What is microsoft access
What is microsoft access
What is Microsoft Access? Here’s how the database management system works, and how it differs from Excel
Twitter LinkedIn icon The word «in».
LinkedIn Fliboard icon A stylized letter F.
Flipboard Facebook Icon The letter F.
Email Link icon An image of a chain link. It symobilizes a website link url.
Microsoft Access is a member of the Microsoft 365 family of applications, and is a powerful productivity tool made for business and enterprise users.
Much like Microsoft Excel, Access lets you view and edit data. But Access is more powerful than Excel, and can handle much more data at once.
Here’s all you need to know about Microsoft Access.
How Microsoft Access is different than Excel
Both Microsoft Excel and Access can be used to store data, so they might seem like similar. But in reality, they’re quite different.
Excel is a spreadsheet program that’s primarily used for individual projects and to perform brief calculations. Most Excel users only work with a few dozen to a few hundred data cells at once. And Excel is great for graphing and charting those calculations and data points.
Microsoft Access, on the other hand, is made to store and manage vast quantities of data in a form that makes it easy to retrieve and use in different applications. While Excel users type directly into their spreadsheets, Access databases are manipulated with pre-made forms and queries. Most businesses also connect Access to other applications, so when those other apps generate data, it’s automatically ported over to Access.
How Microsoft Access is used
Here’s an overview of the major elements of Access and how they’re used.
Taken together, these components allow businesses and organizations to manage and understand the large amounts of data they need to store.
For example, a business might use Access to track its inventory and sales, while a school can use Access to track its students, their personal information, grades, performance, coursework, and teacher data. Access can be used on specific projects, such as to manage co-workers, tasks, accomplishments, deadlines, and follow-up activities.
Database.Guide
Beginners
Categories
What is Microsoft Access?
Microsoft Access is a relational database management system (RDBMS) developed by Microsoft. It’s part of the Microsoft Office suite, included in the Professional and higher editions or sold separately.
Microsoft Access provides a quick and easy way to develop databases and is particularly well suited for individuals and small business. Access is the most popular desktop database on the market.
Main Tasks
Some of the main tasks performed in Access include:
Benefits of Access
Some of the main benefits of using Access, when compared to some of the more “enterprise level” database management systems, include:
Limitations of Microsoft Access
While it can be the perfect choice for many scenarios, Access does have its limits. It was never intended as an enterprise solution. Access’ strengths lie in providing individuals and businesses with an efficient way to store and retrieve data and generate useful reports without needing to hire developers or get the IT department involved.
For enterprise level applications – such as a corporate CRM – a more sophisticated system such as SQL Server would be a better choice. SQL Server is a database server, and is designed to have many users accessing it at the same time. SQL Sever databases can also hold a lot more data than Access databases. SQL Server has more advanced security features, more optimisation options, networking features, and more.
In practice, these numbers would probably be much lower. An Access database might run into trouble with 1 user, 10 users, or 100 users, depending on its design.
Mind you, the same is true for SQL Server. One poorly designed database could bring the whole database server crashing down. However, the key point is, SQL Server is more robust and scalable than Access.
But even if its not an enterprise level application, sometimes SQL Server is still a better choice. For example, most websites use database servers such as SQL Server or MySQL, even if its a small website with low traffic.
This makes the website more scalable. If it suddenly attracts a lot of traffic, it should be able to handle it.
Also, for smaller websites on shared hosting accounts, it’s easier for the hosting provider to use SQL Server or MySQL because they can have many hundreds, or even thousands, of websites accessing a single database server. Plus even a small website can end up with huge amounts of data in its database over time.
Custom Web Apps
More recent versions of Access have allowed the user to create web applications for their Access databases.
Access 2010 introduced the ability for databases to be published to SharePoint 2010 web sites running Access Services, and uses SharePoint lists to store its data.
Access 2013 introduced “custom web apps”. The web apps can be created from within Access, and when the app is saved, it is saved directly into the SharePoint 2013 server running Access Services or Office 365 site. Access 2013 web solutions store its data in an underlying SQL Server database.
Microsoft Access
Microsoft Access
Developer
Released
Latest release version
Licensing
Operating system
Platform
Website
Access was also the name of a communications program from Microsoft, meant to compete with ProComm and other programs. This Access proved a failure and was dropped. Years later Microsoft reused the name for its database software.
Contents
History
Access 1.1 Manual
Access version 1.0 was released in November 1992.
Microsoft specified the minimum operating system for Version 2.0 as Microsoft Windows 3.0 with 4 MB of RAM. 6 MB RAM was recommended along with a minimum of 8 MB of available hard disk space (14 MB hard disk space recommended). The product was shipped on seven 1.44 MB diskettes. The manual shows a 1993 copyright date.
The software worked well with very large records sets but testing showed some circumstances caused data corruption. For example, file sizes over 700 MB were problematic. (Note that most hard disks were smaller than 700 MB at the time this was in wide use.) The Getting Started manual warns about a number of circumstances where obsolete device drivers or incorrect configurations can cause data loss.
Access’ initial codename was «Cirrus». This was developed before Visual Basic and the forms engine was called «Ruby». Bill Gates saw the prototypes and decided that the Basic language component should be co-developed as a separate expandable application. This project was called «Thunder». The two projects were developed separately as the underlying forms engines were incompatible with each other; however, these were merged together again after VBA.
Access is used by small businesses, within departments of large corporations, and hobby programmers to create ad hoc customized desktop systems for handling the creation and manipulation of data. Access can be used as a database for basic web based applications hosted on Microsoft’s Internet Information Services and utilizing Microsoft Active Server Pages ASP. Most typical web applications should use tools like ASP/Microsoft SQL Server.
Some professional application developers use Access for rapid application development, especially for the creation of prototypes and standalone applications that serve as tools for on-the-road salesmen. Access does not scale well if data access is via a network, so applications that are used by more than a handful of people tend to rely on Client-Server based solutions. However, an Access «front end» (the forms, reports, queries and VB code) can be used against a host of database backends, including JET (file-based database engine, used in Access by default), Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, and any other ODBC-compliant product.
Many developers who use Access use the Leszynski naming convention, though this is not universal; it is a programming convention, not a DBMS-enforced rule.[2] It is also made redundant by the fact Access categorises each object automatically and always shows the object type, by prefixing Table: or Query: before the object name when referencing a list of different database objects.
MS Access should not be used over a wireless link as this can cause failure and data corruption.
Features
One of the benefits of Access from a programmer’s perspective is its relative compatibility with SQL (structured query language) —queries may be viewed and edited as SQL statements, and SQL statements can be used directly in Macros and VBA Modules to manipulate Access tables. In this case, «relatively compatible» means that SQL for Access contains many quirks, and as a result, it has been dubbed «Bill’s SQL» by industry insiders. Users may mix and use both VBA and «Macros» for programming forms and logic and offers object-oriented possibilities.
MSDE (Microsoft SQL Server Desktop Engine) 2000, a mini-version of MS SQL Server 2000, is included with the developer edition of Office XP and may be used with Access as an alternative to the Jet Database Engine.
Unlike a complete RDBMS, the Jet Engine lacks database triggers and stored procedures. Starting in MS Access 2000 (Jet 4.0), there is a syntax that allows creating queries with parameters, in a way that looks like creating stored procedures, but these procedures are limited to one statement per procedure. Microsoft Access does allow forms to contain code that is triggered as changes are made to the underlying table (as long as the modifications are done only with that form), and it is common to use pass-through queries and other techniques in Access to run stored procedures in RDBMSs that support these.
In ADP files (supported in MS Access 2000 and later), the database-related features are entirely different, because this type of file connects to a MSDE or Microsoft SQL Server, instead of using the Jet Engine. Thus, it supports the creation of nearly all objects in the underlying server (tables with constraints and triggers, views, stored procedures and UDF-s). However, only forms, reports, macros and modules are stored in the ADP file (the other objects are stored in the back-end database).
Development
Access allows relatively quick development because all database tables, queries, forms, and reports are stored in the database. For query development, Access utilizes the Query Design Grid, a graphical user interface that allows users to create queries without knowledge of the SQL programming language. In the Query Design Grid, users can «show» the source tables of the query and select the fields they want returned by clicking and dragging them into the grid. Joins can be created by clicking and dragging fields in tables to fields in other tables. Access allows users to view and manipulate the SQL code if desired.
The programming language available in Access is, as in other products of the Microsoft Office suite, Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications. Two database access libraries of COM components are provided: the legacy Data Access Objects (DAO), which was superseded for a time (but still accessible) by (ADO) ActiveX Data Objects however (DAO) has been reintroduced in the latest version, MS Access 2007.
MS Access can be applied to small projects but scales poorly to larger projects involving multiple concurrent users because it is a desktop application, not a true client-server database. When a Microsoft Access database is shared by multiple concurrent users, processing speed suffers. The effect is dramatic when there are more than a few users or if the processing demands of any of the users are high. Access includes an Upsizing Wizard that allows users to upsize their database to Microsoft SQL Server if they want to move to a true client-server database. It is recommended to use Access Data Projects for most situations.
Since all database queries, forms, and reports are stored in the database, and in keeping with the ideals of the relational model, there is no possibility of making a physically structured hierarchy with them.
Access allows no relative paths when linking, so the development environment should have the same path as the production environment (though it is possible to write a «dynamic-linker» routine in VBA that can search out a certain back-end file by searching through the directory tree, if it can’t find it in the current path). This technique also allows the developer to divide the application among different files, so some structure is possible.
Versions
| Date | Version name | Version number | Supported OS | Corresponding office suite |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | Access 1.0 | 1.0 | Windows 3.0 | |
| 1993 | Access 1.1 | 1.1 | Windows 3.1 | |
| 1994 | Access 2.0 | 2.0 | Windows 3.1 | Office 4.3 Pro |
| 1995 | Access 95 | 7.0 | Windows 95 | Office 95 Pro |
| 1997 | Access 97 | 8.0 | Windows 95, NT 3.51 SP5 and up | Office 97 Pro/Developer |
| 1999 | Access 2000 | 9.0 | Windows 95, NT 4.0 and up | Office 2000 Pro/Premium/Developer |
| 2001 | Access 2002 | 10 | Windows 98, NT 4.0 SP6 and up | Office XP Pro/Developer |
| 2003 | Access 2003 | 11 | Windows 2000 SP3 and up | Office 2003 Pro/Pro Enterprise |
| 2007 | Access 2007 | 12 | Windows XP SP2 and up | Office 2007 Pro/Pro Plus/Ultimate/Enterprise |
| 2010 | Access 2010 | 14 | Windows XP SP3 and up | Office 2010 Pro/Pro Academic/Pro Plus |
| 2012 | Access 2013 | 15 | Windows 7 and up | Office 2013 Pro/Pro Plus |
| 2015 | Access 2016 | 16 | Windows 7 and up | Office 2016 Pro/Pro Plus |
| 2018 | Access 2019 | 16 | Windows 10 | Office 2019 Pro/Pro Plus |
| 2021 | Access 2021 | 16 | Windows 10 and up | Office 2021 Pro |
Note: There is no Access 3.0 to 6.0 because the Windows 95 version was launched with Word 7. All of the Office 95 products have OLE 2 capabilities, and Access 7 shows that it was contemporary with Word 7.
Download Microsoft Access for Windows
Part of the Microsoft Office productivity suite, Microsoft Access is perhaps the most recognizable name in the database management industry. Individuals, entrepreneurs, school teachers, software developers, data architects, and other types of PC users resort to this database management system (DBMS) daily.
Many Microsoft Office users are familiar with MS Word, PowerPoint or Excel, but few have casually experimented with Access to understand its purpose or how it works. It’s actually not that complicated.
When it comes to data management, MS Access is more advanced than Excel but easier than SQL Server. Therefore, you don’t need experience with client/server databases to use it to your advantage. A simple Microsoft Access tutorial on how to create forms and query data should get you started.
Thanks to its user-friendly interface and powerful set of features, MS Access can be used to create and manage databases for any reason, from organizing a household inventory at home to keeping track of personnel files at work. It’s the perfect fit for individual users and teams.
Screenshots
Our Review
Check out the Microsoft Access versions and product cycles, set of features, and the new features of the latest version. You can also find out more details about the system requirements for each version available for download, how to download and install, interface, a brief comparison with SQL Server, our verdict, and a couple of alternative database management solutions that are just as easy to use.
Microsoft Access versions and end of life
Microsoft released Access version 1.0 in 1992, but it gained popularity when it was integrated with Microsoft Office 95. Since then, the Microsoft Office suite has received a major update every 3 years: Office 97, 2000, 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, and 2019.
When it comes to the product lifecycle, you should know that all versions until MS Access 2010 are no longer supported. Access 2010 has extended support until October 2020, Access 2013 until April 2023, and Access 2016 and 2019 until October 2025. Microsoft strongly recommends users to upgrade to the latest version.
Microsoft Access features
Here’s what you can do with this great database management system provided by Microsoft:
Microsoft Access latest version
The newest edition is Microsoft Access 2019, which brings a wide range of new features, improvements, and fixes:
Microsoft Access system requirements
Before downloading and setting up this data management tool on your PC, check if you meet these conditions:
How to download and install Microsoft Access
Since it’s part of the Microsoft Office suite, you need to download Microsoft Office and choose Microsoft Access for installation. To do this, it’s necessary to visit this page, sign in with your Microsoft account and enter your product key. Then you can download Microsoft Office to your PC and choose Access for setup.
If you prefer using the online version of Microsoft Access, which is part of Microsoft 365, you need a Microsoft 365 Premium account.
However, if you’re just interested in the free trial of Microsoft Access and don’t want to complicate yourself with the sign-up process, you can download the standalone, runtime, retail version of Microsoft Access from this WindowsReport page. We listed direct download links to the IMG files of Microsoft Access 2019, 2016 and 2013, so take your pick and be patient until the download finishes (the setup files are very large).
After setup, you will obtain a free trial that you can use to evaluate the entire set of options and configuration settings provided by MS Access. At the end of the trial, you can either remove the product from your PC or buy a license. It’s not mandatory to purchase a license for the Office 365 complete package but only for Access.
Microsoft Access interface
As far as the user interface is concerned, Microsoft Access is wrapped in a clear-cut window with a sophisticated look. The newest version perfectly blends with Windows 10, given its flat buttons and streamlined UI. The File menu provides you with quick access to the database properties that you can edit, as well as to the password protection, optimization, and repair tool.
The MS Access templates become available when trying to create a new file, and you can choose from multiple styles such as business, logs, lists, and inventories. For example, you can use templates to manage tasks, create custom web apps, keep your list of contacts updated, manage events, or put together a product inventory.
The main window of Microsoft Access shows all key options in the ribbon bar, spread across the Home, Create, External Data, Database Tools, Fields, and Table tabs.
Microsoft Access vs. SQL Server
Although both Microsoft Access and SQL Server are designed to handle databases, they are quite different. While MS Access is great for casual users and professionals who need to quickly organize databases, it’s not made to deal with countless database operations in large-scale businesses. In that case, Microsoft SQL Server is better.
On the other hand, it’s easier to learn Access from scratch than SQL Server because you don’t need to know database management code. You can use simple wizards and drag-and-drop functionality to design tables and create forms. SQL Server offers more possibilities but needs to be told exactly what to do through code.
What is Microsoft Access?
Taking everything into account, we can safely say that Microsoft Access must belong to your toolkit if you operate a small business and need to manage databases without coding skills. It’s packed in a user-friendly interface, contains numerous templates, and offers to help you every them of the way through the Tell Me assistant.
For instance, you can use Microsoft Access home inventory and project management templates to quickly get started. And, thanks to the Microsoft Access Database Engine, MS Access easily integrates with Office and non-Office products to facilitate interoperability.
Microsoft Access alternatives
There aren’t many database management tools as easy to use as Access. If you’re looking for a Microsoft Access alternative, you could check out Navicat. It’s a great database administration tool for team collaboration, which can be used with DBMS utilities like MySQL or PostgreSQL.
Another great replacement for Microsoft Access is LibreOffice Base, which is free and open-source. It’s a feature-rich database management solution with versatile options, offering support for MS Access, MySQL, MariaDB, and PostgreSQL. And, just like MS Office, Base integrates with other products from its suite, like LibreOffice Writer.
FAQ: Learn more about the Microsoft Access database management tool
No, Microsoft Access isn’t freeware, but you can test it at no cost during a free trial. Microsoft provides a free trial for Office 365 as well as for standalone, runtime, retail versions of Microsoft Access. You don’t need to sign up for anything to activate the trial.
The Google equivalent of Microsoft Access could be considered Google Cloud Databases. It’s a business solution for database management and migration, which can be used through the Google Cloud Platform. It’s mostly oriented toward app, website and service developers.
Open your database in Microsoft Access, go to the External Data tab, click Excel, and select the Excel spreadsheet you wish to import into your database to turn it into a data source using the wizard.
Databases
These days, databases are an essential part of websites and blogs all over the web. Whether you look after a corporate website, run a forums based website, or simply run your own blog, your job would be made much harder if it weren’t for databases.
In this section of Quackit, you will find a comprehensive range of quality articles and tutorials covering various database concepts. My main focus initially, is to «de-mystify» the whole concept of databases so that beginners can develop an understanding of what a database is and where it fits in the larger picture of website development.
What is a Database?
A database is a collection of data. That may sound overly simplistic but it pretty much sums up what any database is.
A database could be as simple as a text file with a list of names. Or it could be as complex as a large, relational database management system, complete with in-built tools to help you maintain the data.
Text File
Imagine we have a text file called «Individual.txt», and that the contents look like this:
We could use this information to do things such as send an email to everyone on our list. We could do this because, due to the way we designed the list, we know that each row contains a different individual, and the information on that row is related to that individual. Also, the items in each row are separated by commas. Therefore, we know that the email address next to «Homer» is his email address. We could also call each row a record. Therefore, we currently have 4 records in our database.
With a small list like this, a text file may serve our purposes perfectly.
Spreadsheet
Another option would be to store it in a spreadsheet using spreadsheet software (for example, Microsoft Excel). That way, we could do some extra things with our list (such as format it, or sort by first name/surname etc).
A spreadsheet program like Excel makes these tasks relatively easy to do. Also, programs like Excel organize the data into rows and columns, making your data easier to comprehend. Something like this:
Database Software
A better option would be to store the data in a database table using specialized database software, such as Microsoft Access. Something like this:
So What’s the Difference?
You may be wondering what the difference is between the last two examples (Excel vs Access). After all, both examples have the data organized into rows and columns.
There are many differences between spreadsheet software and database software. The rest of this tutorial will show you why database software is a much better option for creating databases.
Database Management Systems
Some of the more popular relational database management systems include:
Throughout this tutorial, you will become familiar with some of the key concepts of database management systems. These include:
What Does a Database Management System Look Like?
Different database management systems look different, but generally, there are a number of common features that you’ll usually see across most of them.
Microsoft Access
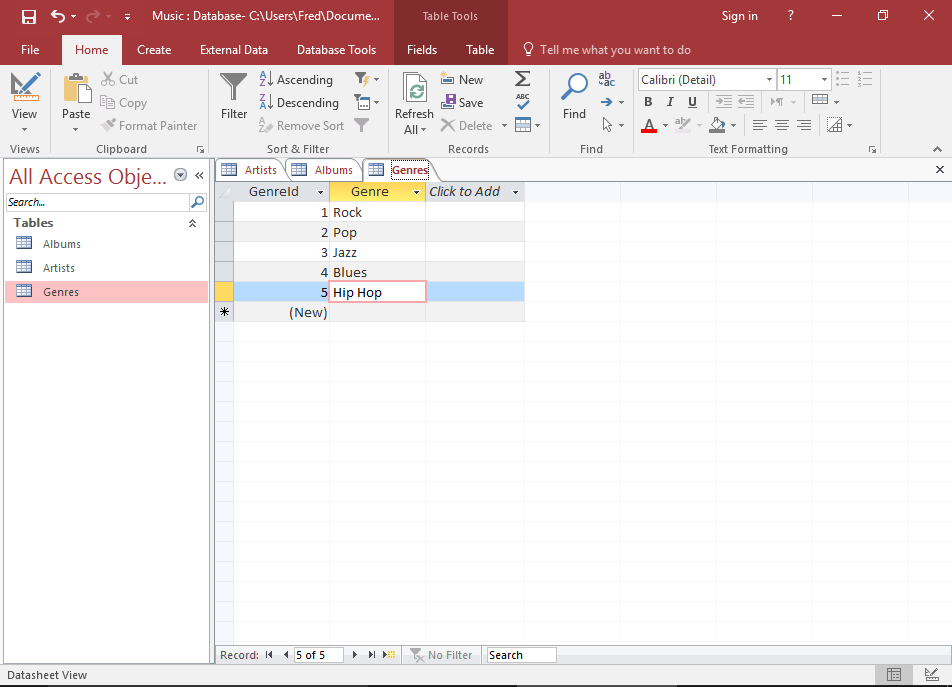
This is the main screen you’ll see when opening up Access to view an existing database. The outer part is the database management system and it’s menu, the middle part is the actual database. In this example, the database is called «dateSite» and has 20 tables. If you were to open a different database, the name of the database would be different and you would see different tables, but the available options would be the same (i.e. Tables, Queries, Forms, Reports, Macros, Modules, Open, Design, New).
Some of these options are common across all database management systems. All database systems allow you to create tables, build queries, design a new database, and open an existing database.
Microsoft SQL Server
Microsoft SQL Server is a more robust database management system than Access. While Access is better suited to home and small office use, SQL Server is more suited to enterprise applications such as corporate CRMs and websites etc.
The above screen is what you see when you open SQL Server through Enterprise Manager. Enterprise Manager is a built-in tool for managing SQL Server and its databases. In this example, there are 6 databases. Each database is represented down the left pane, and also in the main pane (with a «database» icon).
Which Database System to Use?
If you are using a database for home or small office use, Microsoft Access or Filemaker should be fine. If you need to create a database driven website, then you’re better off using a more robust system such as SQL Server, Oracle, or MySQL.
The examples in this tutorial use Microsoft Access. If you don’t have Microsoft Access, you should still be able to follow the examples. The tasks we perform are the same tasks you would need to perform regardless of which database management system you use. The key goal with this tutorial is to provide you with an overview of what is involved in creating and maintaining a database.
Access is known as a desktop database system because it’s functions are intended to be run from a single computer. This is in contrast to a server database application (such as SQL Server), where it is intended to be installed on a server, then accessed remotely from multiple client machines.
Microsoft (or MS) Access is a software package that you install just like any other software package, and is bundled as part of the Microsoft Office suite.
Access Versus Excel
You may be wondering what the benefits of using Access are compared with using an Excel spreadsheet. Well, it really depends on what you want to do with the data that you’re storing and how much data you intend to store.
Excel may be fine if you’ve only got a small amount of data, and if you don’t have many attributes against each piece of data. It may be fine if you don’t have much in the way of relational data across multiple worksheets. Once you start storing many attributes against each piece of data, and perhaps you find yourself repeating information across multiple worksheets, then it’s time to start using Access (or another database system if you prefer).
Another important reason for using Access over Excel is, if you need to generate a lot of queries and reports. Access is much better suited for doing this compared to Excel.
Microsoft Access Database File Extension
When you create (and save) a database in Microsoft Access, the database is saved with a .mdb extension. This is the file extension you will use the most, when developing Access databases. Once you’ve established your database, you also have the option of saving it as an MDE file, which gives you some benefits over the MDB file. An MDE file uses a .mde extension.
Downloading Microsoft Access
Access Versions
A database is much more than just a list or table.
It gives you true command of your data, enabling you to retrieve it, sort it, analyze it, summarize it, and report results in moments. It can combine data from various files, so that you never have to enter information twice. It can even make data entry more efficient and accurate.
In this lesson, we’ll show you some benefits of a database and introduce its most important parts.
Let’s say that you’re the secretary of a large hiking club. You have a list of recycling volunteers, a list of holiday party volunteers, addresses for newsletter labels, a membership list, and so on.
Suppose that a club member, who appears on a number of lists, changes her e-mail for the second time this year. With only a set of lists, you’d have the tiresome job of changing that information everywhere it occurs. With a well-structured database, you’d have to change it only once. The database takes care of everything else.
If you’re just working with 10 or so items, then you’ll probably want to create a simple list, perhaps as a worksheet in Microsoft Excel or a bulleted list or table in Microsoft Word.
If your data is more complex, or changes frequently, then an Access database gives you an advantage.
Access creates relational databases, which means that data is stored in various separate tables by subject or task, but the data is related and can be brought together in ways that you specify.
Even though a club’s database might store member contact information separately from its lists of recycling volunteers or holiday planning data, the database can pull all this information together whenever you want.
So, you could quickly print a list of who’s volunteered to recycle newspapers this Saturday, along with their up-to-date addresses and phone numbers.
The two sets of data are relational, so that information in one set of data (such as Nancy Davolio’s name on the recycling list) is associated with, or «knows about,» the applicable information in the other set of data (Nancy Davolio’s contact information).
To make the most of your database, you’ll want to set up the tables of data to reflect the subjects and tasks associated with your data.
While planning your database, consider the scenarios in which people will be entering data, looking up data, or reporting data. A little forethought can go a long way.
Access databases consist of objects. Later in this course, we’ll describe the following four important objects in more detail:
Tables store your data in rows and columns. All databases contain one or more tables.
Queries retrieve and process your data. They can combine data from different tables, update your data, and perform calculations on your data.
Forms control data entry and data views. They provide visual cues that make data easier to work with.
Reports summarize and print your data. They turn the data in your tables and queries into documents for communicating ideas.
This practice session does not involve using Access or downloading any file; all you need is pen and paper or a word processing program to jot down your thoughts.
Think about recent situations in which you’ve seen a database in use. Most likely, a store that you’ve visited recently uses a database to manage inventory, update customer information, and produce receipts or invoices. Or perhaps your company uses a database for managing customer or employee information.
Jot down how people used the database: Did they look up your customer information? Scan price tags into the register or computer? Check inventory for availability of merchandise? Print receipts?
If you’re planning to create a database, jot down two or more situations in which you (or someone else in your organization) are likely to use the data, such as creating a monthly status report, reviewing sales data, sending out form letters, or entering student grades on assignments.
Starting Microsoft Access
Microsoft Access is a computer application used to create and manage computer-based databases on desktop computers and/or on connected computers (a network). Microsoft Access can be used for personal information management (PIM), in a small business to organize and manage data, or in an enterprise to communicate with servers.
If you have a Microsoft Access database such as an E-Mail attachment, a file on a floppy disk, on the network, or in any other means, once you see its icon, you can double-click it. Not only will this action launch Microsoft Access, but also it will open the file.
You can also launch Microsoft Access from a shortcut. If you happen to use the software on a regular basis, you can create a shortcut on your desktop or on the Quick Launch area.
If you are working on a network of related computers, your database may be located in another computer. In this case the network or database administrator would create a link or shortcut to the drive that is hosting the database. You can then click or double-click this link or shortcut to open the database and, as a result, launch Microsoft Access.
The Database as a File
A Microsoft Access database is primarily a Windows file. It must have a location, also called a path, which indicates how the file can be retrieved and made available. Although you can create a database on the root directory such as the C: drive, it is usually a good idea to create your files, including your databases, in an easily recognizable folder.
When you installed the computer (or when it was installed), it (the operating system) might have created a folder called My Documents that provides a convenient place for you to create your files. If various people use the same computer, there is a different My Documents folder for each one. When you log in, the computer (the operating system) locates your corresponding My Documents folder and makes it available.
Creating a Database
In our lessons, we will learn different techniques of creating a database. For now, a database is first of all a Windows file. It is mainly created from Microsoft Access. If you have just started Microsoft Access, to create a database, you can use one of the links in the main (middle section of the interface).
You can proceed from one of these options. Like every file in the computer, a database must have a name that identifies it. This name must be specified when creating the database.
In our description of the Microsoft Access interface, we saw that the right section displayed an empty area. If you start creating a database as we will see in the next sections and lessons, the right side gets filled with some options, such as prompting you to name your database.
The Database Wizard
Many techniques allow you to create a database, the fastest of which consists of using one of the provided templates. To create a database using one of the samples, in the left section, first click Local Templates, then, in the main section, select one of the samples under Local Templates: