What is chat bot
What is chat bot
What is a chatbot?
At the most basic level, a chatbot is a computer program that simulates and processes human conversation (either written or spoken), allowing humans to interact with digital devices as if they were communicating with a real person. Chatbots can be as simple as rudimentary programs that answer a simple query with a single-line response, or as sophisticated as digital assistants that learn and evolve to deliver increasing levels of personalization as they gather and process information.
You’ve probably interacted with a chatbot whether you know it or not. For example, you’re at your computer researching a product, and a window pops up on your screen asking if you need help. Or perhaps you’re on your way to a concert and you use your smartphone to request a ride via chat. Or you might have used voice commands to order a coffee from your neighborhood café and received a response telling you when your order will be ready and what it will cost. These are all examples of scenarios in which you could be encountering a chatbot.
How do chatbots work?
Driven by AI, automated rules, natural-language processing (NLP), and machine learning (ML), chatbots process data to deliver responses to requests of all kinds.
There are two main types of chatbots.
Advanced digital assistants are also able to connect several single-purpose chatbots under one umbrella, pull disparate information from each of them, and then combine this information to perform a task while still maintaining context—so the chatbot doesn’t become “confused.”
The value chatbots bring to businesses and customers
Chatbots boost operational efficiency and bring cost savings to businesses while offering convenience and added services to internal employees and external customers. They allow companies to easily resolve many types of customer queries and issues while reducing the need for human interaction.
With chatbots, a business can scale, personalize, and be proactive all at the same time—which is an important differentiator. For example, when relying solely on human power, a business can serve a limited number of people at one time. To be cost-effective, human-powered businesses are forced to focus on standardized models and are limited in their proactive and personalized outreach capabilities.
By contrast, chatbots allow businesses to engage with an unlimited number of customers in a personal way and can be scaled up or down according to demand and business needs. By using chatbots, a business can provide humanlike, personalized, proactive service to millions of people at the same time.
Consumer research is showing that messaging apps are increasingly becoming the preferred method for connecting with businesses for certain types of transactions. Delivered through messaging platforms, chatbots enable a level of service and convenience that in many cases exceeds what humans can provide. For example, banking chatbots save an average of four minutes per inquiry compared to traditional call centers. The same capabilities that help businesses achieve greater efficiency and cost reductions also deliver benefits to customers in the form of an improved customer experience. It’s a win/win proposition
Why were chatbots created?
Digitization is transforming society into a “mobile-first” population. As messaging applications grow in popularity, chatbots are increasingly playing an important role in this mobility-driven transformation. Intelligent conversational chatbots are often interfaces for mobile applications and are changing the way businesses and customers interact.
Chatbots allow businesses to connect with customers in a personal way without the expense of human representatives. For example, many of the questions or issues customers have are common and easily answered. That’s why companies create FAQs and troubleshooting guides. Chatbots provide a personal alternative to a written FAQ or guide and can even triage questions, including handing off a customer issue to a live person if the issue becomes too complex for the chatbot to resolve. Chatbots have become popular as a time and money saver for businesses and an added convenience for customers.
How chatbots have evolved
The origin of the chatbot arguably lies with Alan Turing’s 1950s vision of intelligent machines. Artificial intelligence, the foundation for chatbots, has progressed since that time to include superintelligent supercomputers such as IBM Watson.
The original chatbot was the phone tree, which led phone-in customers on an often cumbersome and frustrating path of selecting one option after another to wind their way through an automated customer service model. Enhancements in technology and the growing sophistication of AI, ML, and NLP evolved this model into pop-up, live, onscreen chats. And the evolutionary journey has continued.
With today’s digital assistants, businesses can scale AI to provide much more convenient and effective interactions between companies and customers—directly from customers’ digital devices.
Common chatbot uses
Chatbots are frequently used to improve the IT service management experience, which delves towards self-service and automating processes offered to internal staff. With an intelligent chatbot, common tasks such as password updates, system status, outage alerts, and knowledge management can be readily automated and made available 24/7, while broadening access to commonly used voice and text based conversational interfaces.
On the business side, chatbots are most commonly used in customer contact centers to manage incoming communications and direct customers to the appropriate resource. They’re also frequently used for internal purposes, such as onboarding new employees and helping all employees with routine activities including vacation scheduling, training, ordering computers and business supplies, and other self-service activities that don’t require human intervention.
On the consumer side, chatbots are performing a variety of customer services, ranging from ordering event tickets to booking and checking into hotels to comparing products and services. Chatbots are also commonly used to perform routine customer activities within the banking, retail, and food and beverage sectors. In addition, many public sector functions are enabled by chatbots, such as submitting requests for city services, handling utility-related inquiries, and resolving billing issues.
Why AI and data matter when it comes to chatbots
Both the benefits and the limitations of chatbots reside within the AI and the data that drive them.
AI considerations: AI is very good at automating mundane and repetitive processes. When AI is incorporated into a chatbot for these types of tasks, the chatbot usually functions well. However, if a demand is made on a chatbot that extends beyond its capabilities or makes its task more complicated, the chatbot might struggle—and that has negative consequences for businesses and customers. There are questions and issues that chatbots simply may not be able to answer or resolve—for example, complex service issues that have a large number of variables.
Developers can work around these limitations by adding a contingency to their chatbot application that routes the user to another resource (such as a live agent) or prompts a customer for a different question or issue. Some chatbots can move seamlessly through transitions between chatbot, live agent, and back again. As AI technology and implementation continue to evolve, chatbots and digital assistants will become more seamlessly integrated into our everyday experience.
Data considerations: All chatbots use data, which is accessed from a variety of sources. As long as the data is high quality and the chatbot is developed correctly, the data will be a chatbot enabler. However, if the data quality is poor, it will limit the chatbot’s functionality. And even if the data quality is good, if the chatbot’s ML training wasn’t modeled properly or is unsupervised, the chatbot can perform poorly—or unexpectedly, at the very least.
In other words, your chatbot is only as good as the AI and data you build into it.
Are chatbots bad?
There are some misconceptions about the term chatbot. Although the terms chatbot and bot are sometimes used interchangeably, a bot is simply an automated program that can be used either for legitimate or malicious purposes. The negative connotation around the word bot is attributable to a history of hackers using automated programs to infiltrate, usurp, and generally cause havoc in the digital ecosystem.
Bots and chatbots, therefore, should not be confused. Generally speaking, chatbots do not have a history of being used for hacking purposes. Chatbots are conversational tools that perform routine tasks efficiently. People like them because they help them get through those tasks quickly so they can focus their attention on high-level, strategic, and engaging activities that require human capabilities that cannot be replicated by machines.
Want to create a chatbot? It’s easier than you might think.
There are many widely available tools that allow anyone to create a chatbot. Some of these tools are oriented toward business uses (such as internal operations), and others are oriented toward consumers.
Creating a chatbot is similar to creating a mobile application and requires a messaging platform or service for delivery. Beyond that, with all the tools that are easily accessible for creating a chatbot, you don’t have to be an expert or even a developer to build one. A product manager or a business user should be able to use these types of tools to create a chatbot in as little as an hour.
Need some help getting started on creating your own chatbot?
The future of chatbots
Where is the evolution of chatbots headed? Chatbots, like other AI tools, will be used to further enhance human capabilities and free humans to be more creative and innovative, spending more of their time on strategic rather than tactical activities.
In the near future, when AI is combined with the development of 5G technology, businesses, employees, and consumers are likely to enjoy enhanced chatbot features such as faster recommendations and predictions, and easy access to high-definition video conferencing from within a conversation. These and other possibilities are in the investigative stages and will evolve quickly as internet connectivity, AI, NLP, and ML advance. Eventually, every person can have a fully functional personal assistant right in their pocket, making our world a more efficient and connected place to live and work.
What is a Chatbot and How to Use It for Your Business
The evolution of artificial intelligence is now in full swing and chatbots are only a faint splash on a huge wave of progress. Today the number of users of messaging apps like WhatsApp, Slack, Skype and their analogs is skyrocketing, Facebook Messenger alone has more than 1.2 billion monthly users. With the spread of messengers, virtual chatterbots that imitate human conversations for solving various tasks are becoming increasingly in demand. Chinese WeChat bots can already set medical appointments, call a taxi, send money to friends, check in for a flight and many many other.
Online chatbots save time and efforts by automating customer support. Gartner forecasts that by 2020, over 85% of customer interactions will be handled without a human. However, the opportunites provided by chatbot systems go far beyond giving responses to customers’ inquiries. They are also used for other business tasks, like collecting information about users, helping to organize meetings and reducing overhead costs. There is no wonder that size of the chatbot market is growing exponentially.
Of course, it is not so simple to create an interactive agent that the user will really trust. That’s why IM bots have not replaced all the couriers, doctors and the author of these lines. In this article, instead of talking about the future of chatbots, we will give you a short excursion into the topic of chatbots, how they work, how they can be employed and how difficult it is to create one yourself.
What is chatbot and what is it for?
According to Oxford Dictionaries, a chatbot is
“A computer program designed to simulate conversation with human users, especially over the Internet.”
It is an assistant that communicates with us through text messages, a virtual companion that integrates into websites, applications or instant messengers and helps entrepreneurs to get closer to customers. Such a bot is an automated system of communication with users.
Why does a business need chatbots? There are reasons for that like getting rid of routine tasks and simultaneous processing of multiple requests from users. Besides, a tremendous speed of processing users’ requests with chatbots helps gaining customers’ loyalty.
Consumers also benefit from chatbots and they are getting increasingly interested in this technology. A study presented at the 4th International Conference on Internet Science in November, 2017 identified reasons why people choose to interact with chatbots. According to this research, the main factors that motivate people to use chatbots are:
Take a look into the history of chatbots
And we will find that the first conversational bot was written in the USA in 1966. It was implemented by Joseph Weizenbaum, computer scientist of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and was named Eliza. The chatbot misled people, so authentic the communication with it was.
In the early 90’s, the Turing test, which allows determining the possibility of thinking by computers, was developed. It consists in the following. A person talks to both the person and the computer. The goal is to find out who his interlocutor is — a person or a machine. This test is carried out in our days and many conversational programs have coped with it successfully.
As for types of chatbots
Depending on how the specific bots were programmed, we can divide them into two large groups: working according to pre-prepared commands (simple chatbot) and trained (smart or advanced chatbot).
Simple chatbots work based on pre-written keywords that they understand. Each of these commands must be written by the developer separately using regular expressions or other forms of string analysis. If the user has asked a question without using a single keyword, the robot can not understand it and, as a rule, responds with messages like “sorry, I did not understand”.
Smart chatbots rely on artificial intelligence when they communicate with users. Instead of pre-prepared answers, the robot responds with adequate suggestions on the topic. In addition, all the words said by the customers are recorded for later processing. However, the Forrester report “The State of Chatbots” points out that artificial intelligence is not a magic and is not yet ready to produce marvelous experiences for users on its own. On the contrary, it requires a huge work:
“Chat developers and designers are the gardeners: they have to tend to the chatbots and coach their growth through continuous, yet gentle, correction. these designers must also beg, coerce, and incent customers to put up with subpar experiences during the process: the learning is really slow.”
The most popular chatbot
There are various search engines for bots, such as Chatbottle, Botlist and Thereisabotforthat, for example, helping developers to inform users about the launch of new talkbots. These sites also provide a ranking of bots by various parameters: the number of votes, user statistics, platforms, categories (travel, productivity, social interaction, e-commerce, entertainment, news, etc.). They feature more than three and a half thousand bots for Facebook Messenger, Slack, Skype and Kik.
Through the chatbot search engines, you can find an interesting application in each category, e.g. the best chatbot for Facebook Messenger is Poncho. It sends you personal weather forecasts with jokes or funny memes and, thus, looks more like a meteorologist friend than a soulless weather reporting service.
What can chatbots do?
“I think chatbots are the future of engagement between a fan and a brand or celebrity.”
Both startups and savvy companies are now incorporating interactive agents into their daily operations, communication with customers and sales processes. Chatbots can help to:
Improve customer service. It is the best option for those who don’t want their customers to:
Streamline the shopping process. It only takes to write what you want to the chatbot and the bot will send the information to the sales department. You don’t need to repeat several times “I need the same, but with metal buttons”. Besides, the chatbot remembers your preferences and uses this information when you return.
Personalize communication. A chatbot answers the specific questions of visitors instead of displaying a long list of information. The more attention a customer gets the greater his desire to buy something.
Improve a response rate. About 90% of questions sent from Facebook business pages remain unanswered. Chatbot responds to 100% of messages and converts more visitors into buyers.
Automate repetitive tasks. Most customers want to get answers on the same questions — When do you work? What is your location? Do you make deliveries? In order not to write the same answers every time, make a chatbot. It reduces your employees’ workload.
How to build a chatbot
If we managed to inspire you to create your own chatbot, here are some tips to help you get started. There are 4 main stages:
1. Define the goals. What should your chatbot do? Clearly indicate the list of functions your chatbot needs to perform.
2. Choose a channel to interact with your customers. Be where your clients prefer to communicate — your website, mobile app, Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp or other messaging platform.
3. Choose the way of creation. There are two of them: using readymade chat bot software or building a custom bot from scratch.
4. Create, customize and launch. Describe the algorithm of its actions, develop a database of answers and test the work of the chatbot. Double check everything before showing your creation to potential customers.
Now let’s look closer at 2 approaches to building chatbots:
Creating from scratch. If you are not a programmer yourself, you will need to hire a software development company as this method requires work with code, manual integration with messengers and customization. Among the advantages of this approach are:
This method may require significant financial and time investments.
Using chatbot builder platforms. You can create a chatbot with the help of services providing all the necessary features and integrations. It can be a good choice for an in-house chatbot serving your team. This option is associated with some disadvantages, including the limited configuration and the dependence on the service. Some popular platforms for building chatbots are:
The challenge of creating chatbots
The main challenge is in teaching a chatbot to understand the language of your customers. In every business, customers express themselves differently and each group of a target audience speaks its own way. The language is influenced by advertising campaigns on the market, the political situation in the country, releases of new services and products from Google, Apple and Pepsi among others. The way people speak depends on their city, mood, weather and moon phase. An important role in the communication of the business with customers may have the release of the film Star Wars, for example. That’s why training a chatbot to understand correctly everything the user types requires a lot of efforts.
Remember:
Conclusion. What to do?
Many business owners are just beginning to understand what benefits chatbots can bring to them. This technology is still in an early stage, its capabilities continue increasing and the best chatbots have yet to be created.
Invest in building a chatbot for your business and be at the forefront of innovation!
Chatbots
What is a chatbot?
A chatbot is a computer program that uses artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP) to understand customer questions and automate responses to them, simulating human conversation.
The value of chatbots
Chatbots can make it easy for users to find the information they need by responding to their questions and requests—through text input, audio input, or both—without the need for human intervention.
Chatbot technology is almost everywhere these days, from the smart speakers at home to messaging applications in the workplace. The latest AI chatbots are often referred to as “virtual assistants” or “virtual agents.” They can use audio input, such as Apple’s Siri, Google Assistant and Amazon Alexa, or interact with you via SMS text messaging. Either way, you’re able to ask questions about what you need in a conversational way, and the chatbot can help refine your search through responses and follow-up questions.
How chatbots work
Historically, chatbots were text-based, and programmed to reply to a limited set of simple queries with answers that had been pre-written by the chatbot’s developers. They operated like an interactive FAQ, and while they worked well for those specific questions and answers on which they had been trained, they failed when presented with a complex question or one that hadn’t been predicted by the developers.
Over time, chatbots have integrated more rules and natural language processing, so end users can experience them in a conversational way. In fact, the latest types of chatbots are contextually aware and able to learn as they’re exposed to more and more human language.
Today’s AI chatbots use natural language understanding (NLU) to discern the user’s need. Then they use advanced AI tools to determine what the user is trying to accomplish. These technologies rely on machine learning and deep learning—elements of AI, with some nuanced differences—to develop an increasingly granular knowledge base of questions and responses that are based on user interactions. This improves their ability to predict user needs accurately and respond correctly over time.
For example, if a user asks about tomorrow’s weather, a traditional chatbot can respond plainly whether it will rain. An AI chatbot, however, might also inquire if the user wants to set an earlier alarm to adjust for the longer morning commute (due to rain).
Chatbots vs. AI chatbots vs. virtual agents
You may notice the terms chatbot, AI chatbot and virtual agent being used interchangeably at times. And it’s true that some chatbots are now using complex algorithms to provide more detailed responses.
However, it is worth noting that the deep learning capabilities of AI chatbots enable interactions to become more accurate over time, building a web of appropriate responses via their interactions with humans. The longer an AI chatbot has been in operation, the stronger its responses become. So an AI chatbot using deep learning may provide a more detailed and accurate response to a query, and especially to the intentions behind the query, than a chatbot with recently integrated algorithm-based knowledge.
Common chatbot uses
Consumers use AI chatbots for many kinds of tasks, from engaging with mobile apps to using purpose-built devices such as intelligent thermostats and smart kitchen appliances. Business use is equally varied. Marketers use AI chatbots to personalize customer experiences, IT teams use them to enable self-service, and customer contact centers rely on chatbots to streamline incoming communications and direct customers to resources.
Conversational interfaces can vary, too. AI chatbots are commonly used in social media messaging apps, standalone messaging platforms, or applications on websites. Some typical use cases include:
Benefits of chatbots
The latest AI chatbots process the data within human language to deliver highly personalized experiences, creating clear benefits for businesses and customers.
Improve customer engagement and brand loyalty
Before the mature e-commerce era, customers with questions, concerns or complaints had to email or call a business for a response from a human. But staffing customer service departments to meet unpredictable demand and retraining staff to provide consistent replies to similar or repetitive queries, day or night, is a constant and costly struggle for many businesses.
Today, chatbots can consistently manage customer interactions 24×7 while continuously improving the quality of the responses and keeping costs down. Chatbots automate workflows and free up employees from repetitive tasks. A chatbot can also eliminate long wait times for phone-based customer support, or even longer wait times for email, chat and web-based support, because they are available immediately to any number of users at once. That’s a great user experience—and satisfied customers are more likely to exhibit brand loyalty.
Reduce costs and boost operational efficiency
Staffing a customer support center day and night is expensive. And for some departments, such as human resources, it might not be possible. Industries have been created to address the outsourcing of this function, but that carries significant cost. It also reduces control over a brand’s interaction with its customers.
A chatbot, however, can answer questions 24 hours a day, seven days a week. It can provide a new first line of support, supplement support during peak periods, or offer an additional support option. At the very least, using a chatbot can help reduce the number of users who need to speak with a human, which can help businesses avoid scaling up staff due to increased demand or implementing a 24-hour support staff.
Generate leads and satisfy customers
Chatbots can help with sales lead generation and improve conversion rates. For example, a customer browsing a website for a product or service may have questions about different features, attributes or plans. A chatbot can provide these answers, helping the customer decide which product or service to buy or take the next logical step toward that final purchase. And for more complex purchases with a multistep sales funnel, the chatbot can qualify the lead before connecting the customer with a trained sales agent.
Best practices and tips for selecting chatbots
Selecting a chatbot platform can be straightforward and the payoff can be significant for companies and users. Providing customers with a responsive, conversational channel can help your business meet expectations for immediate and always-available interactions while keeping costs down.
For example, an e-commerce company could deploy a chatbot to provide browsing customers with more detailed information about the products, highlight differences between models, and offer additional user guides and how-to videos. Likewise, the HR department in an enterprise organization may ask a developer to find a chatbot that can give employees 24/7 access to information about benefits and facilitate navigating that information — all without having to speak with someone in person.
Whatever the case or project, here are five best practices and tips for selecting a chatbot platform.
Chatbots and IBM
IBM Watson Assistant is an AI chatbot that can help solve customer problems the first time. It provides fast, consistent and accurate answers across applications, devices and channels. Using AI, Watson Assistant learns from customer conversations, improving its ability to resolve issues the first time while alleviating long wait times, tedious searches and unhelpful chatbots. Coupled with IBM Watson Discovery, you can enhance user interaction with information from documents and websites using AI-powered search functionality.
Watson Assistant optimizes interactions by asking customers for context around their statements. This reduces the frustration of having to rephrase questions, providing a more positive customer experience. In addition, Watson Assistant provides customers with an array of options in response to their questions. If it’s unable to resolve a particularly complex customer issue, it can seamlessly pass the customer to a human agent, right in the same channel.
Watson Assistant is designed to plug into your customer service ecosystem, integrating with your platforms and tools, making the entire customer experience smarter and simpler from start to finish. This makes your customers’ interactions with your business feel more like a meaningful relationship with someone who genuinely cares, and less like a series of random, fragmented conversations with strangers.
IBM also understands that a customer experience isn’t just about the conversation—it’s about protecting sensitive data, too. That’s why we bring world-class security, reliability, and compliance expertise to the design of all Watson products. In addition, IBM helps you protect your investment by giving you the flexibility to deploy Watson Assistant on-premises, in the IBM Cloud or with another cloud provider of your choice via IBM Cloud Pak® for Data.
The bottom line
Chatbots play an important role in cost reduction, resource optimization and service automation. It’s vital to understand your organization’s needs and evaluate your options to ensure you select the AI solution that will help you achieve your goals and realize the greatest benefit.
Take this 5-minute assessment to find out where you can optimize your customer service interactions with AI to increase customer satisfaction, reduce costs and drive revenue.
What is a chatbot & how do they work? The ultimate guide
The number of tickets handled by AI-powered chatbots increased by over 50 percent in 2021. But what, exactly, is a chatbot and how do chatbots work?
By Hannah Wren, Content Marketing Associate
Published October 22, 2020
Last updated July 14, 2022
Illustration by Julie Campbell
Messaging support has become a go-to for customers, with tickets jumping 370 percent over WhatsApp alone, according to our CX Trends Report. As messaging rates have risen, so has the use of AI bots. The number of tickets handled by automations and AI-powered chatbots year over year increased by over 50 percent from 2020 to 2021, with customers using chatbots to do everything from checking if they have COVID-19 symptoms to finding the perfect lipstick color.
But what, exactly, is a chatbot? How do chatbots work? And will they steal customer service representatives’ jobs? We’ll answer all your chatbot questions.
What is a chatbot?
A chatbot is a type of conversational AI that enables businesses to put a layer of automation or self-service in front of customers in a friendly and familiar way. And with companies increasingly adding messaging channels to provide faster resolutions and always-on support, bots have quickly become a key component of any messaging strategy. They can be deployed over any messaging app or channel and ensure customers get instant responses when an agent is busy helping other customers—or watching Bridgerton.
How do chatbots work?
Bots use predefined conversation flows, natural language processing, and/or machine learning to answer questions and guide customers through different scenarios, such as login issues, payment problems, or booking instructions–to name a few. AI bots can also learn from each interaction and adjust their actions to provide better support.
Chatbots work best with straightforward, frequently-asked questions. Unless their underlying technology is especially sophisticated, bots typically can’t handle difficult, multi-part questions like a support agent can.
Types of chatbots
Read on to learn the three main types of chatbots.
Chatbots that recommend knowledge base articles
Service has moved from calling at the first sign of trouble to adopting a “Google it” mantra. Research tells us that customers want to resolve as many issues as possible with a company’s online resources and prefer to resolve issues independently via self-service.
Chatbots can learn based on content in your knowledge base and recommend the right help articles to answer FAQs on any page of your website, inside your mobile app, over email, or via messaging channels. Since bots provide one-to-one support, they make the effort of searching for answers easier and more personalized than using a generic search engine. The business benefit of a bot that works alongside your knowledge base is that it uses your existing resources to deflect questions you already have answers to for the fastest time to value, which makes it easy to get started.
Decision tree chatbots
Decision tree bots enable you to design customized conversation flows that direct customers to quick answers, suggest knowledge base articles, and include points for handoffs to a live agent. Companies that are just getting started with a decision tree bot should look for a builder tool, like Zendesk’s own, that doesn’t require coding and provides a visual interface to help them create decision trees.
Task-specific bots
These chatbots are designed to help customers with a specific task and are typically highly specialized. They require more resources and a bigger budget because they need more comprehensive training and deeper natural language processing. Task-specific bots understand many different types of questions, and with access to the right customer data, can deliver personalized responses. For instance, a recruiting company might use this kind of bot for automating the first step of the recruiting process by helping potential employees submit their applications. Zendesk makes it easy to integrate third-party task-specific chatbots into your support system for seamless bot-human handoffs and more personalized conversations.
Why are chatbots important?
The benefits of chatbots go beyond “increasing efficiency” and “cutting costs”—those are table stakes. Bots are at their most powerful when humans can work in tandem with them to solve key business challenges.
Convenient one-on-one service, 24/7
In deploying a chatbot across customers’ preferred channels, businesses ensure customers get seamless, always-on support. If Sally’s sushi delivery is late, she can text a chatbot and get an update on her California roll in real-time. If Rachel lost her credit card, a virtual assistant can help her freeze it, so she doesn’t have to worry about mysterious charges.
Deliver better customer service with a chatbot
Try our chatbot software for free.
Businesses can scale quickly
In our trends report, we found that 42 percent of customer service leaders expect customer requests to grow, yet only 36 percent can expand headcount. This gap represents a sweet spot where a chatbot can help. Chatbots can act like extra support reps, triaging simple questions and basic requests.
Consider Spartan Race, which deployed Answer Bot to help its small team of agents tackle spikes in customer requests during races. Spartan Race has seen a 9.5 percent decrease in chat volume, extending its team’s live chat availability by three hours every day.
France’s national rail carrier, SNCF, needed to provide quick support to on-the-go passengers using its mobile app. But it couldn’t hire another team of agents to deal with the influx of requests. Mindsay’s Zendesk integration helped SNCF take the pressure off its overwhelmed agents. They deployed a chatbot to help find travel itineraries, provide departure information, and send alerts. And the integration led to a 50 percent reduction in incoming support tickets.
Chatbots give support teams the ability to scale without having to hire more staff.
More opportunities for conversion
Customer service bots can boost conversions with smarter self-service.
A chatbot can enable customers to self-serve outside of a help center, like on a checkout page, with knowledge tailored to their context.
Chatbots can also convert customers within the message chat by providing ecommerce opportunities for immediate action. Messaging types like carousels, forms, and picklists let customers book a hotel reservation or purchase a pair of shoes—all within the chat.
Chatbots can also automate cross-sell and upsell activities. With the right context, a bot can check if a consumer is eligible for a discount on a hotel room with a view or ask if he wants a pair of socks to match his new Nikes. In fact, 50 percent of companies say they use AI to make recommendations based on purchase or search history.
Best practices for getting started with chatbots
Ready to incorporate a chatbot into your customer service strategy? Here are some best practices to guide the way.
1. Make it clear to users when they’re interacting with a bot
We already know that customers are open to, and even prefer, to resolve their issues with a chatbot for simple queries. A study by Goldsmiths University and Mindshare, even found that one in four people are more willing to trust customer service chatbots with their sensitive information than a human.
But that same study also revealed that 48 percent of people feel it’s “creepy” if a chatbot pretends to be human. It’s always important to disclose to users when they’re interacting with a bot. Customers are open to communicating with bots, but they don’t want businesses to deceive them.
2. Always include an option to reach a live agent
Zendesk’s CX Trends Report found that the topmost frustrating chatbot experiences are when customers:
In fact, 46 percent of customers get frustrated that they don’t have a choice in human vs. bot at the start of service. Chatbots aren’t meant to resolve every issue, so it’s crucial to include an easy option to reach a live agent. It’s also important to ensure that your bot can pass on context and conversation history, so agents have all the details they need, and customers don’t have to repeat themselves. (Nearly half of customers believe AI should keep people from having to repeat things.)
3. Let bots handle simple issues
Here’s where your chatbots should play a starring role, according to customers:
But when it comes to filing a complaint or asking for technical support, 40 percent of customers prefer to interact with a human agent. Customers prefer bots for simple issues but still want the option to speak to a human for more sensitive and complex queries. Chatbots work best when their task is clear and simple. A good starting point is to look at the one-touch tickets that your agents see frequently. These are good issues to hand over to a chatbot.
4. Incorporate bots into your self-service strategy
Eighty-one percent of customers attempt to take care of matters themselves before reaching out to an agent, according to Harvard Business Review. What’s more, mid-to-large-sized businesses saw nearly a 40 percent increase in knowledge base views from customers during the pandemic. Customers prefer to resolve issues via a knowledge base or self-service portal because it’s simple and convenient.
A chatbot can help your customers self-serve more efficiently by highlighting your FAQs outside your knowledge base, such as on your checkout page or website homepage. You can also incorporate a chatbot into your knowledge base to personalize the experience. A bot can help customers find the right articles for their issue on a one-to-one level.
5. Use chatbots to collect key customer information upfront
Chatbots can collect key customer information upfront, such as order number, email address, or location, to ensure agents have all the details they need to personalize conversations and resolve the issue more efficiently. Chatbots can use this information to route customers to the right agent for the problem based on things like language, skill, or account type. This also makes chatbots a helpful lead generation tool, as they can collect prospect contact information and route them to the right salesperson for their inquiry.
6. Use data to improve your bot
Getting your bot up and running isn’t the end of your chatbot strategy. You also need to track metrics to improve and get the greatest value out of the tool. Here are a few metrics to watch:
This is the percentage of customers who choose to engage with a bot when prompted or given the option. It will help you determine if customers like using bots, if they respond to nudges to use bots, and what channels they look to bots for answers.
This refers to the number of questions answered by your bot, which will allow you to understand how cost-efficient and time-efficient your bots are.
This is the rate of questions your chatbots can’t respond to because they don’t understand them. This will help you get an idea of what people are looking for when using self-service and see where you can improve your bot flows.
Most answered questions: Tracking this metric can highlight common areas of frustration and opportunities for improving customer experience.
This metric indicates how often a bot transfers an interaction to an agent. The referral data can help you determine how bots integrate with agents’ workflows and give you insight into how customers approach complex support questions.
Customer-reported bot success metrics: Ask your customers to rate their service after using your bots so you can find out whether or not your bots provide good service.
What are examples of chatbots?
Read on for some chatbot examples to give you inspiration for the kind of bot your company might want to implement.
1. Fintiba
Fintiba offers online solutions for people who want to work or study in Germany. Human agents are critical for resolving high-empathy issues, like when a customer’s visa gets declined. Chatbots help streamline this process. Every conversation goes through Fintiba’s virtual agent first before going to a human agent. That takes the pressure off the support team, so they have the time they need to solve problems chatbots can’t handle. For example, when customers want to change their phone number, they complete a form and send a selfie inside the chat. An agent can then jump in with the process already started.
Fintiba’s chatbot solution, Solvemate, integrates with its customer service software. The bot is able to route chats with context and conversation history to live agents. When chatbots enhance the agent experience—instead of replacing it—it’s a better experience for everyone.
2. Discord
Discord is a free service that makes it easy for groups to communicate over voice, video, and text. During the pandemic, the number of unique visitors to its customer service site doubled, and pageviews increased by 70 percent as a flood of new users began using the service. The company was easily able to shoulder this unprecedented surge in users and support queries thanks to an early decision to make big investments in automation, deflection, and AI. These tools enabled Discord to help customers quickly and easily get the answers they needed, while freeing agents to focus on more complex, high-priority conversations.
“Automation and scaling is always at the forefront of our minds, and we’re always looking for ways to do more with less,” said Danny Duong, Discord’s Director of Customer Experience and Community Management. “We’re focused on getting customers the help they need as quickly as possible, while never sacrificing the human touch.”
To date, Discord has made more than one million suggestions to customers through its chatbot, and resolved more than 100,000 tickets. In 2020 alone, the team has also used AI to resolve approximately 14 percent of all email inquiries. In total, the team has an overall deflection rate of 10 percent, meaning that one in 10 of its customers have their problems solved without ever engaging with an agent.
3. Carousell
Carousell is one of the world’s largest and fastest growing marketplaces across Southeast Asia, Taiwan, and Hong Kong. A majority of the questions Carousell’s customer-facing team receives are straightforward and transactional, like how to create an account or how to accept payments. This is where Carousell’s chatbot comes into play, which serves customers in English, Chinese, and Indonesian. It guides customers to relevant help center articles, which in turn drives ticket deflection.
This investment in self-service tools has been a boon for Carousell’s support team. The help center receives more than a million views a month, and its chatbot responses have a 22 percent click-through rate. As a result, the company is able to successfully deflect 24 percent of inbound general enquiries, and 7 percent of all incoming requests. And since the team spends less time on low-level requests, it has been able to dramatically improve its response time—77 percent of the 30,000 monthly tickets are answered in less than 24 hours.
4. LendingClub
LendingClub connects U.S. borrowers and investors through an online marketplace that offers ethical and easy ways to access credit. To help surface help center articles and anticipate customer questions, its support team adds some of the most popular articles to automated replies with LendingClub’s chatbot.
The team has seen valuable cost savings when its chatbot handles a ticket, with the potential for further savings month over month, and a resolution rate of 12 percent. Its chatbot has been helpful in addressing quick questions for customers. “We’re happy to see customers find the answers they need, when they need it. [Our chatbot] points them in the right direction to find solutions independently,” said Alina Doyle, a LendingClub Specialist.
Limitations and drawbacks of full chatbot automation
Chatbots weren’t built to take over customer support. Rather, they were designed to serve as intermediaries, to keep customer support accessible when agents are off the clock and free them to handle tricky requests.
Chatbots are most successful when they work together with human agents. Bots aren’t meant to solve every issue: 56 percent of customers say bots are helpful for simple requests. For example, bots do a good job offering basic troubleshooting, but the number of variables and the complexity of deeply technical troubleshooting makes it better suited to a well-trained agent.
Bots can help your brand scale 1:1 communication, but agents bring empathy to the table, and efficient handoffs between bots and their human counterparts mean customers don’t ever have to repeat themselves.
How have chatbots evolved?
Chatbots might seem like a relatively new concept since companies are still figuring out how they fit into their overall business strategies. But bots have been around for decades. The first chatbot was developed by Joseph Weizenbaum, a scientist at MIT’s AI lab, in 1966—that’s even before the first personal computer. It was named ELIZA. The next chatbot was PARRY, a natural language program built in 1972. Another early chatbot is Dr. Sbaitso. Dr. Sbaitso was constructed in 1992 and is considered one of the first AI chatbots.
But if chatbots have been around for decades, why are we starting to see a boom now?
Chatbots have come a long way since the 1990s, partly due to advances in AI and machine learning. But most recently, the rise of messaging has made bots an essential part of any customer service and engagement strategy. Today, nearly all the top messaging platforms offer APIs so businesses can offer seamless messaging experiences with a bot.
What is the future of chatbots?
Here are a few key points to consider when it comes to the future of chatbots.
There are already 300,000 active Facebook Messenger chatbots, and messaging will only become a more critical customer engagement channel.
Businesses need to engage over the channels that matter most to their customers. With support that’s fast, personal, convenient, and secure, it’s no surprise that messaging has seen an upswell of adoption by both customers and businesses.
AI isn’t new technology at the workplace anymore; however, many companies are still learning how it fits in their overall business strategies. But as AI continues to improve and chatbots become more sophisticated, more businesses will adopt it. In fact, the Chatbots Market was worth USD 1274.428 million in 2018 and is projected to reach USD 7591.82 million by 2024, registering a CAGR of 34.75 percent over 2019–2024, according to Research And Markets.
Even as chatbot technology gets smarter, bots shouldn’t replace human agents but help them perform their jobs even better. Businesses get the greatest value from AI when using augmented intelligence—human intelligence and machine intelligence combined.
What chatbot platform is right for you?
Today there are many chatbot examples. Chatbots can be deployed across any messaging channel. But chatbots are relatively new to customer service, and companies are still figuring out how they fit within their support strategy. That can make it tough to know how to find the right chatbot solution for your business. Answering these questions will help you find a solution that best fits your support team’s needs.
1. What problem are you looking to solve—and what resources do you need to solve it?
For starters, you need to decide what use cases to automate. Decide based on the problem you need to solve and what resources you have to solve it.
Some companies may need a bot to deliver help center articles across a variety of channels and capture basic customer context. Other companies may need bots for personalized requests, like telling a customer how much data her iPhone used this month or recommending a new plan based on usage.
Offering personalized service with a chatbot requires more resources and a bigger budget. You’ll need a chatbot solution that integrates with customer service software and other relevant systems.
2. Is your chatbot flexible enough to work across different channels?
Customers expect to get support over their preferred touchpoints—whether they’re interacting with a human or a bot. And 40 percent of companies are already using AI to engage with customers via their preferred contact methods.
Research tells us customers want to interact with brands on channels they use with friends and family. Messaging and social media channels, like Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, Twitter Direct Message, LINE, Apple Business Chat (which integrates with iMessage), and SMS lend themselves to more convenient conversational experiences. For instance, Samsung Australia created a Twitter chatbot to give customers personalized TV recommendations.
It’s important for your chatbot to work across all these different channels. With a chatbot platform that’s flexible, you can connect your bot to any channel, without any heavy lifting. For example, Zendesk lets a business build once and deploy anywhere. In other words, you can use the best version of a rich bot experience across all your channels, even those with no native bot support.
3. What level of context will your chatbot need?
44 percent of customers say it is most frustrating when they have to start all over with a human agent after interacting with a bot. More context leads to better chatbots—and more personalized conversations.
Freelance platform Upwork’s chatbot displays proactive CTAs tailored to what a user is trying to accomplish, like what help center article they’re viewing.
Upwork’s bot also uses contextual metadata, like a user’s name for a personalized greeting. It knows if a user is a client or a freelancer, tailoring quick replies accordingly. It also integrates with our Support Suite, so agents have the context they need to handle every escalated chat.
Beyond passing on relevant information to agents, bots can also pass on context to a CRM or other software. This enables things like:
Bots can read context coming from a conversation, too. With sentiment analysis, a virtual agent can understand when a customer is frustrated and react accordingly.
4. How will you manage conversations between chatbots and agents?
Businesses need tools to both deploy chatbot conversations on the front end and manage them on the back end. This ensures agents can understand the intent behind every conversation and streamline hand-offs between agents and chatbots.
With the help of triggers, automation, and workflows, support teams can centrally define engagement rules and track, manage, and prioritize chatbot interactions at scale. In fact, 39 percent of companies already use AI to prioritize customers based on their status or account type. This opens up possibilities, like automatically assigning:
To effectively control bot interactions, a business will need to integrate its chatbot solution with its customer service software.
The agent workspace in Zendesk provides agents with a real-time, conversation-focused interface to seamlessly manage conversations between agents and bots.
The best bot experiences are built with Zendesk
Zendesk makes it easy to enhance your customer support experience with a chatbot. Answer Bot can leverage your existing help center resources to guide customers to a resolution via self-service and collect customer context. And if you want a little more control, our click-to-build flow creator enables you to create rich, customized bot conversations without writing code. Most importantly, our award-winning support platform provides teams with a real-time, conversation-focused interface to seamlessly track and manage conversations between agents and bots. It also integrates with all the systems your team depends on, including third-party bots.
What is a Chatbot: Definition and Guide
Learn how to create a chatbot for Facebook Messenger, Instagram, and Telegram for free with SendPulse
A chatbot is an application that can imitate a real conversation with a user in their natural language. Chatbots enable communication via text or audio on websites, messaging applications, mobile apps, or telephone.
In this video, Caleb Smith, marketer at SendPulse, explains how to use a chatbot effectively for your business.
Contents
Why are chatbots important for a business?
Let’s highlight some of the advantages that chatbots offer businesses going by findings in the State of Chatbots report of 2018.
Benefits of a Chatbot
Below are more benefits of using chatbots for your business:
How does a chatbot work?
Chatbots work based either on artificial intelligence or rules. We’ll consider rules-based chatbots because they don’t require the knowledge of code or any technical skills. Non-tech-savvy marketers can select a platform providing chatbot functionality. Such a service lets create auto-replies and advanced scenarios based on triggers. Subscription to a chatbot, any keyword or message sent by a user can work as a trigger. For example, a user subscribes to your bot. You can create a welcome flow that will be sent to users automatically after subscription. Include quick replies with several options available, such as «About us», «Learn more about the product», and «Contact sales department.» Then you can send different messages based on subscribers’ replies. You can even assign tags to users to provide them with relevant offers later.
Consider as many potential triggers as possible that users are most likely to type in. If you sell products, they may include «price,» «size,» «exchange,» «refund,» etc. After you list these possible triggers, design auto-reply flows to provide leads with the necessary information. This way, your sales reps and support team will manage to deal with high-priority tasks and automate answering FAQs. Read on to learn how to create a chatbot with SendPulse for free.
Now that you know the benefits of chatbots, take a look at platforms providing chatbot functionality.
5 Best Chatbot Platforms
In this section, you’ll get to know the important factors to consider when choosing a chatbot platform. We’ll cover the features and pricing of the 5 best services. Stay tuned!
SendPulse
SendPulse is a unified marketing platform that helps small and medium businesses automate communication with clients through email campaigns, chatbots, web push notifications, and SMS. It provides a simple and functional chatbot builder that requires no coding to create a powerful chatbot.
SendPulse allows you to design a chatbot for Instagram, Facebook Messenger, Telegram, and WhatsApp. You can turn website visitors into chatbot subscribers with the help of multichannel subscription widgets. SendPulse chatbot builder functionality enables brands to reduce the workload of their customer support teams by setting up auto-replies to answer users’ everyday questions. You can encourage chatbot users to answer several questions about their product preferences and provide them with personalized offers which will result in higher sales.
SendPulse chatbot builder features
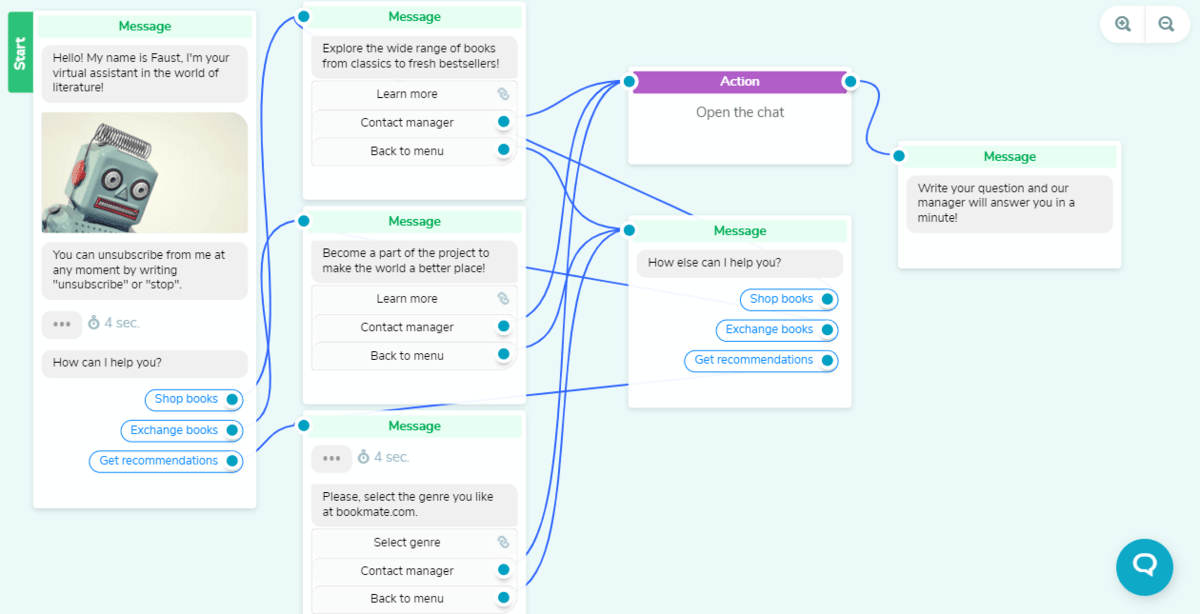
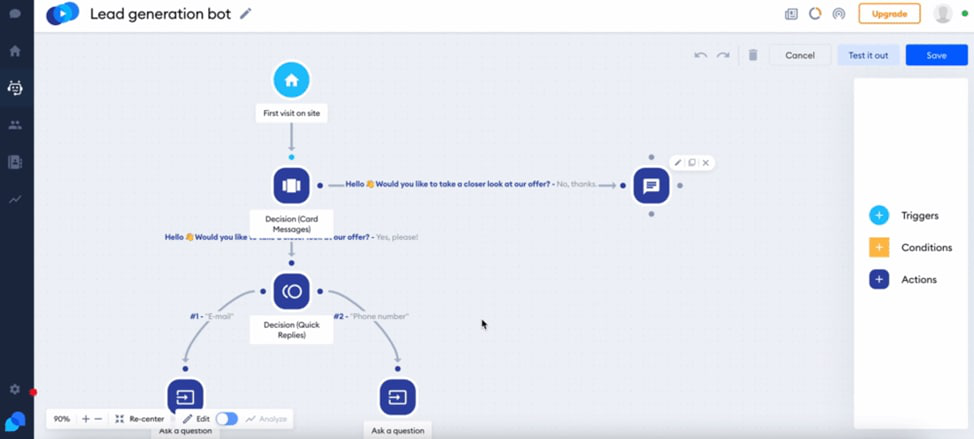
It won’t take you more than an hour to create a chatbot flow with SendPulse. Check below a flow created for a bookshop with the SendPulse chatbot builder. Users can choose several scenarios and get help with making a perfect choice.
Pricing
SendPulse offers a free plan which allows you to create up to 3 bots, have up to 1,000 contacts, send up to 10,000 messages per month across all of your bots, and add up to 10 variables. With this plan, you can evaluate the benefits of the service.
ManyChat
ManyChat is a platform that allows users to supercharge their Facebook Messenger and Instagram marketing with chatbots. They help reach more leads, engage prospects, blow up sales, and automate conversations with customers without much sweat even if you’re not a tech-savvy marketer.
ManyChat allows its clients to provide their customers with instant support, improve lead generation, increase sales and qualify leads by automating conversations for Instagram Direct Messages and Facebook Messenger. Drag and drop functionality lets you design advanced flows without much stress. You can conduct contests, giveaways, and promotions to boost subscriber engagement with your brand. If needed, your team will be informed that customers want to have a live chat.
ManyChat features
ManyChat offers a drag and drop conversation builder, so you need to add the necessary blocks to build a flow. Check out an example below. You can also learn detailed stats of each action and block to improve your chatbot on the go.
Pricing
ManyChat provides a free plan which allows you to create a chatbot for Instagram Direct Messenger and Facebook Messenger, automate conversations with up to 1,000 contacts, use basic Growth Tools, have 10 customer tags, and get email support.
Tidio
Tidio is a customer service tool that helps supercharge your conversations with clients via chatbots for Facebook Messenger and live chats. You can add a live chat to any website without having to code. Customize a live chat widget to fit your brand style. You can build a chatbot scenario with an intuitive drag and drop editor or use one of 20 chatbot templates.
Tidio lets its users communicate with leads and never lose a customer via any channel from one place. Increase sales by collecting customer personal data, advanced lead qualification, and recovering clients’ abandoned carts. Let your support team deal with more complex tasks and delegate part of their workload to chatbots. This way, you can automate answering repeated questions, segment users, and inform operators about certain customers’ actions to respond immediately. Drag and drop the necessary nodes (blocks) to build a chatbot flow that can consist of actions, triggers, and conditions.
Tidio chatbot builder features
Although Tidio lacks some advanced features like a Facebook website widget, comments auto-reply, webhooks, and growth tools, this platform can be a perfect choice for beginners looking for a straightforward solution without wide functionality.
Below you can see an example of a lead generation bot created with Tidio. The interface is pretty simple, so it won’t take you much time to learn. This is the bot for users who engage with your website for the first time.
Pricing
Tidio provides a free plan which lets you have up to 100 unique visitors per month, unlimited chats, and add up to 3 agents.
Every new user gets a 7-day free trial of the paid plan to evaluate the premium features of the platform.
Chatfuel
Chatfuel is one of the leading chatbot platforms in the world used by Levi’s, Adidas, and Netflix. Users appreciate the service for its functional chatbot builder and clean interface that require no coding skills to build an advanced chatbot flow for your business. You can collect customer data, attract new clients, automate support, and boost sales via a website, Facebook Messenger, and Instagram chatbots.
Chatfuel allows you to attract new prospects in Facebook Messenger, cover their demands, answer FAQs, send auto-replies and promos, and segment customers. With this platform, it’s easy for users to make bookings in a few seconds, collect client feedback after the purchase, retain and bring customers back, and qualify leads saving each interaction in the built-in CRM system. You can easily capture leads’ information through direct messages and Instagram ads to nurture and segment them effectively.
Chatfuel features
Below you can see the process of creating a chatbot for a bookshop. You can add different blocks on the left panel and customize them by enriching them with media on the right. Test your chatbot before launching.
Pricing
Chatfuel offers a free plan which allows you to create a full-featured bot for 50 subscribers and have priority support for the first 30 days.
MobileMonkey
MobileMonkey is a chatbot marketing platform with enormous potential for your business growth. It enables marketers to automate outreach, convert inbound and outbound prospects into clients, and boost sales via social messaging channels. With its tools, you can find targeted prospects, qualify and convert leads, and close more sales. MobileMonkey’s technology OmniChat enables marketers to write automated chat conversations working across multiple apps.
MobileMonkey lets you either develop a bot using the framework or create a bot without a line of code with a visual builder. It won’t take you more than 15 minutes to create a bot scenario. Alternatively, you can use pre-made templates for different industries. You can optimize answering customers’ FAQs with automated sequences. A bot can effectively walk your user down the sales funnel and provide a positive user experience.
MobileMonkey features
Below you can the process of creating a chatbot flow for a bookshop with MobileMonkey.
Pricing
MobileMonkey provides a free plan which allows you to send up to 1,000 messages every month to unlimited subscribers. You can create widgets, and add attributes and tags.
Now you can choose the platform which fits best your business goals. Now, we’ll walk you through creating a chatbot with SendPulse.
How to Create a Chatbot with SendPulse
How to create a chatbot for Facebook Messenger
Facebook Messenger, being the second most used messenger app in the world and the first in America, is the best place to set up a bot. Set up chatbot marketing with SendPulse by following these steps:
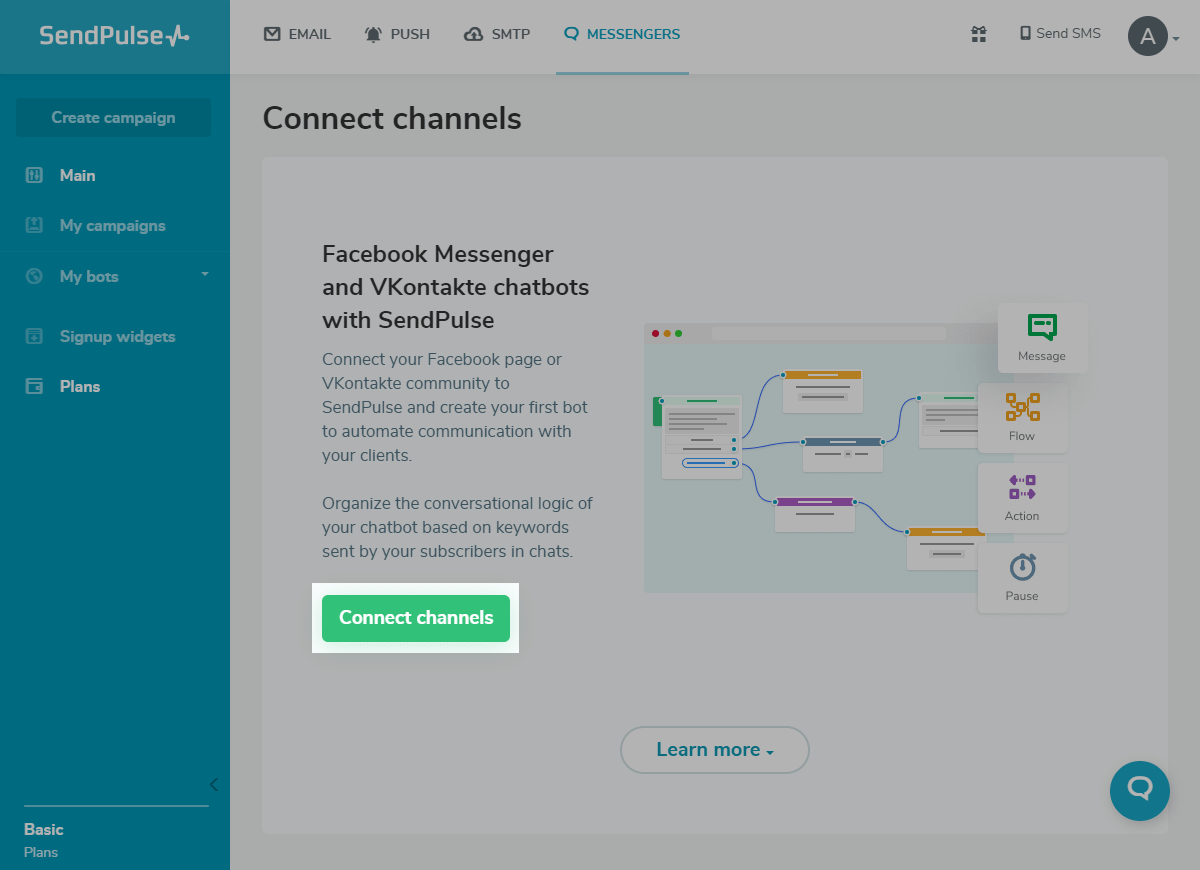
Step 1: Create an account with SendPulse and go to the “Messengers” tab
If you are not already on SendPulse, sign up. If you are already logged in, click “Facebook chatbot” under products. Go to “Messengers” tab at the top of the page and click the «Connect channels» button.
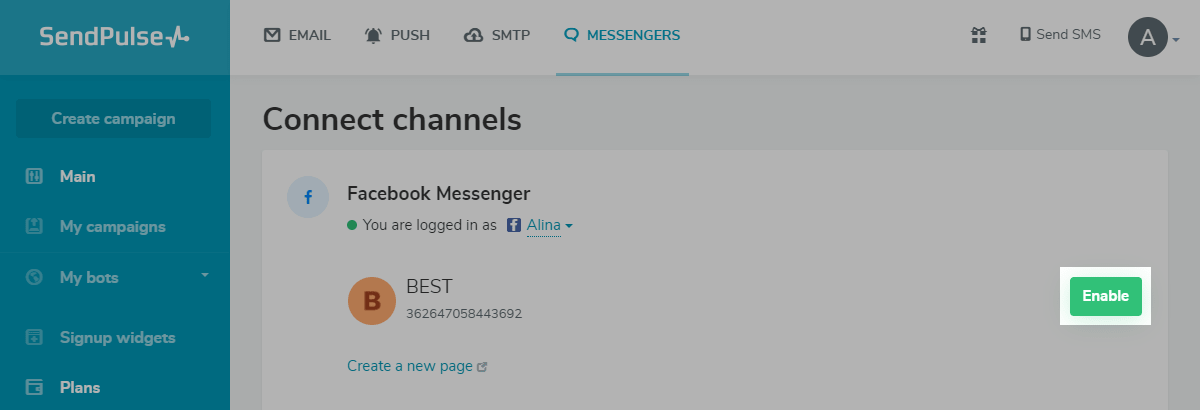
Step 2: Sign in with Facebook and create a bot
Select group pages for which you want to create chatbots. Click «Enable» opposite a group to enable a chatbot.
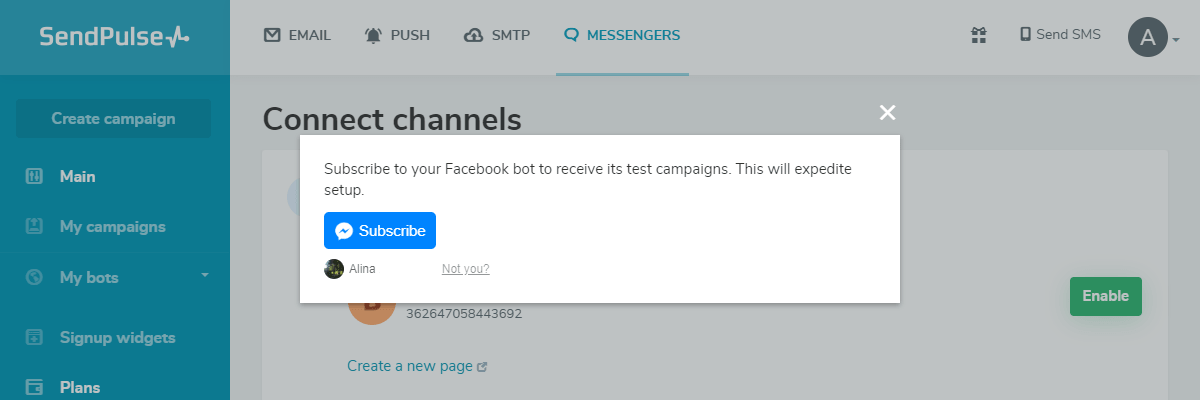
Step 3: Send a test message
Subscribe to your chatbot and send yourself automated messages and campaigns to test them.
When a prospect subscribes through a widget, the chatbot automatically sends them the first message. Launch messenger marketing strategy with SendPulse and send Facebook campaign anywhere faster!
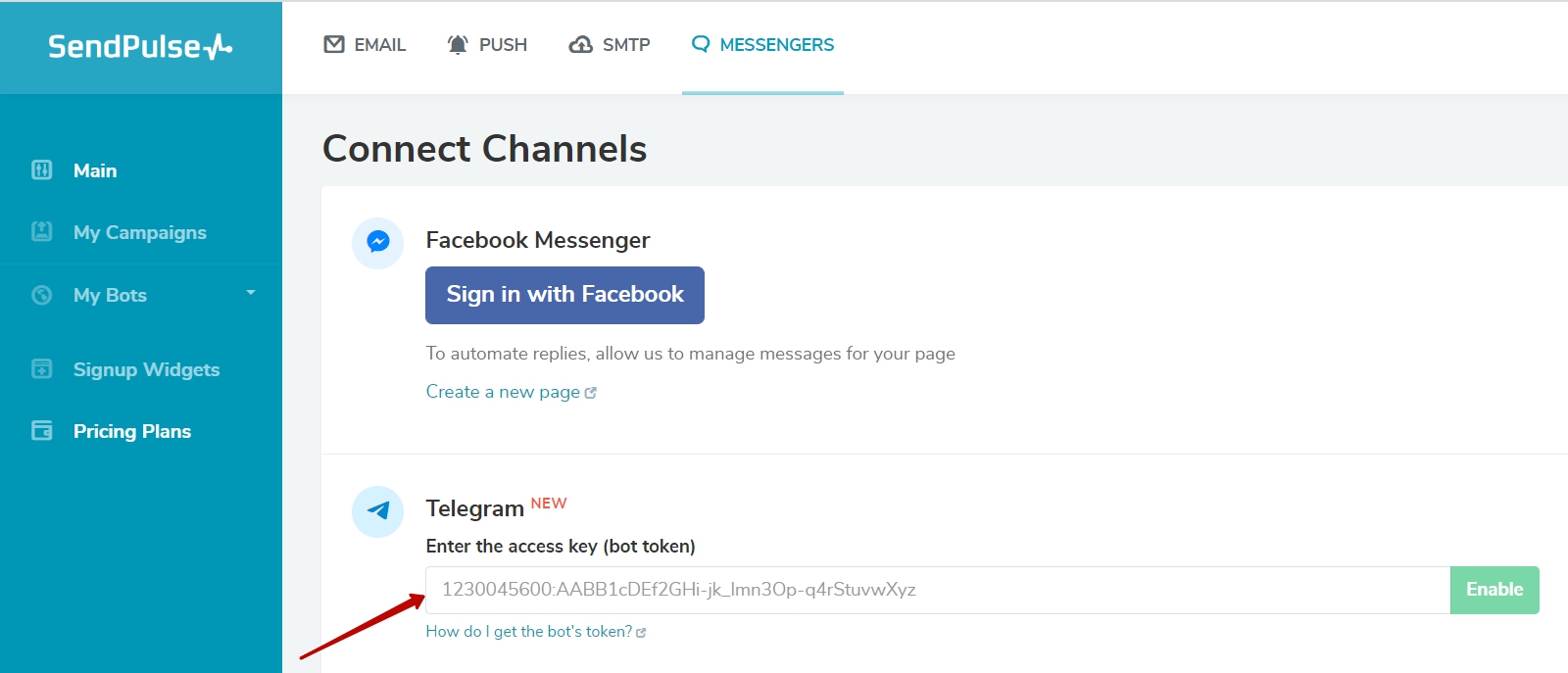
How to create a chatbot for Telegram?
Creating a Telegram chatbot is as easy as pie with SendPulse. You don’t need to code or have any technical background. You can create up to three bots each month and send up to 10,000 messages for free. Follow this step-by-step guide to get started.
Create a bot with @BotFather
Sign in to your Telegram account, enter @BotFather in the search tab, choose the bot that has a blue checkmark beside it, and click «Start» to activate it.
Then, create a name and username for your bot
Connect your bot to SendPulse
Copy your token value and add it to your SendPulse account.
After you are redirected to the Telegram app, click «Start» and you will be subscribed to your bot. Look for more precise instructions in this guide.
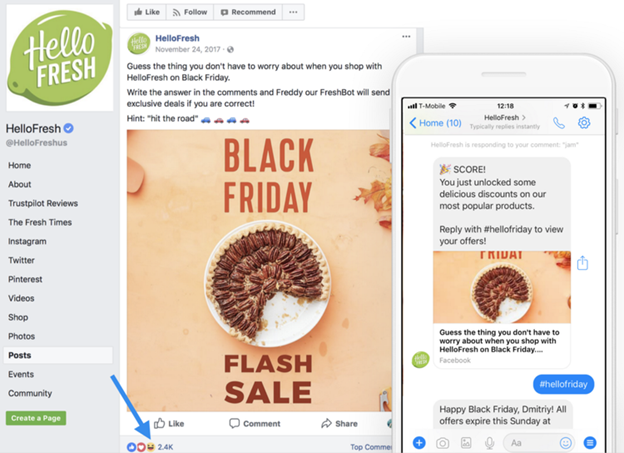
Chatbot Examples
Below is a Hello Fresh chatbot.
Here is how the Score uses a chatbot to provide fans with updates regarding their favorite teams.
Eddy Travels bot allows users to find the necessary flight. Check out below.
Finally, HipMunk’s Facebook chatbot helps travelers book flights and hotels quickly.
Chatbot Best Practices
Here are the best practices for building, testing, and using a chatbot: