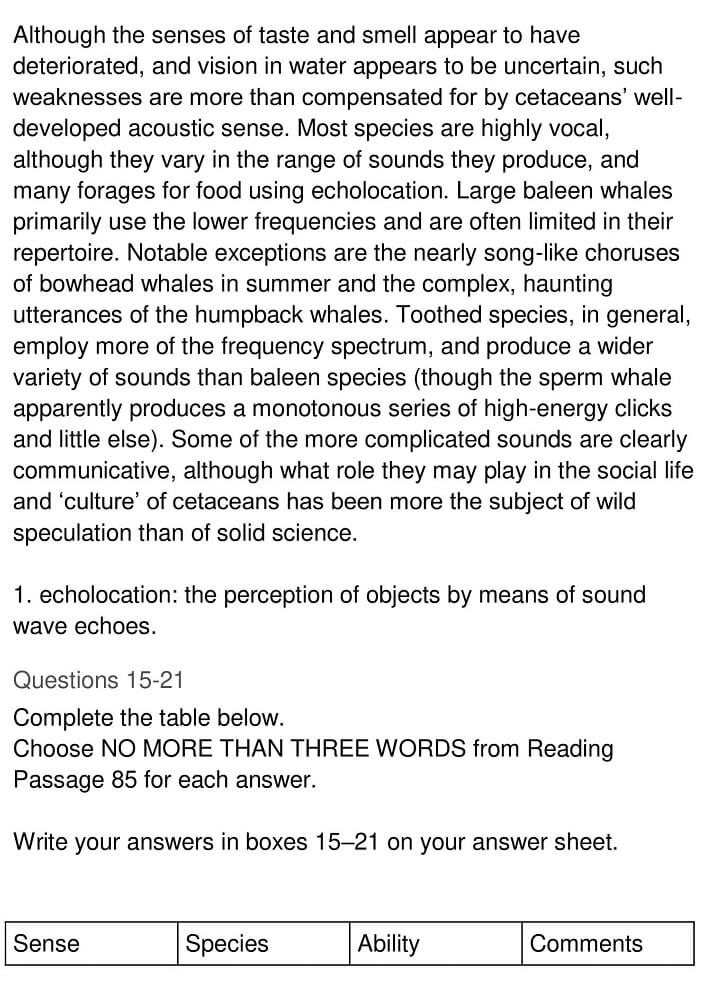
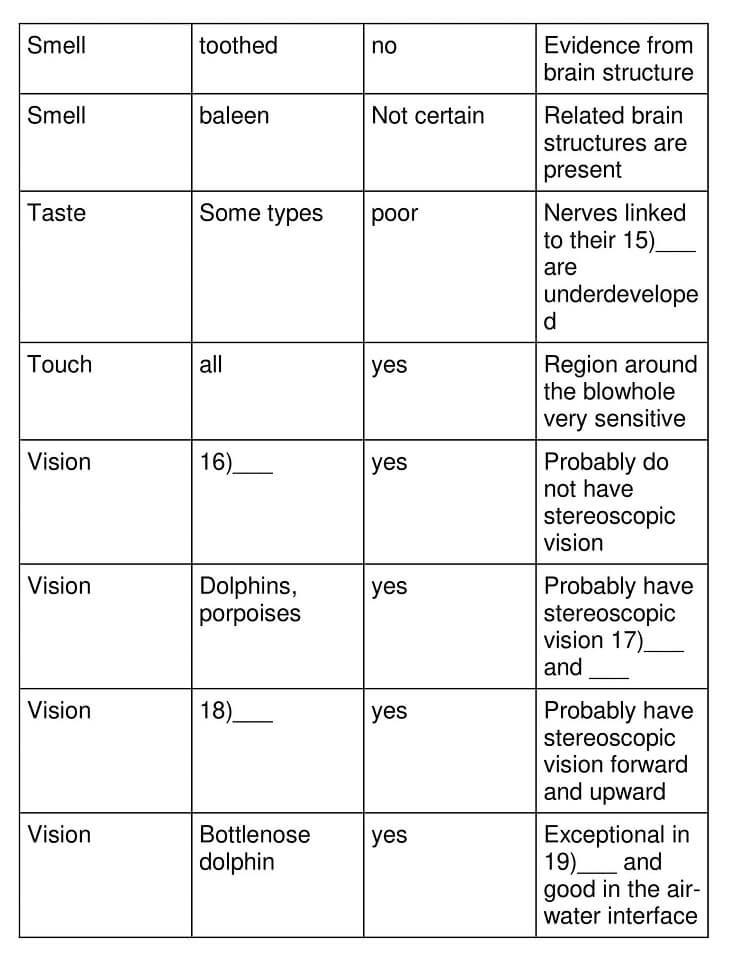
Although the senses of taste and smell appear to have deteriorated, and vision in water appears to be uncertain, such weaknesses are more than compensated for by cetaceans’ well-developed acoustic sense. Most species are highly vocal, although they vary in the range of sounds they produce, and many forage for food using echolocation. Large baleen whales primarily use the lower frequencies and are often limited in their repertoire. Notable exceptions are the nearly song-like choruses of bowhead whales in summer and the complex, haunting utterances of the humpback whales. Toothed species in general employ more of the frequency spectrum, and produce a wider variety of sounds, than baleen species (though the sperm whale apparently produces a monotonous series of high-energy clicks and little else). Some of the more complicated sounds are clearly communicative, although what role they may play in the social life and ‘culture’ of cetaceans has been more the subject of wild speculation than of solid science.
What do whales feel ielts reading answers
The IELTS reading section is responsible for assessing candidates based on their ability to read a passage and answer associated questions. These are the major elements that are used to evaluate a candidate’s ability to read and interpret in IELTS examination. The details are required to be remembered in IELTS reading from the passage that is presented to them. IELTS academic reading is a crucial section and students are required to look after their preparation accordingly. What do whales feel reading answers is an appropriate topic that can be utilized by candidates to prepare for the IELTS reading test. The topic includes questions mentioned below:
Section 1
Read the Passage to Answer the Following Questions
What do Whales Feel Reading Answers






Section 2
Solution and Explanation
Questions 15-21:
Complete the table below.
Choose NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS from Reading Passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet.
Answer : taste buds
Supporting Answer : Similarly, although at least some cetaceans have taste buds, the nerves serving these have degenerated or are rudimentary.
Keywords : cetaceans, taste buds, nerves serving
Keyword Location : Final lines of the first paragraph
Explanation : As the lines suggest, although there have been many stages of evolution, the taste buds remain underdeveloped and basic.
Answer : baleen/the baleen whales
Supporting Answer : However, the position of the eyes so restricts the field of vision in baleen whales that they probably do not have stereoscopic vision.
Keywords : restricts the field of vision, baleen whales, stereoscopic vision
Keyword Location : Paragraph 3
Explanation : Although baleen whales can see quite well in water as well as air, their eyes are positioned in such a way that it restricts their field of vision.
Read More IELTS Reading Related Articles
Answer : forward, downward (in either order; both required for 1 mark)
Supporting Answer : On the other hand, the position of the eyes in most dolphins and porpoises suggests that they have stereoscopic vision forward and downward.
Keywords : stereoscopic vision, dolphins and porpoises
Keyword Location : Paragraph 4
Explanation : The eyes are positioned in such a way that the dolphins and porpoises enable them to view in both forward and downward directions.
Answer : freshwater dolphin(s)/the freshwater dolphin(s)
Supporting Answer : Eye position in freshwater dolphins, which often swim on their side or upside down while feeding, suggests that what vision they have is stereoscopic forward and upward.
Keywords : freshwater dolphins, stereoscopic forward
Keyword Location : Paragraph 4
Explanation : freshwater dolphins swim usually on their side or upside down while feeding, which suggests that their eye position is stereoscopic.
Answer : water/the water
Supporting Answer : By comparison, the bottlenose dolphin has extremely keen vision in water.
Keywords : bottlenose dolphin, keen vision
Keyword Location : Paragraph 4
Explanation : bottlenose dolphins have very good vision in water as well as in the air.
Answer : lower frequencies/ the lower frequencies
Supporting Answer : Large baleen whales primarily use the lower frequencies and are often limited in their repertoire.
Keywords : baleen whales, lower frequencies
Keyword Location : Paragraph 6
Explanation : Larger baleen whales use low frequencies as a means of communication. Their means of communication are limited.
Answer : bowhead
Supporting Answer : Notable exceptions are the nearly song-like choruses of bowhead whales in summer and the complex, haunting utterances of the humpback whales.
Keywords : song-like choruses, bowhead whales
Keyword Location : Paragraph 6
Explanation : Humpback whales have been known to communicate using song-like frequencies. They are said to produce a wider variety of sounds and spectrum.
Questions 22-26:
Answer the questions below using NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 8-12 on your answer sheet.
Answer : touch/sense of touch
Supporting Answer : Trainers of captive dolphins and small whales often remark on their animals’ responsiveness to being touched or rubbed, and both captive and free-ranging cetacean individuals of all species (particularly adults and calves, or members of the same subgroup) appear to make frequent contact.
Keywords : captive dolphins and small whale, aptive and free-ranging cetacean individuals
Keyword Location : Paragraph 2
Explanation : it has been observed by trainers that the sense of touch is a good effective method to get a response from the cetaceans. Even though some sources say the sense of touch is a weak method of contact, it has garnered positive results from the cetaceans.
Answer : freshwater dolphin(s)/the freshwater dolphin(s)
Supporting Answer : Eye position in freshwater dolphins, which often swim on their side or upside down while feeding, suggests that what vision they have is stereoscopic forward and upward.
Keywords : stereoscopic, freshwater dolphins
Keyword Location : Paragraph 4
Explanation : as it states in the paragraph mentioned above, freshwater dolphins swim either on their side or upside down to feed.
Answer : airborne flying fish
Supporting Answer : Judging from the way it watches and tracks airborne flying fish, it can apparently see fairly well through the air-water interface as well.
Keywords : tracks airborne, air-water interface
Keyword Location : Paragraph 4
Explanation : bottlenose dolphins have a good vision in water as well as air, and can track flying fish because of this.
Answer : clear water(s)/clear open water(s)
Supporting Answer : For example, vision is obviously more useful to species inhabiting clear open waters than to those living in turbid rivers and flooded plains.
Keywords : vision, inhabiting
Keyword Location : Paragraph 5
Explanation : clear water for obvious reasons makes it easier for aquatic life to have better vision and track their food. The better they can see their surroundings, the easier it is for them to acquire their food.
Answer : acoustic sense/the acoustic sense
Supporting Answer : Although the senses of taste and smell appear to have deteriorated, and vision in water appears to be uncertain, such weaknesses are more than compensated for by cetaceans’ well-developed acoustic sense.
Keywords : taste and smell, deteriorated, weaknesses
Keyword Location : Paragraph 6
Explanation : there have been many changes in the cetaceans, but the one sense which has best developed is the ability of their acoustic sense. Makes it easier to look for food by using methods such as echolocation to communicate.
What do Whales Feel Reading Answers
Updated On Mar 05, 2022
The Academic passage ‘What do Whales Feel’ is a reading passage that appeared in an IELTS Test.
Since questions get repeated in the IELTS exam, these passages for ideal for practice. If you want more practice, try taking an IELTS reading practice test.
The question types found in this passage are:
Table Completion
A table of information with some gaps will be provided in the table completion question. You are required to fill the gaps with relevant responses from the given reading passage. Focus on the instructions because here, you will be asked to fill the gaps with only a few words. Read them carefully. Some of the options might confuse you, e.g., not more than three words.
Short Answer Questions
In the short answer type of question, you’ll have to take words from the given text to write the short answers. It is important to pay close attention to the instructions that are given in the question because in some instructions there will be a word limit mentioned and you may lose marks if you don’t follow it.
What do Whales Feel


Answers
Unlock All Answers
15 Answer: taste buds
Question Type: Table Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 1, last line
Answer explanation: The last line of paragraph 1 states that at least some cetaceans have ‘taste buds’ and the ‘nerves’ ‘serving’ (linked) ‘these’ (taste buds) have degenerated or are ‘rudimentary’ (underdeveloped). Hence, the answer is ‘Taste buds.’
16 Answer: Baleen whales
Question Type: Table Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 3, last line
Answer explanation: The last line of paragraph 3 mentions that the position of the eyes restricts the field of vision in ‘baleen whales’ in such a way that they probably ‘do not have stereoscopic vision’. Hence, the answer is ‘Baleen whales’.
17 Answer: forward, downward
Question Type: Table Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 4, line 1
Answer explanation: The first line of paragraph 4 observes that the position of the eyes in most ‘dolphins and porpoises’ suggests that they ‘have stereoscopic vision forward and downward’. Hence, the answer is ‘forward, downward’.
18 Answer: freshwater dolphins
Question Type: Table Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 4, line 2
Answer explanation: The second sentence in paragraph 4 points out that the ‘eye position in freshwater dolphins’, which often swim on their side or upside down while feeding, suggests that the ‘vision they have is stereoscopic forward and upward’. Hence, the answer is ‘freshwater dolphins’.
19 Answer: water
Question Type: Table Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 4, line 4
Answer explanation: Paragraph 4 informs that the ‘bottlenose dolphin’ has extremely ‘keen vision in water’. Moreover, judging from the way it watches and tracks airborne flying fish, it can apparently see ‘fairly well through the air–water interface’ as well. Hence, the answer is ‘water’.
20 Answer: lower frequencies
Question Type: Table Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 6, line 3
Answer explanation: Paragraph 6 points out that ‘large baleen whales’ primarily ‘use the lower frequencies’ and are often ‘limited in their repertoire’. Hence, the answer is ‘lower frequencies’.
21 Answer: bowhead, humpback
Question Type: Table Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 6, line 4
Answer explanation: In paragraph 6, the writer notes that most species are highly vocal, but they vary in the range of sounds they produce, and many forages for food using echolocation. Notable exceptions are the nearly ‘song-like choruses’ of ‘bowhead whales’ in summer and the ‘complex, haunting utterances’ of the ‘humpback whales’. Hence, the answer is ‘Bowhead, humpback’.
22 Answer: touch
Question Type: Summary Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 2, line 2
Answer explanation: In paragraph 2, the writer is discussing that the ‘sense of touch’ of the dolphins and whales has sometimes been described as weak, but this view is probably mistaken. The contact may help to maintain order within a group, and ‘stroking or touching’ are ‘part of the courtship ritual’ (mating) in most species. Hence, the answer is ‘touch’.
23 Answer: freshwater dolphin
Question Type: Summary Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 4, line 2
Answer explanation: Paragraph 4 writes about the eye position in ‘freshwater dolphins’, which ‘often swim’ on their side or ‘upside down while feeding’ suggesting that their vision is stereoscopic forward and upward. Hence, the answer is ‘freshwater dolphin’.
24 Answer: airborne flying fish
Question Type: Summary Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 4, line 4
Answer explanation: Paragraph 4 states that the ‘bottlenose dolphin’ has extremely ‘keen vision in water’. Moreover, judging from the way it ‘watches and tracks airborne flying fish’, it can apparently see ‘fairly well through the air–water interface’ as well. Hence, the answer is ‘airborne flying fish’.
25 Answer: clear water
Question Type: Summary Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 5, line 2
Answer explanation: Paragraph 5 points out that ‘vision’ (good visual ability) is obviously ‘more useful’ to species ‘inhabiting’ (living in a specific habitat) ‘clear open waters’ than to those living in turbid rivers and flooded plains. Hence, the answer is ‘clear water’.
26 Answer: acoustic sense
Question Type: Summary Completion
Answer location: Paragraph 6, line 1
Answer explanation: The first sentence of paragraph 6 hints that although the senses of taste and smell appear to have deteriorated, and vision in water appears to be uncertain, such weaknesses are more than compensated for by ‘cetaceans’ ‘well-developed’ (best developed) ‘acoustic sense’. Hence, the answer is ‘acoustic sense’.
What do whales feel ielts reading answers
This Academic IELTS Reading post focuses on solutions to IELTS Cambridge 4 Reading Test 1 Reading Passage 2 titled ‘What Do Whales Feel?’. This is a targeted post for IELTS candidates who have great problems finding out and understanding Reading Answers in the AC module. This post can guide you the best to understand every Reading answer quite easily. Finding out IELTS Reading answers is a gradual process, and this post will assist you in this respect.
IELTS Cambridge 4 Test 1: AC Reading Module
Reading Passage 2: Questions 15-26
The headline of the passage: What Do Whales Feel?
Questions 15-21: Completing table: NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS
[In this type of question candidates need to fill in the gaps in a table with NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS. Skimming and scanning, both reading skills are essential for this question-type.]
Question no. 15:
| SENSE | SPECIES | ABILITY | COMMENTS |
| Taste | all | poor | nerves linked to their ___________ are undeveloped |
Keywords for the question: taste, nerves, liked to, undeveloped
Here, some cetaceans = all species, nerves serving these = nerves linked to their taste buds, degenerated = undeveloped, rudimentary = basic or poor,
So, the answer is: taste buds
Question no. 16:
| SENSE | SPECIES | ABILITY | COMMENTS |
| Vision | ___________ | yes | probably do not have stereoscopic vision |
Keywords for the question: vision, probably, do not have, stereoscopic vision,
So, the answer is: baleen/ the baleen whales
Question no. 17:
| SENSE | SPECIES | ABILITY | COMMENTS |
| Vision | dolphins, porpoises, | yes | probably have stereoscopic vision __________ and __________ |
Keywords for the question: vision, dolphins, porpoises, probably, have, stereoscopic vision,
Have a look at the first few lines of paragraph no. 4, “On the other hand, the position of the eyes in most dolphins and porpoises suggests that they have stereoscopic vision forward and downward.”
So, the answer is: forward, downward (in either order)
Question no. 18:
| SENSE | SPECIES | ABILITY | COMMENTS |
| Vision | ____________ | yes | probably have stereoscopic vision forward and upward |
Keywords for the question: vision, probably, have, stereoscopic vision, forward, upward,
So, the answer is: (the) freshwater dolphin(s)
Question no. 19:
| SENSE | SPECIES | ABILITY | COMMENTS |
| Vision | bottlenose dolphins | yes | exceptional in __________ and good in air-water interface |
Keywords for the question: vision, bottlenose dolphins, exceptional, good in, air-water interface,
So, the answer is: (the) water
Question no. 20:
| SENSE | SPECIES | ABILITY | COMMENTS |
| Hearing | most large baleen | yes | usually use ___________; repertoire limited |
Keywords for the question: hearing, most large baleen, usually use, repertoire, limited,
Here, primarily use = usually use, limited in their repertoire = repertoire limited,
So, the answer is: (the) lower frequencies
Question no. 21:
| SENSE | SPECIES | ABILITY | COMMENTS |
| Hearing | __________ whales and __________ whales | yes | song-like |
Keywords for the question: hearing, song-like,
Here, song-like choruses & haunting utterances = song-like ability,
So, the answer is: bowhead, humpback (in either order)
Questions 22-26: Short answer to open questions (NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS)
[In this kind of question candidates have to answer some questions, only with some conditions like NO MORE THAN THREE/TWO WORDS and/or A NUMBER or, ONE WORD ONLY. Each question has keywords which will lead to the answer. This question type generally follows a sequence.]
Question no. 22: Which of the senses is described here as being involved in mating?
Keywords for the question: being involved in, mating,
Here, stroking or touching = sense of touch, courtship ritual = mating,
So, the answer is: (sense of) touch
Question no. 23: Which species swims upside down while eating?
Keywords for the question: swims, upside down, while eating,
Here, feeding = eating,
So, the answer is: (the) freshwater dolphin(s)
Question no. 24: What can bottlenose dolphins follow from under the water?
Keywords for the question: bottlenose dolphins, follow from, under the water,
Here, the way it watches and tracks = follow from under the water,
So, the answer is: airborne flying fish
Question no. 25: Which type of habitat is related to good visual ability?
Keywords for the question: habitat, related to, good visual ability,
Here, vision is obviously more useful = related to good visual ability, inhabiting = habitat,
So, the answer is: clear (open) water(s)
Question no. 26: Which of the senses is best developed in cetaceans?
Keywords for the question: best developed, cetaceans,
Here, well-developed = best developed,
So, the answer is: (the) acoustic sense
Источники информации:
- http://ieltsoracle.com/ielts-reading-what-do-whales-feel/
- http://collegedunia.com/news/e-482-what-do-whales-feel-reading-answers
- http://ieltsmaterial.com/what-do-whales-feel-reading-answers/
- http://www.ieltsdeal.com/ielts-academic-reading-cambridge-4-test-1-reading-passage-2-what-do-whales-feel-with-best-solutions-and-best-explanations/






