What is the area of belarus
What is the area of belarus
What is the area of belarus
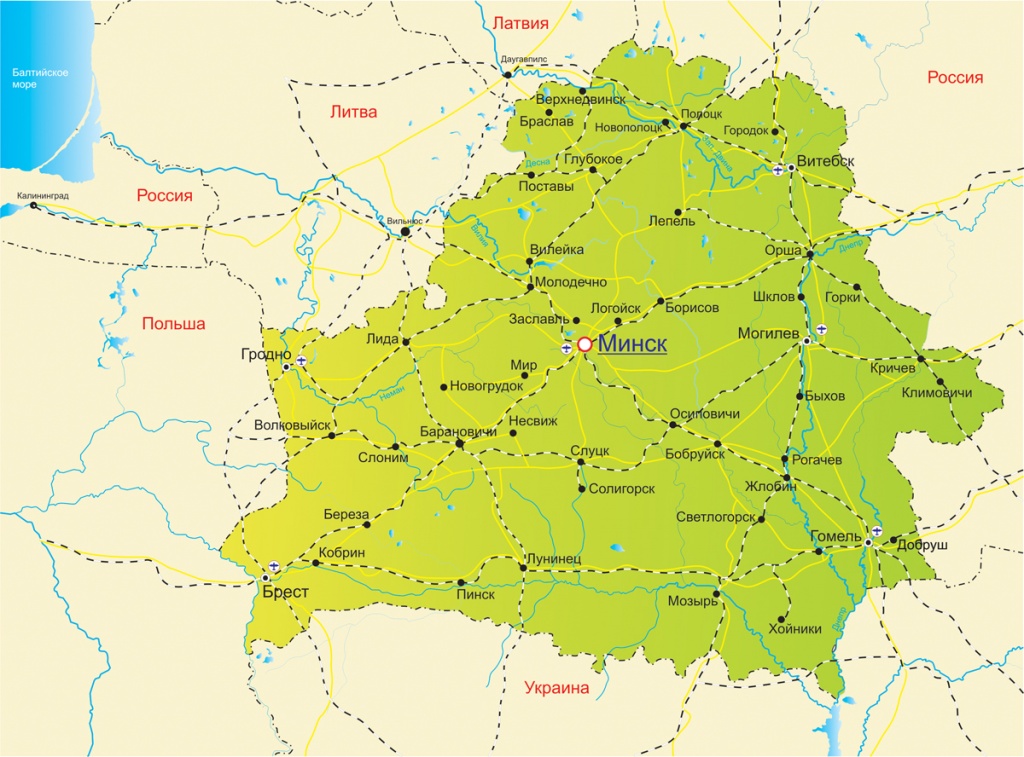
Belarus is situated in the center of Europe, and has international borders with five countries: Russia, Ukraine, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia. The total land area of Belarus is more than 207,000 square kilometers.
The country doesn’t have access to sea, but due to the location Belarus is an important trade and transport corridor between Europe and the CIS.
The capital of Belarus
The main oblast of Belarus
Climate and weather in Belarus
Average temperatures in Belarus
Precipitation
The best time to travel in Belarus
Belarusian people
Languages of Belarus
Religions in Belarus
There are up to 25 religious confessions in Belarus, the number of religious communities amounts to more than 3.4 thousand (1 January, 2014).
Orthodox is the principal religion of Belarus.
There are over 1000 Orthodox churches and cloisters in Belarus, and its number is increasing every year.
Many of the most famous country’s monuments and architectural attractions reflect the Orthodox traditions.
Religious freedom and tolerance
In Belarus religious freedom is guaranteed by the Constitution. In the country the number of believers and the number of churches is increasing every year. The network of educational establishments is developing constantly where representatives of various faiths can get religious education. Among them there is the Institution of theology named after St. Cyril and Methodius of Belarusian State University is, where the rector is His Holiness Metropolitan Pavel. Students, practicing Orthodoxy, Catholicism and Uniatism, can get here theological education.
The government supports constructive initiatives of representatives of various faiths. Also state bodies are working to prevent activity of destructive religious sects.
Traditional crafts in Belarus
Belarus has a long and rich history of traditional arts and crafts, and many of which exist today. The main crafts are weaving, woodworking, pottery, straw.
Traditional folk dancing remains popular with a number of folk theaters around Belarus.
Music and art also play an important role in the national life of Belarus. National and international festivals are held regularly across the country. The best known of these is «The Slavyanskiy Bazar» in Vitebsk.
Currency
The national currency of the Republic of Belarus is Belarusian ruble. In circulation there are eight denominations of coins (1, 2, 5, 10, 20 and 50 kopecks, and 1 and 2 rubles) and seven denominations of banknotes (5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200 and 500 rubles). The most common currencies are US dollars, Euro and Russian rubles.
Communication
The reference service of public telephone networks: 109, the reference service of bus station: 114, the reference service of rail transport: 105, the reference service of air transport: 106, emergency: 103, police: 102, rescue service: 101. There are some city codes: Brest: 162, Vitebsk: 212, Gomel: 232, Grodno: 152, Minsk: 17, Mogilev: 222.
Tips for tourists
International credit cards, including American Express, Visa, MasterCard, Cirrus, Electron, Eurocard and others, are accepted in big hotels, restaurants and supermarkets.
The electricity voltage is 220 V, 50 Hz. Mostly plug sockets are 2-pin but in some new buildings there can be European plugs with three prongs. The system of weights and measures is metric.
Key Facts
Geography
The Republic of Belarus is located in the center of Europe, is part of Eastern Europe. It is crossed by major transit routes of the entire continent, including one of Eurasia’s main transport corridors from southwest to northeast. The shortest transport links connecting the Baltic Sea and the Black Sea also run through Belarus’ territory.
Border
Belarus shares border with five countries: Poland in the west, Lithuania in the northwest, Latvia and the Russian Federation in the north, the Russian Federation in the northeast and east, Ukraine in the south. The total length of the state border is 3,617km. The distance between Minsk and the closest capital city of the neighboring country – Lithuania’s Vilnius – is 215km. Latvia’s Riga is 470km far from Minsk; the distance to Poland’s Warsaw is 550km, Ukraine’s Kiev is 580km, Russia’s Moscow is 700km.
Belarus is a compact country with a slightly longer horizontal axis. The country stretches 560km from north to south, and 650km from west to east.
Total area
Belarus is a medium-sized European state. The total area is 207,600km2, or about 2% of the total area of Europe.
Belarus is the 13th largest country among 44 continental European states (the world’s 84th largest country). It is bigger than Greece, Portugal, Austria, the Netherlands, Belgium, Czechia. Belarus is nearly as big as Romania and the UK.
Terrain
Belarus is located in the East European Platform. The country has a predominantly flat terrain intersected by hills, flatlands, and lowlands with marshes and lakes.
Lowlands with absolute heights of up to 200m account for about 70% of the country’s territory, hills – for about 30%. The lowest area is in the Neman River valley in Grodno Oblast (80-90m above the sea level); the highest point of Belarus is Dzerzhinsky Hill in Dzerzhinsk District, Minsk Oblast (345m).
The northern part is called the Belarusian Lake District. It features glacial relief, hills and ridges. The middle part is located in the glaciolacustrine zone of the Belarusian Ridge and in the East Belarusian plateau-like lowland. The southern part features morainic and aquaglacial plains of sub-Polesie and flat, often marshy lowlands of Polesie.
Rivers and lakes
Belarus is located in the water basins of the Baltic Sea and the Black Sea. There are 20,800 rivers with the total length of 90,600km in the country. The biggest rivers are the Dnieper, the Western Dvina, and the Neman. The Dnieper is the country’s longest river stretching 700km through Belarusian territory.
There are almost 11,000 lakes in Belarus. The biggest lakes located in the north (the Braslav Lake District, aka «the blue necklace”) were formed nearly 15,000-20,000 years ago when the Valdai glacier melted. The biggest lake in Belarus is Naroch (79.6m2), the deepest lake is Dolgoye (53.6m deep).
Administrative division
Belarus is divided into six oblasts: Brest Oblast, Vitebsk Oblast, Gomel Oblast, Grodno Oblast, Minsk Oblast, and Mogilev Oblast. They are further divided into 118 districts.
Minsk – the capital city of the Republic of Belarus – is an independent city that does not make part of any other oblasts.
Minsk Oblast is the central region of Belarus. It is the only oblast without external borders.
Population
According to the National Statistical Committee, as of 1 January 2021 the population of Belarus was 9,349,645. This is 0.1% of the global population and about 1.3% of the European population. Belarus is the world’s 94th and the CIS’ 6th most populated country.
The urban population of 7,280,320 accounts for 77.9% of Belarus’ population. Some 2,069,325 people are rural residents. There are 115 towns, 85 urban-type settlements, and 23,050 villages in Belarus.
The population of regions and oblast capitals (as of 1 January 2021):
The population of Minsk is 2,009,786.
The average population density is 45 people per 1km2 (as of 1 January 2021).
The ethnic structure includes Belarusians (85%), Russians, Poles, Ukrainians, Jews, and representatives of other ethnicities (according to the 2019 population census).
State structure
The Republic of Belarus is a unitary democratic welfare rule-of-law state. It is a presidential republic by political structure with the socially oriented economy.
The Fundamental Law of Belarus is the Constitution of 1994 with amendments and addenda which were passed at the national referendums of 24 November 1996 and 17 October 2004.
The official languages are Belarusian and Russian.
Belarus in Figures
Economy, demographics, international rankings, numbers that illustrate healthcare, culture, and sport. How many tonnes does Belarus’ gold reserve weigh? What is the length of the country’s motorways? How many Belarusians have turned 100 years old? Learn facts that will help you get to know Belarus better!
Geography of Belarus – Key Facts
In Belarus, people like to boast that the country is located in the centre of Europe. On the political map, Belarus belongs more to Eastern Europe and is regarded as an important link where central routes between Europe and Asia converge. The Republic of Belarus borders on five neighbouring states: Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland, Lithuania and Latvia to the west and northwest.
Endless road | Photo: Benny Reiter
In Belarus there are no high mountains, the country has no access to the sea. Nevertheless, it surprises with flat, seemingly endless expanses, dense forests and water-rich lakes and rivers.
The territory of Belarus is located in the western part of the Eastern European Plain. The relief of Belarus is predominantly flat and hilly, with an average altitude of 160 metres above sea level. Hills make up about one fifth of the country, the rest consists of 80 percent lowlands and plains. The highest regions are located in the centre of the country, while the relief gradually sinks to the north and south. The highest peak of the country is 345 meters above sea level of Gora Dzerzhinskaya. The elevation is located west of Minsk, near the small town of Dzerzhinsk. The lowest situated area is in the valley of the river Neman (Memel), on the border with Lithuania. The altitude is 80-90 meters above sea level. The wide and flat surface area favours settlements, agricultural development and the construction of industrial plants and utility lines.
The higher regions are characterised by a changing landscape with swamps and lakes. The main features of today’s relief were created by the effects of the ice ages. In the northern part of the country there is the Belarusian Poozerje (derived from the Russian word “ozero”, the lake) with a relatively young glacial relief, with numerous elevations and lakes.
In the last million years glaciers have played a decisive role in the formation of the relief, five times the area of today’s Belarus was covered by ice masses. During these ice ages, glacial and fluvioglacial forms of the relief (moraine relief) were formed by glacial movements.
In the central part of the country lie the Belarusian ridge (area: 13,000 km²) and the East Belarusian plateau. The two landscapes were formed under the influence of the last ice age. The origin of the watershed between the Black Sea and the Baltic Sea lies in the formation of these elevations. The ridge is characterised by steep hills crossed by deep river valleys. The slopes and plains are covered with forests and crossed by hollows and gorges. Next to the town of Orscha in the east of the country, not far from the Russian border, lies the Orshanskoe hill (255 metres above sea level), which gradually merges into the Orshansko-Mogilevskaya plain (between the towns of Orscha and Mogilev). To the south are the plains of Predpolesje and the flat, marshy lowlands of Polesia.
Prypjat marshes at Polesia | Photo: Benny Reiter
The region of Polesia extends from the city of Brest in the very southwest of the country directly on the Polish border to the Russian border in the southeast. Brest Polesia is characterised by valleys 50 to 300 metres wide, mostly with a swampy flat underground. The lowlands with 100 to 150 meters above sea level in the southeast are called Gomel Polesia and are characterized by a wave-like relief. On both sides of the river Pripyat there is the Pripyatskoe Polesien, which is characterized by large peat massifs and shallow lakes.
The river valleys are also interesting in the relief. They are of different ages and their final shape was obtained when the last glaciers retreated. Some, such as the river Dvina, have deep, canyon-like valleys, others, such as the Pripyat, have wide, flat valleys with marshy meadows.
The relief has also changed due to human influences. In recent decades, it has been greatly altered by the mining and construction of quarries, dumps, road dams, melioration canals and reservoirs and the drainage of swamps. In addition, seismic processes taking place on the mainland influence the relief. The epicentre of seismic activity in Belarus is located next to the potash salt deposit in Starobin south of Minsk.
The territory of Belarus has a multitude of untouched wet biotope ecosystems. With its 20,800 rivers, 10,800 lakes, 53 reservoirs and 1,500 ponds, it offers numerous habitats for endangered animals and plants. The total length of all rivers is 90,600 kilometres.
The Belarusian rivers connect the Black Sea with the Baltic Sea.
The largest rivers with a length of over 500 kilometres are the Dnepr and its tributaries Pripyat, Beresina and Sosch; the Neman (Memel) and its tributary Wilija; the western Dwina (Dvina). All major rivers, with the exception of the Beresina, cross borders.
It’s for a reason that Belarus is attributed “blue-eyed”, as the Belarusian lakes on the map are almost perceived as blue eyes. The largest of them are the Narotsch (79.6 km² area), the Oswejskoe (52.8 km² area) and the Tscherwonoe (43.6 km² area). The deepest and most picturesque lakes are located in the north of Belarus (on the Belarusian Poozerje, also called Braslaw Lakes).
Thanks to the potential of numerous rivers, the use of hydropower in Belarus has developed strongly. Nevertheless, only low-pressure power plants can be used, the flat territory excludes other variants.
Republic of Belarus
The Republic of Belarus is located in the center of Europe. The shortest transport links connecting the CIS countries with the states of Western Europe run through its territory. Belarus has a common border with Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Russia and Ukraine.
Year of People’s Unity
Belarus in Figures
Republic of Belarus
The central position of Belarus in Europe is of great importance for the development of trade, economic and humanitarian ties, international tourism.
Brest Oblast
Brest Oblast is the western gate of Belarus and of the Eurasian Economic Union. Landmarks and tourist attractions: Brest Hero Fortress, the Belovezhskaya Pushcha National Park, the Kossovo Palace and Park Ensemble, Ruzhany Palace Complex of the Sapieha family, Belaya Vezha (the White Tower).
Vitebsk Oblast
Vitebsk Oblast is the cradle of Belarusian statehood, the oldest city in the country is located here. Landmarks and tourist attractions: the International Festival of Arts Slavianski Bazaar in Vitebsk, Braslav Lakes, Saint Sophia Cathedral in Polotsk.
Gomel Oblast
Gomel Oblast is the only region in Belarus where oil is produced. Landmarks and tourist attractions: the Palace of the Rumyantsevs and Paskeviches, the Castle Hill and stone crosses in Turov, the Neglubka weaving.
Grodno Oblast
Mogilev Oblast
Mogilev Oblast is situated in the east of the country. The city of Gorki in Mogilev Oblast is a home to Belarusian State Agricultural Academy, the oldest agricultural university in the CIS and Europe. Landmarks and tourist attractions: the Kupala Night Festival Alexandria Gathers Friends, Trofimov’s Spring, the memorial Buinichi Field.
Minsk Oblast
Minsk Oblast is the largest region of Belarus with a powerful industry. Landmarks and tourist attractions: BelAZ, the national landscape reserve Nalibokskaya Pushcha (Naliboki Forest), Nesvizh Castle, Khatyn Memorial Complex, ski resorts in Logoisk and Silichi.
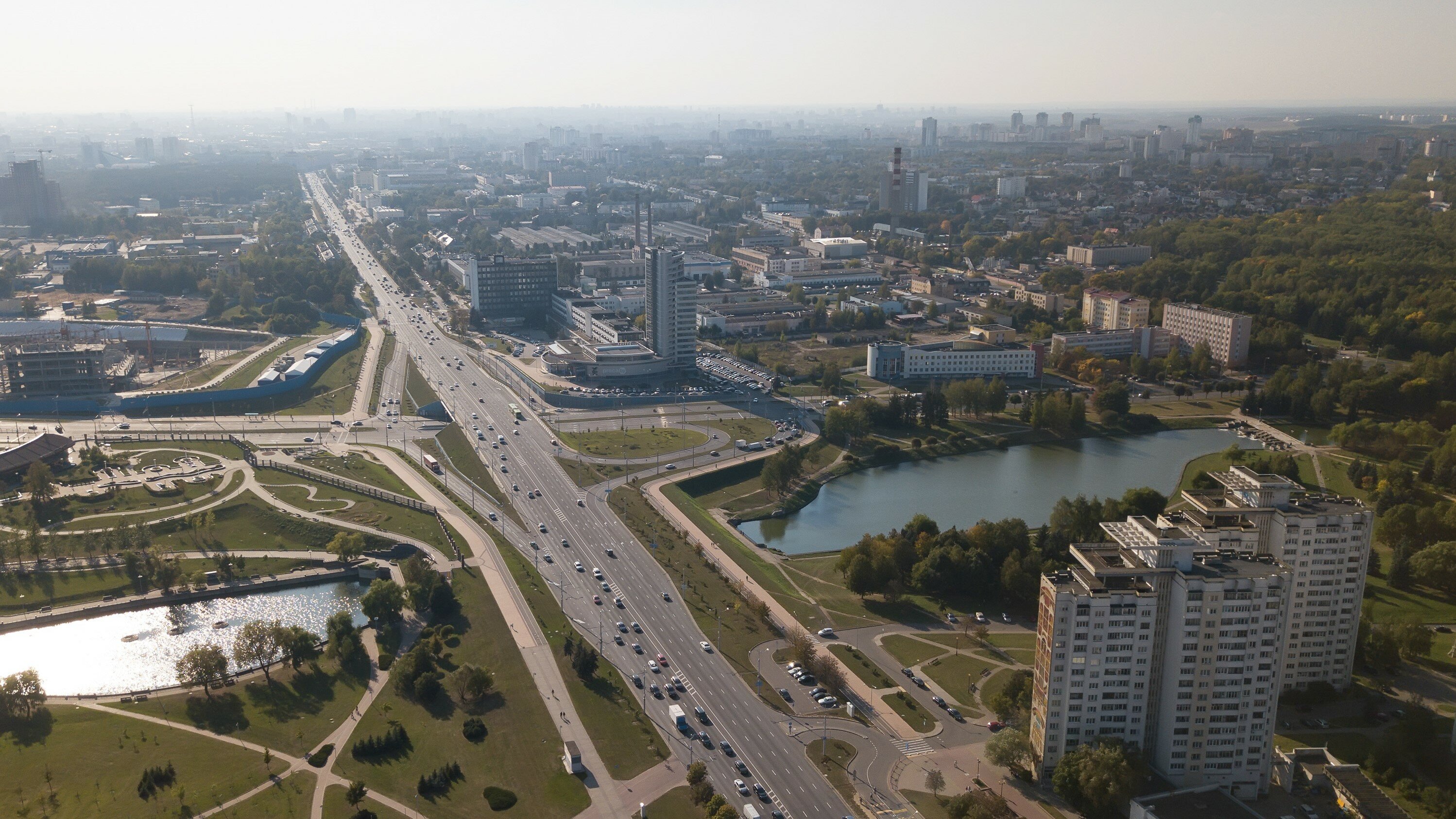
Minsk
Minsk is the capital of Belarus, one of the internationally recognized peace brokering centers of the 21st century. Landmarks and tourist attractions: the Minsk Gate, the Palace of the Republic, Victory Square, the National Library of Belarus.
Geography of Belarus
Belarus, a landlocked, generally flat country (the average elevation is 162 meters (531 ft) above sea level) without natural borders, occupies an area of 207,600 square kilometers (80,200 sq mi), or slightly smaller than the United Kingdom or the state of Kansas. Its neighbors are Russia to the east and northeast, Latvia to the north, Lithuania to the northwest, Poland to the west, and Ukraine to the south.
Contents
Topography and drainage
Belarus’s mostly level terrain is broken up by the Belarusian Range (Byelaruskaya Hrada), a swath of elevated territory, composed of individual highlands, that runs diagonally through the country from west-southwest to east-northeast. Its highest point is the 346-meter (1,135 ft) Mount Dzyarzhynskaya, named for Felix Dzerzhinsky, head of Cheka. Northern Belarus has hilly landscape with many lakes and gently sloping ridges created by glacial debris. In the south, about one-third of the republic’s territory around the Pripiac River is taken up by the low-lying swampy plain of Palyessye, shared with Ukraine, Poland and Russia.
Glacial scouring accounts for the flatness of Belarusian terrain and for its numerous lakes.
Belarus’s 3,000 streams and 4,000 lakes are major features of the landscape and are used for floating timber, shipping, and power generation. Major rivers are the west-flowing Western Dvina and Nyoman rivers, and the south-flowing Dniapro River with its tributaries, Berezina River, Sozh, and Prypyat rivers. The Prypyat River has served as a bridge between the Dnepr flowing to Ukraine and the Vistula in Poland since the period of Kievan Rus’. Lake Narach, the country’s largest lake, covers eighty square kilometers.
Nearly one-third of the country is covered with pushchas, large unpopulated tracts of forests. In the north, conifers predominate in forests that also include birch and alder; farther south, other deciduous trees grow. The Belavezhskaya Pushcha (shared with Poland) in the far west is the oldest and most magnificent of the forests; a reservation here shelters animals and birds that became extinct elsewhere long ago.
Climate
Environmental concerns
Chernobyl Disaster
The most notorious legacy of pollution from the Soviet era is the Chernobyl Disaster of 1986. Some 70% of the radiation spewed was carried by the wind to Belarus, where it affected at least 25% of the country—especially the Homyel and Mahilyow provinces, in the south and southeast, and 22% of the population. Although more than 2 million people (including 600,000 children) lived in areas affected by fallout from the disaster, the Soviet government tried to cover up the accident until [ citation needed ] Swedish scientists pressed for an explanation of the unusually high levels of atmospheric radiation in Sweden.
The Belarusian government’s request to the Soviet government for a minimum of 17 billion rubles to deal with the consequences was answered with Moscow’s offer of only 3 billion rubles. According to one official in 1993, the per capita expenditure on the accident was one kopeck in Russia, three kopecks in Ukraine, and one rouble (100 kopecks) in Belarus.
Despite the government’s establishment of the State Committee for Chernobyl, the enactment of laws limiting who may stay in contaminated areas, and the institution of a national program for research on the effects, little progress was made in coping with the consequences of the disaster, owing to the lack of money and the government’s sluggish attitude. In 1994 a resettlement program for 170,000 residents was woefully underbudgeted and far behind schedule. To assist victims of Chernobyl, a Western organization, the Know-How Fund, provided many Belarusian doctors with training in the latest bone-marrow techniques in Europe and the United States.
The long-range effects of the disaster include an increasing incidence of various kinds of cancer and birth defects; congenital defects in newborns are reported to be 40 % higher than before the accident. Tainted water, livestock, farm produce, and land are widespread, and the extensive wetlands retain high concentrations of radiation. Cleanup of the disaster accounted for 14 % of the state budget in 1995. Other environmental problems include widespread chemical pollution of the soil, which shows excessive pesticide levels, and the industrial pollution found in nearly all the large cities.